| S.No | Question | Option A | Option B | Option C | Option D | Answer | Solution | Comments | Status | Action |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Loss in pump head mismatch between the blade angles and the inlet flow direction, especially significant at high flow rates is known as ______. | friction loss | impeller recirculation | heat loss | shock loss | d | Shock loss in a pump occurs when there is a mismatch between the direction of the fluid flow entering the impeller and the angle of the impeller blades. This mismatch causes the fluid to abruptly change direction, resulting in a sudden, turbulent flow that is characterized by eddies and vortices at the blade inlet. This turbulence dissipates energy, leading to a loss in the pump's head and a reduction in efficiency. Friction loss: This loss is due to the friction between the fluid and the pump's internal surfaces (impeller, casing, etc.) and is proportional to the square of the flow velocity. Impeller recirculation: This refers to the leakage of fluid from the high-pressure side of the impeller back to the low-pressure side, which reduces efficiency but is not the same as shock loss. Heat loss: While some energy is converted to heat due to friction and turbulence, "heat loss" is a general term and not the specific name for the phenomenon described. |
Comments | Active | |
| 2 | Kinematic viscosity also known as stoke is equal to: | 10−3 m/s | 10−1 m/s | 10−4 m/s | 10−2 m/s | c | The stoke (St) is the CGS unit of kinematic viscosity. It is defined as: 1 stoke = 1 cm²/s To convert this to the SI unit (m²/s), we use the conversion factor: 1 m = 100 cm, so 1 m² = (100 cm)² = 104 cm² Therefore, \(1 cm²/s = 1041 m²/s = 10^{-4} m^{2}/s\) So, 1 stoke is equal to \(10^{-4} m²/s.\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 3 | Which of the following is NOT a limitation of brazing? | Brazing cannot join thin walled parts | Joint strength is less than welded joint | Colour of brazed joint may not match base metal colour | High service temperatures may weaken brazed joint. | a | The correct option is (a) because it is a false statement about brazing. Brazing is actually an excellent process for joining thin-walled parts and dissimilar materials because it does not involve melting the base metals. The other options are true limitations of the brazing process. Joint strength is less than welded joint: This is true. A brazed joint's strength is typically less than that of a properly welded joint because it relies on adhesive and cohesive forces of the filler metal rather than a full metallurgical fusion of the base materials. Colour of brazed joint may not match base metal colour: This is true. The filler metal used in brazing often has a different composition and color than the base metals, which can be a cosmetic drawback. High service temperatures may weaken brazed joint: This is true. Since the filler metal has a lower melting point than the base metals, the strength of the brazed joint can be compromised if the operating temperature of the assembly approaches the melting point of the filler metal. |
Comments | Active | |
| 4 | ______ line on the Mollier chart represents ______process. | Vertical, isentropic | horizontal, adiabatic | Horizontal, Isentropic | Vertical, Isenthalpic | a | A Mollier chart is an enthalpy-entropy (h-s) diagram. On this chart, the vertical axis represents enthalpy and the horizontal axis represents entropy. A vertical line on this chart represents a constant entropy (s) process, which is also known as an isentropic process. A horizontal line represents a constant enthalpy (h) process, or an isenthalpic process. |
Comments | Active | |
| 5 | According to Lami’s theorem, if three coplanar forces are acting at a point b in equilibrium, then each force is proportional to the ______ of the angle between the other two. | sec | sine | cosine | tangent | b | Lami's Theorem states that for three coplanar and concurrent forces in equilibrium, each force is proportional to the sine of the angle between the other two forces. Mathematically, for forces P, Q, and R, the theorem is expressed as: \(\frac{P}{sin(α)}=\frac{Q}{sin(β)}=\frac{R}{sin(γ)}\) where , and are the angles opposite to forces P, Q, and R, respectively. \(α, β\) \( γ\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 6 | Which of the following statements is/are true with respect to friction? I. Application of grease reduces friction II. Rolling friction produces least friction III. Static friction is less than rolling friction |
Both I and III are true | Both II and III are true | Both I and II are true | Only I is true | c | I. Application of grease reduces friction: This statement is true. Grease and other lubricants are applied between moving surfaces to reduce the coefficient of friction, thereby decreasing frictional resistance and wear. II. Rolling friction produces least friction: This statement is true. Rolling friction, which occurs when an object rolls over a surface (e.g., a wheel on a road), is significantly less than sliding friction (also known as kinetic friction) for the same surfaces. This is why wheels are used for transportation. III. Static friction is less than rolling friction: This statement is false. Static friction is the force that prevents an object from starting to move. The maximum static friction is always greater than the rolling friction for the same set of surfaces. It takes more force to initiate motion from a standstill than to keep it rolling. |
Comments | Active | |
| 7 | The dimensionless parameter describing flow-induced boiling is known as ______. | Cavitation number | boiling number | Curing number | Reynolds number | a | It is defined as the phenomenon of the formation of vapour bubbles of a flowing liquid in a region where the pressure of the liquid falls below its vapour pressure and the sudden collapsing of these vapour bubbles in a region of higher pressure. When the vapour pressure collapse, very high pressure is created. It is defined as: \(σ=\frac{P_{a}-P_{v}}{\frac{1}{2}ρv^{2}}\) Where Pa, is the local pressure, Pv is vapor pressure is the density of the fluid, V is the characteristic velocity of flow. \(ρ\) If the value of is negative, then cavitation will take place. \( σ\) Boiling or cavitations may damage the pump. |
Comments | Active | |
| 8 | ______ is defined as the force, that while acting upon a mass of 1 kg, produces an acceleration of 1m/s2 in the direction in which it acts. | Density | Ohm | Newton | Poise | c | A Newton (N) is the SI unit of force. It is defined based on Newton's Second Law of Motion Specifically, one Newton is the amount of force required to accelerate a mass of one kilogram at a rate of one meter per second squared. \((F=ma).\) | Comments | Active | |
| 9 | Lateral strain/longitudinal strain is equal to ______. | Jump’s law | Hooke’s law | Poisson’s ratio | Newton’s law | c | Poisson's ratio (ν) is a material property that quantifies the relationship between transverse (lateral) strain and axial (longitudinal) strain. It is defined as the negative ratio of lateral strain to longitudinal strain. The negative sign is included because for most materials, a positive longitudinal strain (stretching) results in a negative lateral strain (contraction). | Comments | Active | |
| 10 | Poise is a unit of ______. | viscosity | weight | velocity | surface tension | a | Viscosity is a measure of a fluid's resistance to flow. The Poise (P) is the CGS (centimetre-gram-second) unit of dynamic viscosity. It is named after the French physician and physicist Jean Léonard Marie Poiseuille. 1 Poise is equal to 0.1 Pascal-second in the SI (International System of Units) system. \((Pa⋅s)\) The centipoise (cP), which is one-hundredth of a poise, is a commonly used unit. For reference, the viscosity of water at room temperature is approximately. \(1 cP or 0.001 Pa⋅s\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 11 | Which of following is true with respect to PMM2? | It violates the Kelvin-Planck statement. | It violates the concept of temperature. | It violates the statement that the total energy of the universe is constant. | It violates joules effect. | a | A Perpetual Motion Machine of the Second Kind (PMM2) is a hypothetical device that violates the Second Law of Thermodynamics. The Kelvin-Planck statement is one of the classic statements of the Second Law. It states that it is impossible to construct a device that operates in a cycle and produces no other effect than the absorption of heat from a single thermal reservoir and the production of an equivalent amount of work. A PMM2 would do exactly this—it would absorb heat from a single source (like the atmosphere or ocean) and convert it completely into work, which is impossible. | Comments | Active | |
