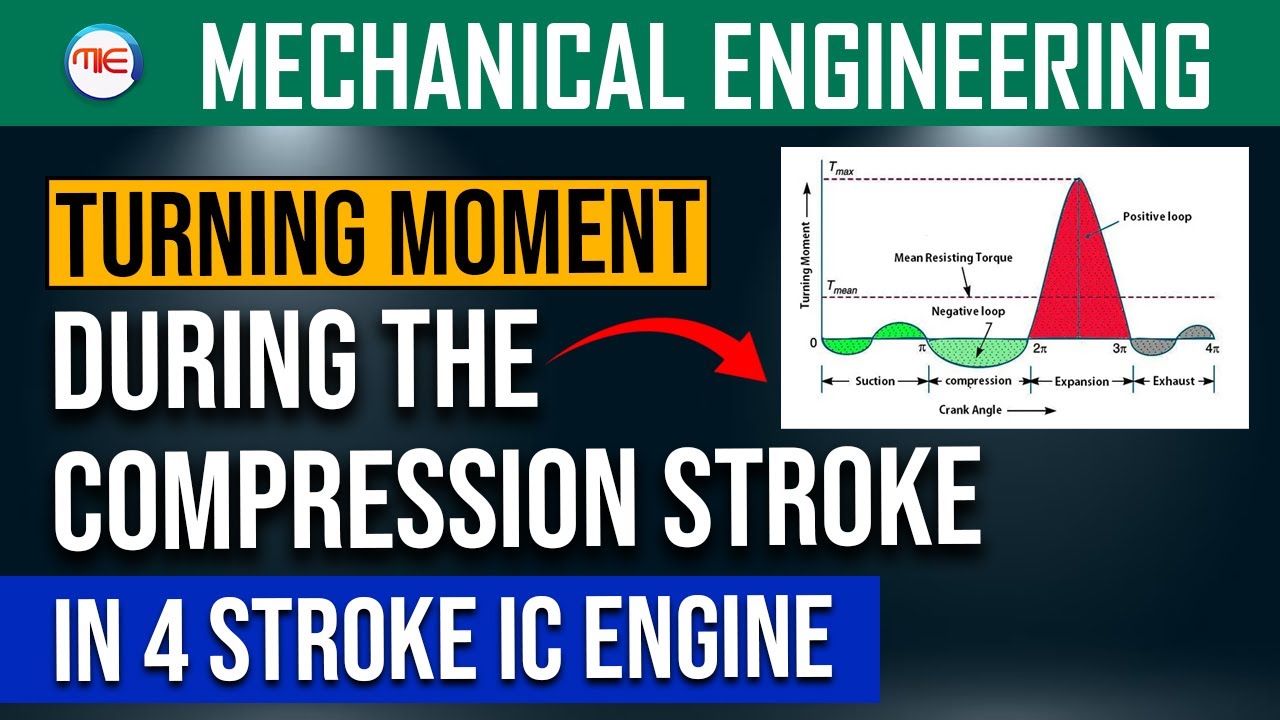
In today’s post, we’re going to solve another commonly asked question from Internal Combustion Engines that appeared in competitive exams like SSC JE and RRB JE. This concept is simple but often confuses students if the basics aren’t clear.
I have covered this question in detail with diagrams in my video explanation. Watch it here:
(b) Compression ratio
When carbon deposits build up on the cylinder head or piston crown, they occupy space in the clearance volume.
Clearance Volume = Volume left in the cylinder when the piston is at Top Dead Center (TDC).
Carbon deposits reduce clearance volume because part of that space is now filled with solid carbon.
Since Compression Ratio (CR) is calculated as:
A smaller clearance volume increases the value of CR, resulting in a higher effective compression ratio.
More heat generation → Risk of knocking.
Increased thermal efficiency initially, but harmful to engine health.
Can cause pre-ignition and reduced engine life.
Exam Tip:
If carbon deposits reduce clearance volume → Compression Ratio increases.
If clearance volume increases (due to wear or design change) → Compression Ratio decreases.

Makeiteasy








.jpeg)
Leave a Comment