| 12 | Which of the following is NOT a law of static friction? | The force of friction is independent of the area of contact between the two surfaces. | Limiting friction × Normal reaction = Constant | The force of friction depends upon the roughness of the surfaces. | The magnitude of force of friction is exactly equal to the force, which tends to move the body. | b | The statement (b) Limiting friction × Normal reaction = Constant is incorrect and is not a law of static friction. The correct law states that the limiting friction force is directly proportional to the normal reaction force. This relationship is expressed as , where μs (the coefficient of static friction) is the constant, not the product. The other options are valid laws of static friction. \(F_{s,max} =μ_{s}N\) | Comments | Active | |
| 13 | The L/D ratio for the barrel of an extrusion machine ranges from: | 40 – 60 | 10 – 30 | 1 – 9 | 70 – 90 | b | The L/D ratio refers to the ratio of the length (L) of the extruder screw to its diameter (D). This ratio is a critical design parameter that affects the machine's performance. For most standard extrusion machines used in plastics and polymers, the typical L/D ratio ranges from 10:1 to 30:1. A higher L/D ratio allows for more efficient melting, mixing, and homogenization of the polymer, leading to better product quality. A lower L/D ratio is used for materials that do not require extensive mixing or when a higher output is desired. |
Comments | Active | |
| 14 | Identify the correct statement pertaining to water tube boilers as compared to fire tube boilers. i. They required more floor area for given output. ii. They can operate safely at higher temperatures. iii. Overall efficiency is less. |
Only iii is correct | Only ii is correct | Both i and ii are correct | Both i and iii are correct | b | The correct statement is that water-tube boilers can operate safely at higher temperatures and pressures compared to fire-tube boilers. The reasons for this are related to their design. i. They require more floor area for a given output: This statement is incorrect. Water-tube boilers are generally more compact and require less floor area for a given steam output because of their higher heating surface area and faster steam generation rate. ii. They can operate safely at higher temperatures: This statement is correct. In water-tube boilers, the water is contained inside small-diameter tubes, which are surrounded by hot combustion gases. This design allows for rapid heat transfer and reduces the risk of explosion at high pressures because a failure in a small tube would be less catastrophic than a rupture of a large shell in a fire-tube boiler. iii. Overall efficiency is less: This statement is incorrect. Water-tube boilers have a higher overall efficiency due to better circulation, more rapid and uniform heating, and a larger heating surface area, allowing them to produce more steam per unit of fuel consumed. |
Comments | Active | |
| 15 | Identify the odd one out of the following. | Lancashire boiler | Locomotive boiler | Babcock and Wilcox boiler | Cochran boiler | c | The Babcock and Wilcox boiler is the odd one out because it is a water-tube boiler. The other three—the Lancashire, Locomotive, and Cochran boilers—are all fire-tube boilers. In a fire-tube boiler, hot gases from combustion pass through tubes surrounded by water, while in a water-tube boiler, water flows through tubes surrounded by hot gases. | Comments | Active | |
| 16 | Air vessel in a reciprocating pump is ______ | Fitted in delivery line | Not fitted | Fitted outside the system | Fitted before the pump | a | An air vessel in a reciprocating pump is used to smooth out the pulsating flow on the delivery line (and sometimes the suction line). It acts as a buffer by absorbing excess fluid and releasing it during moments of low flow, ensuring a more continuous discharge and reducing power consumption. | Comments | Active | |
| 17 | Identify the correct option with respect to the second law of thermodynamics. I) It gives the concept of temperature II) It gives the concept of internal energy III) it gives the concept of entropy |
I and III are correct | I and II are correct | Only II is correct | Only III is correct | d | The Second Law of Thermodynamics introduces the concept of entropy, which is a measure of the disorder or randomness in a system. It states that the total entropy of an isolated system can only increase over time. The First Law of Thermodynamics, on the other hand, gives the concept of internal energy. The concept of temperature is based on the Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics, which establishes thermal equilibrium and is the basis for temperature measurement. | Comments | Active | |
| 18 | Which of the following hold true with respect to the flow in volute casing outside the rotating impeller of a centrifugal pump? i. Flow is Free vortex ii. Flow is Forced vortex iii. Flow is radial |
Both i and ii | Only i | Only ii | Both ii and iii | b | The flow in a volute casing outside the rotating impeller of a centrifugal pump is a free vortex flow. This means that the fluid rotates due to its own inertia without any external torque applied to it. | Comments | Active | |
| 19 | Strain energy stored in cantilever beam loaded as shown will be ______. |
 |
 |
 |
 |
b | \(U=\frac{P^{2}}{2EI} .\frac{L^{3}}{3}=P^{2}L^{3}/6EI \) | Comments | Active | |
| 20 | ______ bearing is also known as Foot step bearing | Peddle | Speed | Flat pivot | Power | c | A flat pivot bearing is also called a footstep bearing because it supports the vertical shaft similar to a footstep and allows rotation with minimal friction. | Comments | Active | |
| 21 | In a centrifugal pump, the doughnut-shaped diffuser section called ______ of the casing decelerates the flow and further increases the pressure. | scroll | casing | impeller | eye | a | In a centrifugal pump, the scroll (or volute) casing is a doughnut-shaped diffuser section that decelerates the fluid and converts velocity into pressure, increasing the pump’s pressure head. | Comments | Active | |
| 22 | Which of the following statements is/are true for rivets? I. Rivets can be removed without breaking their heads. II. Rivets are used for achieving mechanically fastened joints. III. Rivets are primarily used for lap joints. |
II and III | Only I | I and II | I and III | a | Statement I: False — Rivets cannot be removed without breaking their heads. Statement II: True — Rivets are used to achieve mechanically fastened joints. Statement III: True — Rivets are primarily used in lap joints. |
Comments | Active | |
| 23 | For a reversible isothermal process undergone by ideal gas heat transfer ______ work Transfer. | is equal to | cannot be related to | is more than | is less than | a | For a reversible isothermal process in an ideal gas: \(ΔU=0(internal energy change is zero) \) From the first law of thermodynamics: \(Q=W\) So, heat transfer is equal to work transfer. |
Comments | Active | |
| 24 | Identify the odd option among the following. | Drum cams | Cylindrical cams | Barrel cams | Spiral cams | d | Drum, cylindrical, and barrel cams are all types of rotating cams used to convert rotary motion into linear or oscillating motion. Spiral cam is a flat cam profile (not a rotating type), so it is the odd one out. |
Comments | Active | |
| 25 | ______ defect is caused due to casting getting solidified before the entire mould cavity is filled. | Hot tears | Cold shots | Misruns | Porosity | c | A misrun occurs when the molten metal solidifies before completely filling the mold cavity, resulting in an incomplete casting. | Comments | Active | |
| 26 | ______ is NOT a non-destructive testing method. | Visual testing | Leak testing | Liquid penetrant testing | Hardness testing | d | Visual testing, leak testing, and liquid penetrant testing are all non-destructive testing (NDT) methods. Hardness testing involves applying a load to the material and can cause permanent deformation, so it is destructive in nature. |
Comments | Active | |
| 27 | ______ in stainless steel imparts corrosion resistance. | Chromium | Iron | Cobalt | Tantalum | a | Chromium in stainless steel forms a thin, stable oxide layer on the surface, which prevents rusting and imparts corrosion resistance. | Comments | Active | |
| 28 | Which of the following figures shows an underfill welding defect? |  |
 |
 |
 |
a | Comments | Active | ||
| 29 | In a manometer, the two ends of a tube are connected to points where ______. | power difference is to be measured | velocity difference is to be measured | density is to be measured | pressure difference is to be measured | d | A manometer measures the pressure difference between two points in a fluid system by comparing the height of a liquid column in the connected tube. | Comments | Active | |
| 30 | The maximum bending moment for a beam fixed at one end and free at the other end, where in load acts at centre will occur at ______. | Between centre and fixed end | Free end | Fixed end | Under the load | c | For a cantilever beam (fixed at one end and free at the other), the maximum bending moment always occurs at the fixed end, regardless of where the load is applied. | Comments | Active | |
| 31 | Calculate the COP of a refrigerator, if work input is 40 kJ/kg and output is 80 kJ/kg, producing a refrigerating effect of 120 kJ/kg. | 1/3 | −3 | 3 | −1/3 | c | Work input, \(W_{in}=40 kJ/kg.\) Refrigerating effect, \(Q_{L}=120 kJ/kg\) The COP of a refrigerator is given by the formula: \(COP_{R}=\frac{Refrigerating Effect}{Work Input}\) \(COP_{R}=\frac{120kJ/kg}{40kJkg}\) \(COP_{R}=3\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 32 | Identify the odd process out of following. | Gas metal arc welding | Tungsten inert gas welding | Metal inert gas welding | Metal active gas welding | b | GMAW, MIG, and MAG are all consumable electrode processes (the electrode melts and becomes part of the weld). TIG welding uses a non-consumable electrode (tungsten), so it is the odd one out. |
Comments | Active | |
| 33 | For a Non - Newtonian fluid, apparent viscosity depends on ______. | proof stress | stress intensity | velocity | shear rate | d | For a Non-Newtonian fluid, the apparent viscosity changes with the shear rate. Unlike Newtonian fluids, its viscosity is not constant and depends on how fast the fluid is sheared. | Comments | Active | |
| 34 | NPSH for a centrifugal pump stands for ______. | near positive section head | net positive suction head | net positive section head | near positive suction head | b | NPSH represents the Net Positive Suction Head, which is the absolute pressure at the pump suction to avoid cavitation. | Comments | Active | |
| 35 | The best example of a/an ______ is seen in the tailor’s manual sewing machine. | flywheel | piston | engine | clutch | a | The tailor’s manual sewing machine uses a flywheel to store rotational energy and maintain uniform motion while stitching. | Comments | Active | |
| 36 | A Carnot heat pump is working between 32°C and 337°(c) Calculate the COP of the same. | 2 | 2.5 | 3 | 1.5 | a | Step 1: Recall the formula for COP of a heat pump For a heat pump operating on a Carnot cycle: \(COP_{HP} =\frac{T_{H}}{T_{H}-T_{C}}\) Where: = temperature of the hot reservoir (in Kelvin) \(T_{H}\) = temperature of the cold reservoir (in Kelvin) \(T_{C}\) \(T_{H} = 337°C + 273 = 610K\) \(T_{C} =32°C+273=305K\) \(COP_{HP} =\frac{T_{H}}{T_{H}-T_{C} } \frac{610}{610-305} =\frac{610}{305} = 2\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 37 | Which of the following is not a type of cylinder arrangement in IC Engines. | Zig zag engines | X-engines | Radial engines | V - engines | a | Among the given options, X-engines are not a standard type of cylinder arrangement for internal combustion engines. The other options are all valid configurations. Radial engines have cylinders arranged radially around a central crankcase, much like the spokes of a wheel. V-engines have cylinders arranged in a V-shape. Zig-zag engines, also known as W-engines, have a cylinder arrangement similar to two V-engines joined together. | Comments | Active | |
| 38 | If the sleeve of a watt governor is loaded with heavy mass, it becomes a ______ governor. | Dortsmouth | Proteas | Hartnell | Porter | d | A Porter governor is a direct modification of a Watt governor. The key difference is that the Porter governor adds a heavy central load to the sleeve. This additional dead weight increases the force required to lift the sleeve, making the governor more sensitive and stable, particularly at higher speeds where a simple Watt governor loses effectiveness. | Comments | Active | |
| 39 | During combustion in CI Engines the period of uncontrolled combustion has ______. | rapid pressure rise | rapid weight rise | rapid pressure reduction | rapid weight reduction | a | The period of uncontrolled combustion in a Compression Ignition (CI) engine is also known as the rapid or uncontrolled combustion phase. During this period, the fuel that has accumulated during the ignition delay period ignites almost simultaneously, leading to a sudden and very fast release of energy. This rapid energy release causes a sharp increase in pressure within the cylinder, resulting in a characteristic "diesel knock" sound. This is distinct from the controlled combustion phase, where the rate of pressure rise is more gradual and managed. | Comments | Active | |
| 40 | Identify the gear in the given figure. |
Zero bevel gear | Spiral gear | Herringbone gear | Bevel gear | c | The gear shown in the figure is a herringbone gear. This type of gear consists of two sets of helical teeth arranged in a V-shape, which appear similar to the bones of a fish like a herring. A key feature of this design is that the opposing helices cancel out the axial thrust, making them suitable for high-power applications without the need for thrust bearings. | Comments | Active | |
| 41 | Which of the following statements is/are true regarding the law of static friction? I) The force of friction is dependent on the area of contact between the two surfaces. II) The force of friction depends on the roughness of the surfaces. III) The ratio of limiting friction to normal reaction is constant. |
I and III | I and II | II and III | Only I | c | The laws of static friction state that the force of friction is independent of the area of contact between the surfaces. This means statement I is false. The friction force is proportional to the normal reaction force and depends on the nature of the two surfaces, which includes their roughness. This makes statement II true. The ratio of the limiting friction to the normal reaction is the coefficient of static friction (μs), which is a constant for a given pair of surfaces, as stated in statement III. Therefore, statements II and III are correct. | Comments | Active | |
| 42 | Which of the following is NOT a feature of weld bead deposited by arc welding? | Heat affected zone | Fuzion zone | Thermo-mechanically affected zone | Partially melted zone | c | The Thermo-mechanically affected zone (TMAZ) is a characteristic zone found in friction stir welding (FSW), not traditional arc welding. In FSW, the material is stirred and plastically deformed at an elevated temperature, leading to a distinct TMAZ where both thermal and mechanical effects have altered the material's microstructure. In contrast, arc welding creates a fusion zone, a heat-affected zone, and a partially melted zone. | Comments | Active | |
| 43 | Identify the defect ‘A’ from the casting product shown in given figure. |
Misrun | Hot tears | Shrinkage cavity | Cold shut | b | The defect shown in the figure is a cold shut. This defect appears as a seam or a line on the surface of the casting, where two streams of molten metal meet but fail to fuse together completely. This incomplete fusion occurs because the molten metal streams have cooled down too much before they converge, resulting in a weak, visible discontinuity. | Comments | Active | |
| 44 | For uniform flow around circular cylinders, the stagnation points are located at: | 90° and 180° | 0° and 90° | 0° and 180° | 90° and 270° | c | In a case of ideal, uniform flow around a circular cylinder, the stagnation points are the locations where the fluid velocity is zero. This occurs at the very front and very back of the cylinder, where the flow comes to a momentary stop before dividing to pass around the body. If we define the angle θ as starting from the front of the cylinder, the stagnation points are at 0° and 180°. At these points, the fluid pressure is at its maximum. | Comments | Active | |
| 45 | As per the ______, if a body in equilibrium is acted upon by four forces, then the resultant of any two forces must be equal, opposite, and collinear with the resultant of the other two forces. | Four Force Principle | Three Force Principle | Five Force Principle | Two Force Principle | a | The Four Force Principle states that if a body is in equilibrium under the action of four forces, the resultant of any two of these forces must be equal, opposite, and collinear with the resultant of the other two forces. This principle is a direct application of the conditions for equilibrium, which require the net force and net torque to be zero. By considering the forces in pairs, we can simplify the problem and apply the principle of equal and opposite forces. | Comments | Active | |
| 46 | Identify the type of motion in the given figure. |
Incompletely constrained motion | Successfully constrained motion | Proportionate constrained motion | Completely constrained motion | d | Completely constrained motion: When the motion between a pair is limited to a definite direction irrespective of the direction of force applied, then the motion is said to be a completely constrained motion. For example, the motion of a square bar in a square hole. Examples of completely constrained motion are the motion of pistons and cylinders in steam engines, the motion of a square bar in a circular hole, and the motion of shafts with the collars at each end in a circular hole. Incompletely constrained motion: When the motion between a pair can take place in more than one direction, then the motion is called an incompletely constrained motion. The change in the direction of the impressed force may alter the direction of relative motion between the pair. For example, a circular bar or shaft in a circular hole. Successfully Constrained Motion: This motion is a special case where the motion is limited to a single direction not by the physical geometry of the pair itself but by an external element or another constraint. An example given is a shaft in a foot-step bearing. The bearing allows the shaft to rotate but prevents it from moving upwards due to gravity or another external load. The motion is only "successful" for its intended purpose (rotation), as it relies on an external factor to constrain the other potential movements. A kinematic chain is a series of links connected by kinematic pairs. |
Comments | Active | |
| 47 | Caulking is a process used to make joints ______. | colour proof | corrosion proof | leak proof | indent proof | c | Caulking is a sealing process that involves applying a flexible, waterproof material (known as caulk or sealant) into gaps, seams, or joints. Its primary purpose is to make these joints leak proof, preventing the passage of air, water, or other fluids. It is commonly used in construction, plumbing, and automotive industries. | Comments | Active | |
| 48 | For orifice meters with sharp edges, the coefficient of velocity is ______ | 0.4 | 1.9 | 0.98 | 0.1 | c | The coefficient of velocity for a sharp-edged orifice is typically close to 1. However, due to minor losses, the value is slightly less than one. The commonly accepted value is around 0.98. It's important to distinguish this from the coefficient of discharge and the coefficient of contraction . \((C_{v}) \) \((C_{d}) \) \((C_{c})\) | Comments | Active | |
| 49 | Which of the following is NOT a basis for classification of cams? | Weight of cam | Follower movement in cam | Shape of cam | Manner constraint of the follower | a | Cams are classified based on several factors, but the weight of the cam is not one of them. The common bases for classification include the shape of the cam (e.g., plate cam, cylindrical cam), the type of follower movement (e.g., oscillating, reciprocating), and the manner of constraint of the follower (e.g., positive drive, gravity return). | Comments | Active | |
| 50 | Orifice meters have ______ head loss as compared to venturimeters. | higher | similar | lesser | half | a | Both orifice meter and venturimeter are flow measuring devices based on the principle of pressure drop due to change in cross-section. In a venturimeter, the fluid is smoothly contracted and expanded, so loss of energy (head loss) is very small. In an orifice meter, the fluid undergoes a sudden contraction and expansion, which causes greater turbulence and energy loss. Therefore, orifice meters have higher head loss compared to venturimeters. |
Comments | Active | |
| 51 | Identify the odd option from among the following. | Zig-zag tube manometer | Inclined U-Tube manometer | Vertical single column manometer | U-Tube manometer | a | Single column manometer: Single column manometer is a modified form of a U-tube manometer in which one side is a large reservoir and the other side is a small tube, open to the atmosphere. There are two type of single-column manometer: Vertical single-column manometer. Inclined single-column manometer. U tube manometer: A U-tube manometer is the simplest pressure measurement device its name comes from the U-shape formed when the two ends of a flexible tube full of liquid are raised to keep the liquid from coming out the ends A U-tube manometer is a liquid balance. U tube differential manometer: A U-tube differential manometer is a type of differential manometer which is used to measure the difference of pressure between the two points of the pipe. |
Comments | Active | |
| 52 | Low pressure casting is a type of ______. | expendable mould casting process | permanent mould casting process | temporarymould casting process | semi-permanent casting process | b | mould, usually made of cast iron or steel. In this process, molten metal is forced upward into the mould cavity under low pressure (typically 0.3–1.5 bar). Since the mould is not destroyed after each casting (it can be reused multiple times), it is a permanent mould casting process. Expendable/temporary mould casting processes (like sand casting, investment casting) use moulds that are broken after each use, which is not the case in LPDC. |
Comments | Active | |
| 53 | Cope and drag in a moulding process are contained in a box, also known as ______. | sand dune | pattern | Flask | core | c | n a moulding process, the cope and drag are the upper and lower sections of the mould respectively. These are held together in a box known as a flask. The flask can be made of wood or metal. It helps contain the sand used to create the mould cavity. | Comments | Active | |
| 54 | Flywheels are termed as a ______ of energy. | demolisher | consumer | reservoir | generator | c | A flywheel is a rotating mechanical device that stores rotational energy. It acts as a reservoir of energy by absorbing energy when the supply is greater than the requirement and releasing it when the requirement is greater than the supply. The main purpose of a flywheel is to smooth out fluctuations in the speed of a machine. | Comments | Active | |
| 55 | Identify the gear train shown in the given figure. |
Compound gear | Spur gear | Reverted gear train | Planetary gear | c | A reverted gear train is a type of compound gear train in which the axis of the first gear and the last gear are coaxial, meaning they lie on the same line. In the figure you provided, the input gear (1) and the output gear (4) are positioned on the same axis, which is the defining characteristic of a reverted gear train. This type of gear train is commonly found in applications like clocks and lathe machines to achieve a large speed reduction in a compact space. | Comments | Active | |
| 56 | The efficiency of an actual Brayton cycle is NOT improved by ______. | providing regeneration | increasing pressure ratio. | providing intercooling arrangement | providing reheating | a | Increasing the pressure ratio in a simple Brayton cycle (ideal or actual) generally improves its efficiency. However, the question asks what does NOT improve the efficiency of an actual Brayton cycle. While regeneration, intercooling, and reheating are all methods specifically used to improve the efficiency of an actual Brayton cycle, simply increasing the pressure ratio can sometimes have a diminishing effect or even a negative effect on the efficiency of an actual cycle due to the significant increase in work required by the compressor and other real-world losses. | Comments | Active | |
| 57 | A closed system that obeys the first law equation dQ = du + pdV, where u = internal energy, Q = heat, p = pressure and V = volume is ______. | a simple compression system undergoing reversible process | undergoing an isentropic process | undergoing an irreversible process | undergoing an infinitesimal small change | a | The First Law of Thermodynamics for a closed system is generally given as . The expression is valid only for a reversible process where the pressure is well-defined throughout the entire process and for a simple compressible substance system. Thus, the equation represents the First Law of Thermodynamics for a closed, reversible, simple compression system. \(dQ=dU+dW\) \(dW=pdV\) \(dQ=du+pdV\) | Comments | Active | |
| 58 | Identify the correct statement(s) pertaining to gas welding from among the given options. I. Gas welding torch tip has separate holes for oxygen and acetylene II. Gas welding employs nitrogen gas. III. Gas welding is also known as oxy-acetylene welding process. |
Statement I is true | Statements I and III are true | Statement III is true | Statement II is true | c | Gas welding, in its most common form, uses a mixture of oxygen and acetylene gas to create a high-temperature flame. For this reason, it is also known as the oxy-acetylene welding process, making statement III correct. Statement I is incorrect because the gases are mixed inside the torch body, not at the tip, to ensure a controlled and stable flame. Statement II is also incorrect; nitrogen is not typically used as a fuel gas in gas welding. | Comments | Active | |
| 59 | The total of all sub-atomic as well as microscopic molecular energies is given by______. | internal energy | entropy | enthalpy | exergy | a | Internal energy is defined as the total energy stored within a system at the microscopic level. It includes the sum of all the kinetic and potential energies of the molecules and their constituent sub-atomic particles. This includes translational, rotational, and vibrational kinetic energy of the molecules, as well as the potential energy associated with intermolecular forces and the energy stored within the atoms themselves. Entropy is a measure of a system's disorder or randomness, enthalpy is the sum of internal energy and the product of pressure and volume, and exergy is the maximum useful work obtainable from a system as it comes into equilibrium with its surroundings. | Comments | Active | |
| 60 | The process in which the part is created through solidification of the metal is called______. | bolting | machining | casting | riveting | c | Casting is a manufacturing process in which a liquid material, typically molten metal, is poured into a mold. The material then solidifies within the mold's cavity, taking the shape of the mold. The solidified object, known as a casting, is then removed. The other options are different manufacturing processes: bolting and riveting are joining processes, while machining is a subtractive process used to remove material from a workpiece. | Comments | Active | |
| 61 | Which law enables us to measure a force, and establishes the fundamental equation of dynamics? | Newton’s third law of motion | Newton’s first law of motion | Newton’s fourth law of motion | Newton’s second law of motion | d | Newton’s second law states that the force acting on a body is proportional to the rate of change of its momentum: \(F=m⋅a \) This law provides the fundamental equation of dynamics and is the basis for measuring force. |
Comments | Active | |
| 62 | For rough pipes having turbulent flow, friction factor is a function of the ______. | weight of the pipe | volume of fluid | relative surface roughness of pipe | density of fluid | c | In turbulent flow through rough pipes, the friction factor becomes independent of Reynolds number. It mainly depends on the relative roughness , where k = average height of surface roughness and D = pipe diameter. \(\frac{k}{D}\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 63 | Which of the following is NOT a type of flame in Gas welding? | Carburising | Oxidising | Neutral | Nitriding | d | In oxy-acetylene gas welding, three types of flames are used: Carburising flame (excess acetylene) Neutral flame (balanced oxygen & acetylene) Oxidising flame (excess oxygen) There is no nitriding flame in gas welding. |
Comments | Active | |
| 64 | A Loeffler boiler is: | a type of water-tube boiler | not a boiler | a type of fire-tube boiler | a type of mixed fired boiler | a | Loeffler boiler is a high-pressure water-tube boiler. It uses evaporated steam to evaporate feed water instead of using hot gases directly, which prevents salt and sediment deposition in tubes. Hence, it belongs to the water-tube boiler category. |
Comments | Active | |
| 65 | Relate the welding processes in increasing order of their power density. | Oxyfuel welding < Electrode beam welding < Resistance welding | Oxyfuel welding < Resistance welding < Electrode beam welding | Resistance welding < Oxyfuel welding < Electrode beam welding | Resistance welding < Electrode beam welding < Oxyfuel welding | b | Oxyfuel welding (OFW): Lowest power density (~10² W/cm²) → uses chemical flame. Resistance welding (RW): Medium power density (~10³ W/cm²) → localized heating by electric resistance. Electron beam welding (EBW): Very high power density (~10⁶–10⁸ W/cm²) → concentrated electron beam. |
Comments | Active | |
| 66 | Which of the following statements is/are true with respect to the force of friction between two bodies in contact? I. It depends on area of their contact II. It depends on relative velocity between them III. Is always normal to surface of their contact |
Both I and III are true | Only III is true | Only II is true | Both I and II are true | b | Statement I is false. For dry friction, the force of friction is generally independent of the apparent area of contact. Statement II is true. The force of friction is different depending on whether the bodies are at rest relative to each other (static friction) or in motion (kinetic friction). This demonstrates a dependence on relative velocity. Statement III is false. The force of friction is a tangential force that acts parallel to the surface of contact, opposing motion. The force that is normal to the surface is the normal force. |
Comments | Active | |
| 67 | In a diamond riveted joint, the number of rivets: | remains same from the innermost row to the outermost row | increases from the innermost row to the outermost row | decreases from the innermost row to the outermost row | in the innermost row to outermost row are not related | c | In a diamond riveted joint, the rivet arrangement looks like a diamond/triangle. The innermost row (at the center) has the maximum number of rivets. As we move towards the outer rows, the number of rivets decreases symmetrically, giving it a diamond shape. |
Comments | Active | |
| 68 | Which of the following holds true for a parson reaction turbine? | It is composed only of moving blades. | It does not have any nozzles. | It is composed of only fixed nozzles. | It is composed of moving blades (nozzles) alternating with fixed nozzles. | d | A Parsons reaction turbine is a 50% reaction turbine. Steam expands partly in fixed blades (acting as nozzles) and partly in moving blades. Hence, it consists of alternate rows of fixed and moving blades, both contributing to steam expansion. |
Comments | Active | |
| 69 | The reciprocal of coefficient of fluctuation of speed is known as ______ | coefficient of steadiness | coefficient of energy | coefficient of vibration | coefficient of readiness | a | Coefficient of fluctuation of speed = \(\frac{N_{max} - N_{min} }{N_{mean}}\) Its reciprocal is called the coefficient of steadiness, which indicates how steadily a machine runs. |
Comments | Active | |
| 70 | Given the theoretical effect of the blade exit angle (β) on the pump head versus discharge, identify the correct option. |
A – Forward curved blades, B- Backward curved blades and C – Radial blades | A – Radial blades, B- Forward curved blades and C – Backward curved blades | A – Forward curved blades, B- Radial blades and C – Backward curved blades | A – Backward curved blades, B- Radial blades and C – Forward curved blades | c | In centrifugal pumps, the H-Q (head vs discharge) curve shape depends on blade exit angle β. Forward curved blades (β < 90°): Head rises sharply with discharge (unstable characteristic). Backward curved blades (β > 90°): Head decreases with discharge (most stable, commonly used). Radial blades (β = 90°): Head remains almost constant with discharge. |
Comments | Active | |
| 71 | Collar bearings are also known as ______ bearings. | thrive | power | thrust | speed | c | Collar bearings are designed to resist axial thrust (axial load) in rotating shafts. Since they take up thrust loads, they are also called thrust bearings. | Comments | Active | |
| 72 | Maximum pressure recovery is offered by ______ amongst below constant area variable head flow meters. | flow nozzle | pitot tube | orifice plate | venturimeter | d | In constant area variable head flow meters, pressure recovery depends on energy losses. Orifice plate → high energy loss, least pressure recovery. Flow nozzle → moderate recovery, less loss than orifice. Pitot tube → measures velocity head, not used for pressure recovery comparison. Venturimeter → has smooth converging and diverging sections, hence minimum energy loss and maximum pressure recovery. |
Comments | Active | |
| 73 | A body at rest remains at rest till we apply external force to move it. This property is called ______. | flowability at rest | inertia of rest | viscosity at rest | friction of rest | b | According to Newton’s first law of motion, a body continues in its state of rest or uniform motion unless acted upon by an external force. Here, the body is at rest and remains so until an external force is applied. This tendency of a body to resist a change in its state of rest is called inertia of rest. |
Comments | Active | |
| 74 | A resistance spot-welding operation is performed on two pieces of 1.5-mm-thick sheet steel using 12,000 A for a 0.20 s duration. The electrodes are 6 mm in diameter at the contacting surfaces. Resistance is assumed to be 0.0001 ohm. Calculate the heat generated in the process. | 288 Joules | 28 Joules | 28800 Joules | 2880 Joules | d | We use Joule’s law of heating: \(Q=I^{2}Rt\) Current, I=12000 A Resistance, R=0.0001 Ω Time, t=0.20 s \(Q=(12000)^{2}×(0.0001)×(0.20)\) \(Q=144×10^{6}×0.0001×0.20\) \(Q=2880J\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 75 | ______ material is widely used as an electrode material. | Wood | Ceramic | Copper | Stainless steel | c | Copper is widely used as an electrode material in various applications, particularly in electrical discharge machining (EDM) and resistance welding. This is due to its excellent electrical and thermal conductivity, which are crucial for these processes. While other materials like stainless steel can also be used in certain situations, and ceramics or wood may be used in other applications, copper's superior conductivity makes it a highly common and effective choice for electrodes. | Comments | Active | |
| 76 | The hemispherical configuration of the crown of a fire box ______. | is easy to fabricate | provides maximum space | gives maximum strength | prevents heat loss | d | A hemispherical crown in a fire box is designed to maximize heat retention by minimizing surface area. The curved shape efficiently radiates heat back into the combustion chamber, preventing significant heat loss to the surrounding environment. This design is crucial for efficient combustion and optimal heat transfer within the boiler. | Comments | Active | |
| 77 | Which of the following is an underbead cracking in the welded joint shown in the given figure? |
D | A | C | B | a | Underbead cracking is a type of crack that forms in the heat-affected zone (HAZ) of the base metal, just beneath the weld bead. This is often caused by hydrogen entrapment. In a standard diagram of weld defects, the letter 'D' typically points to this location. Other common cracks include: A: Toe crack (at the weld toe). B: Longitudinal crack (running along the length of the weld bead). C: Crater crack (at the end of the weld). |
Comments | Active | |
| 78 | For an extrusion process, in ______ section, melt is homogenised, and sufficient pressure is developed to pump it through the die opening. | expansion | feed | compression | metering | d | In a screw extruder, the barrel is divided into three main sections: Feed Section: This is the first section where the raw material (e.g., plastic pellets) is fed into the extruder. The material is heated and conveyed forward. Compression Section: In this section, the material is fully melted and its volume is reduced, which helps to remove trapped air and compact the melt. The pressure begins to build up here. Metering Section: This is the final section. Its primary functions are to homogenize the melt and to build up the necessary and consistent pressure required to force the molten material through the die opening at a uniform rate. The channel depth is constant and shallow in this section, ensuring a final mixing and pumping action. |
Comments | Active | |
| 79 | A pitot static tube is used to measure the velocity of air flowing through a duct. The manometer shows a difference in head of 5 cm of water. If the density of air and water are 1.13 kg/m3 and 1000 kg/m3, respectively, determine the velocity of air. Assume the coefficient of the pitot tube as 0.98. | 288.6 m/s | 0.2886 m/s | 2.886 m/s | 28.86 m/s | d | Dynamic pressure from manometer: \(∆p=(ρ_{ω}-p_{a})gh=(1000-1.13)×9.81×0.05≈489.95Pa\) Pitot velocity (with coefficient C = 0.98): \(V=C\frac{2∆p}{ρ_{a}}=0.98\frac{2×489.95}{1.13}≈28.9m/s\) \(28.86 m/s\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 80 | For venturimeters, the coefficient of discharge range is ______. | 0.90 - 0.93 | 0.93 - 0.94 | 0.95 - 0.98 | 0.85 – 090 | c | The coefficient of discharge (Cd) for a flow meter is a dimensionless number that relates the actual flow rate to the theoretical flow rate. For a venturimeter, the flow path is carefully designed to be smooth and gradually converging and diverging, which minimizes energy losses due to turbulence and friction. As a result, the actual discharge is very close to the theoretical discharge. Therefore, the coefficient of discharge for a venturimeter is typically very high, ranging from 0.95 to 0.98. In contrast, devices like an orifice meter have a much lower coefficient of discharge due to higher energy losses. | Comments | Active | |
| 81 | Identify the odd option among the following with respect to the property they measure. | Orifice meter | Pitot tube | Rotameter | Venturimeter | b | The Pitot tube is the odd option. It measures local fluid velocity at a specific point by converting the kinetic energy of the flow into potential energy. The other three instruments—the Orifice meter, Rotameter, and Venturimeter—are all types of flow meters used to measure the flow rate (or discharge) of a fluid passing through a pipe or conduit. While they all rely on fluid dynamics principles, their primary measured property and application are different. | Comments | Active | |
| 82 | ______ casting is a type of permanent casting process. | Shell | Investment | Vacuum | Slush | d | Slush casting is a type of permanent mold casting process. In this process, the molten metal is poured into a metal mold, allowed to solidify for a short time on the mold walls to form a skin, and then the remaining liquid is poured out, leaving a hollow casting. Shell casting and investment casting are types of expendable mold casting processes, where the mold is destroyed to remove the cast part. Vacuum casting is a variation of these, often used with sand or shell molds. Therefore, slush casting is the correct option as it uses a permanent, reusable mold. | Comments | Active | |
| 83 | ______ is NOT a component of extrusion process. | Ram | Flux coated electrode | Die | Hopper | b | The extrusion process is a manufacturing technique used to create objects of a fixed cross-sectional profile. It involves pushing or drawing a material (like a metal or plastic) through a die. The key components of this process are a ram or a screw that applies force, a die that shapes the material, and a hopper which feeds the raw material. A flux-coated electrode, however, is a component used in welding processes, specifically in shielded metal arc welding (SMAW). It serves to create an arc and provide filler material and a shielding gas for the weld. | Comments | Active | |
| 84 | Viscosity of a lubrication oil for an IC engine is measured by ______. | manometer | thermometer | barometer | viscometer | d | The viscosity of a liquid, such as a lubrication oil, is a measure of its resistance to flow. The instrument used to measure this property is called a viscometer. A manometer is used to measure pressure, a thermometer measures temperature, and a barometer measures atmospheric pressure. Therefore, the correct instrument for measuring viscosity is a viscometer. | Comments | Active | |
| 85 | Identify the odd option from among the following. | Modulus of viscosity | Bulk modulus | Modulus of elasticity | Modulus of rigidity | a | The modulus of viscosity (or dynamic viscosity) is a measure of a fluid's resistance to shear flow. It is a property of fluids. The other three options, Bulk modulus, Modulus of elasticity (Young's modulus), and Modulus of rigidity (shear modulus), are all elastic moduli. They are measures of a solid material's resistance to different types of deformation (volumetric, tensile/compressive, and shear, respectively). Therefore, Modulus of viscosity is the odd one out as it relates to fluids, while the others relate to solids. | Comments | Active | |
| 86 | For an anisotropic medium, number of elastic constant are ______. | 11 | 41 | 21 | 31 | c | The number of independent elastic constants for a general anisotropic material is 21. These constants are required to define the relationship between stress and strain in the material, which is described by a 6x6 stiffness or compliance matrix. For other types of materials, the number of independent constants is reduced due to symmetry: for a transversely isotropic material, it is 5; for an orthotropic material, it is 9; and for an isotropic material, it is only 2. | Comments | Active | |
| 87 | There is no geometrical distinction between streamline, pathline and streakline in case of: | Irrotational flow | Steady flow | Laminar flow | Uniform flow | b | The geometrical distinction between streamlines, pathlines, and streaklines vanishes in the case of steady flow. Streamline: A line that is tangent to the velocity vector of the fluid at a given instant in time. Pathline: The actual path traced by a single fluid particle over a period of time. Streakline: The locus of all fluid particles that have passed through a particular fixed point in space at some earlier time. In a steady flow, the velocity at any fixed point in space does not change with time. Because of this, the path a particle takes (pathline) and the line connecting all particles that have passed through a point (streakline) will be the same as the instantaneous velocity field (streamline). In unsteady flow, these three lines are generally different. |
Comments | Active | |
| 88 | In a manometer, the tube should contain a liquid whose specific gravity is ______ the specific gravity of the liquid whose pressure is to be measured. | similar to | smaller than | greater than | half of | c | In a manometer, the liquid used in the tube (manometric fluid) must have a specific gravity greater than the specific gravity of the liquid whose pressure is being measured. This is to ensure that the two liquids do not mix and to provide a stable, measurable column height. If the manometric fluid were lighter, the liquid being measured could easily push it out of the manometer tube, making an accurate measurement difficult or impossible. | Comments | Active | |
| 89 | Identify the feature ‘A’ in the casting figure given. |
Cope | Drag | Parting line | Chaplet | c | In sand casting, the mold is typically made in two or more parts. The top half of the mold is called the cope and the bottom half is called the drag. The line or plane that separates the cope and drag is the parting line. Chaplets are metal inserts used to support a core within the mold cavity. In the provided figure, 'A' clearly indicates the line separating the two halves of the mold, which is the parting line. | Comments | Active | |
| 90 | Which of the following is/are correct with respect to entropy? I) It is a measure of net work done by system II) It is a measure of randomness in the system III) It is a measure of heat trfer potential of the system . |
III is correct | I and II are correct | I is correct | II is correct | d | Entropy is a fundamental concept in thermodynamics. It is often described as a measure of the randomness, disorder, or chaos within a system. This is statement II. The other statements are incorrect. Statement I describes work, which is energy transferred in a mechanical process, and statement III describes temperature, which determines the direction of heat transfer. | Comments | Active | |
| 91 | If a column is fixed at one end and free at the other end, the effective length is ______ the original length. | four times | twice | thrice | half | b | The effective length of a column fixed at one end and free at the other is twice its original length. This is because the free end can move laterally and rotate, causing the column to buckle as if it were a pin-ended column of twice its original length. | Comments | Active | |
| 92 | Steels having carbon level between 0.77 % to 2.1 % is called ______. | hyper-eutectoid steel | peritectoid steel | hypo-eutectoid steel | cementoid steel | a | Hypo-eutectoid steel has a carbon content less than 0.77%. | Comments | Active | |
| 93 | For a streamline flow of an ideal liquid in varying cross section tube, total energy per unit volume ______ throughout the fluid. | remains constant | becomes zero | decreases | increases | a | This principle is known as Bernoulli's theorem. For an ideal, incompressible fluid (like an ideal liquid) in steady, streamlined flow, the total energy per unit volume remains constant along a streamline. | Comments | Active | |
| 94 | Baffles in water tubes in a Babcock and Wilcox boiler is provided ______. | for regulation of steam flow | for preventing cavitation | for regulation of water flow | for providing better contact between flue gases and water tube | d | Baffles in a Babcock and Wilcox water-tube boiler are strategically placed plates or walls. Their primary function is to direct the flow of hot flue gases through the tube banks. This zig-zag or serpentine path forces the gases to move across the water tubes instead of simply moving straight up and out. This extended and more turbulent contact time ensures maximum heat transfer from the hot gases to the water in the tubes, thereby increasing the boiler's thermal efficiency. | Comments | Active | |
| 95 | A simple conical governor is also called______ governor. | centripetal | centrifugal | Inertia | watt | d | A simple conical governor is also known as a Watt governor. It is one of the earliest and simplest types of centrifugal governors, invented by James Watt to regulate the speed of his steam engines. It consists of a vertical spindle with two balls attached by arms. As the engine speed increases, the balls fly outwards due to centrifugal force, which in turn lifts a sleeve that controls the throttle valve, thereby regulating the engine's speed. | Comments | Active | |
| 96 | Identify the incorrect statement related to tungsten inert gas welding process out of the given options. | Arc is comparatively silent and has less spatter. | Argon gas is used in the process | Flux is used in this process | It employs a non-consumable electrode | c | Tungsten Inert Gas (TIG) welding, also known as Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW), is a welding process that uses a non-consumable tungsten electrode to produce the weld. The weld area is shielded from atmospheric contamination by an inert shielding gas, such as argon or helium. The inert gas shield eliminates the need for a flux. Flux is used in processes like Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW) or brazing to clean the joint and prevent oxidation. The absence of flux means no slag is produced. |
Comments | Active | |
| 97 | Which of following holds true for an otto cycle? | Otto cycle is a constant volume combustion cycle | Otto cycle is a constant velocity combustion cycle | Otto cycle is a constant pressure combustion cycle | Otto cycle is a partly constant volume and pressure combustion cycle | a | The Otto cycle is the ideal thermodynamic cycle for spark-ignition (petrol) internal combustion engines.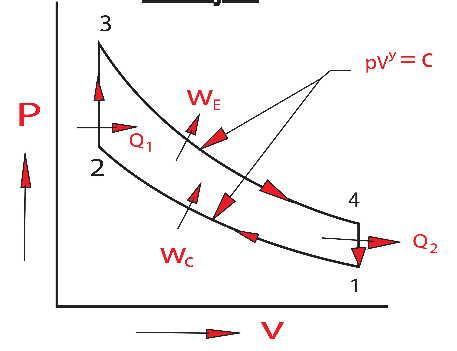 The processes are considered constant volume combustion and heat rejection, which distinguishes it from other cycles like the Diesel cycle (constant pressure heat addition) or the Dual cycle (partly constant volume and partly constant pressure heat addition). |
Comments | Active | |
| 98 | A Newtonian fluid is filled in the clearance between a shaft and a concentric sleeve. The sleeve attains a speed of 80 cm/s, when a force of 40 N is applied to the sleeve parallel to the shaft. Determine the speed if a force of 300N is applied. | 200 cm/s | 600 cm/s | 300 cm/s | 250 cm/s | b | This problem is based on the fundamental property of a Newtonian fluid, where the shear stress is directly proportional to the shear rate (or velocity gradient). In this scenario, the force required to move the sleeve is directly proportional to the velocity of the sleeve, as the viscosity, area, and clearance remain constant. This linear relationship can be expressed as: \(\frac{F_{1}}{V_{1}}=\frac{F_{2}}{V_{2}}\) Where: = Initial force = 40 N \(F_{1}\) = Initial speed = 80 cm/s \(V_{1}\) = New force = 300 N \(F_{2}\) = New speed (to be determined) \(V_{2}\) To find , rearrange the formula: \(V_{2}\) \(V_{2}=\frac{F_{2}.V_{1}}{F_{1}}\) Substitute the given values: \(V_{2}=\frac{F_{2}.V_{1}}{F_{1}}\) \(V_{2}=6.10.8.\frac{80}{40}cm/s\) \(V_{2}=300.2 cm/s\) \(V_{2}=600 cm/s\) Therefore, the speed of the sleeve will be 600 cm/s when a force of 300 N is applied. |
Comments | Active | |
| 99 | Identify the odd option from among the following with respect to firing (internal/external). |
Stirling boiler | Cochran | Locomotive boiler | Lancashire | a | Boilers can be classified based on whether the furnace is inside or outside the main boiler shell. An internally fired boiler has the furnace and grate located within the boiler shell. This design is simple and compact. The Cochran, Locomotive, and Lancashire boilers are all internally fired. An externally fired boiler has the furnace situated outside the main boiler shell. This design is more common in large, high-pressure industrial applications. The Stirling boiler is a type of water-tube boiler, and it is externally fired. Therefore, the Stirling boiler is the odd one out. |
Comments | Active | |
| 100 | In the case of tool wear, diffusion occurs at the ______ causing the tool surface to become depleted of the atoms responsible for its hardness. | workpiece – chip boundary | tool - workpiece boundary | triple zone | tool - chip boundary | d | Tool wear is the gradual loss of material from the surface of a cutting tool. One of the primary mechanisms of tool wear at high temperatures is diffusion wear. Diffusion occurs at the tool-chip boundary because this is the interface where the highest temperatures and pressures are generated during machining. At these extreme conditions, atoms from the tool material (like tungsten, carbon, or cobalt) migrate and diffuse into the hot, soft, and chemically receptive workpiece material or chip. This loss of atoms, particularly those responsible for hardness, makes the tool surface softer and more susceptible to further wear, reducing its effective life. | Comments | Active | |
| 101 | Identify the correct statements out of the given options with respect to inclined UTube manometer. i. More accurate than U-tube manometer ii. Measures volume directly iii. Measures velocity also |
Only ii is correct | Only iii is correct | Both ii and iii are correct | Only i is correct | d | U Tube manometer is used for pressure measurement. And inclined U tube manometer is used for measure pressure more acurately. | Comments | Active | |
| 102 | Identify the correct statement related to gas metal arc welding process. i. Slag is formed in the process ii. Consumable electrode is in form of wire iii. Acetylene is used in the process for welding. |
Only ii is correct | Only i and iii is correct | Only i is correct | Both i and ii are correct | a | Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW), also known as MIG welding, is a widely used welding process. Let's analyze each statement: i. Slag is formed in the process. This statement is incorrect. GMAW is a clean welding process that uses a shielding gas (like Argon or a mixture of Argon and CO2) to protect the weld from the atmosphere. Unlike processes like Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW), there is no flux used in GMAW, and therefore, no slag is formed. ii. Consumable electrode is in the form of a wire. This statement is correct. GMAW uses a continuously fed, solid metal wire electrode that is consumed during the welding process. The wire melts and becomes the filler metal. iii. Acetylene is used in the process for welding. This statement is incorrect. Acetylene is a fuel gas primarily used in Oxy-acetylene welding (gas welding), where it is burned with oxygen to produce a high-temperature flame. It is not used in GMAW, which uses an electric arc to melt the electrode wire. |
Comments | Active | |
| 103 | Which of the following gases CANNOT be used as a shielding gas in tungsten inert gas welding process? | Helium | Oxygen | Argon | Nitrogen | b | Tungsten Inert Gas (TIG) welding, as its name suggests, requires an inert shielding gas. This gas prevents atmospheric gases like oxygen and nitrogen from contaminating the molten weld pool and the hot tungsten electrode. Oxygen is a highly reactive gas. Using it as a shielding gas would cause the molten metal and the tungsten electrode to oxidize immediately, leading to a brittle, porous, and poor-quality weld. Therefore, it is strictly avoided. |
Comments | Active | |
| 104 | A smaller version of the Lancashire boiler is ______. | Package boiler | Babcock and Wilcox boiler | Stirling boiler | Cornish boiler | d | A Cornish boiler is a smaller and simpler version of the Lancashire boiler. Both are horizontal, fire-tube boilers. The Lancashire boiler has two large internal flue tubes, which provides a larger heating surface and a higher steam output. It's known for its robust construction and was widely used in industrial settings. The Cornish boiler has only one large internal flue tube. Because of this single tube, it has a smaller heating surface area, making it suitable for applications with lower steam demands. It was a popular choice for small factories and workshops. |
Comments | Active | |
| 105 | ______ is a unique phase of Iron-carbon system having harness generally induced by quenching. | Pearlite | Ferrite | Austenite | Martensite | d | Martensite is a unique, non-equilibrium phase of the iron-carbon system. It has a body-centered tetragonal (BCT) crystal structure and is known for its extreme hardness and brittleness. This phase is not formed by slow cooling, but is instead created by the rapid quenching (cooling) of austenite (a high-temperature phase of steel). This rapid cooling traps the carbon atoms in the iron's crystal lattice, causing a significant lattice distortion that is responsible for its high hardness. | Comments | Active | |
| 106 | Which equilibrium is indicated by the given figure? |
Neutral equilibrium | Wavy equilibrium | Unstable equilibrium | Stable equilibrium | d | The figure shows a ball resting at the bottom of a curved surface. In stable equilibrium, if a body is slightly disturbed from its position, it will return to its original position after the disturbance is removed. In the provided figure, if you push the ball slightly, gravity will pull it back to the bottom of the curve, where its potential energy is at a minimum. In unstable equilibrium, if a body is slightly disturbed, it will move further away from its original position. An example would be a ball balanced on top of a hill. In neutral equilibrium, if a body is disturbed, it will remain in its new position. An example is a ball resting on a flat, horizontal surface. |
Comments | Active | |
| 107 | Which of the following is NOT a basis of classification of boilers? | Construction of boilers | Weight of boilers | Position of water | Position of furnace | b | Boilers are classified based on a number of characteristics, but their weight is not a primary basis for classification. Construction of boilers: This is a major classification method. Boilers are categorized as fire-tube or water-tube depending on whether the hot gases or the water flow through the tubes. Position of water: This relates to the classification as fire-tube or water-tube boilers. In a fire-tube boiler, the water surrounds the tubes, and in a water-tube boiler, the water is inside the tubes. Position of furnace: This is another basis for classification, categorizing boilers as either internally fired (the furnace is inside the boiler shell) or externally fired (the furnace is located outside the main boiler shell). |
Comments | Active | |
| 108 | Detonation in IC Engines ______. | do not occur | occurs near beginning of combustion | occurs near end of combustion | occurs at mid of combustion | b | Detonation, or engine knock, is a form of abnormal combustion that occurs in spark-ignition engines. It happens when the unburned air-fuel mixture, ahead of the flame front initiated by the spark plug, spontaneously ignites due to high pressure and temperature. This autoignition occurs near the beginning of combustion, creating a violent pressure wave that causes the characteristic knocking sound and can lead to engine damage. The process is a rapid, uncontrolled explosion rather than the smooth, progressive burn of normal combustion. It's often associated with low-octane fuels and can be a sign that the engine is not operating efficiently or correctly. |
Comments | Active | |
| 109 | Bending moment at the supports for a simply supported beam would be ______. | 0 | >1 | 1 | −1 | a | A simply supported beam is a type of structural element that is supported at both ends by a pinned support (allowing rotation but preventing vertical movement) and a roller support (allowing both rotation and horizontal movement). By definition, these supports cannot resist a bending moment. Therefore, the internal bending moment at the exact points where the supports are located is always zero.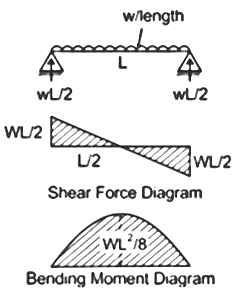 |
Comments | Active | |
| 110 | Which of the following is NOT usually used as a flux for soldering? | Zinc chloride | Lead | Ammonium chloride | Borax | b | A flux is a chemical cleaning agent used in soldering to remove oxides and other impurities from the surfaces of the metals to be joined. This process, known as wetting, ensures that the molten solder can form a strong metallurgical bond. Zinc chloride, ammonium chloride, and borax are all well-established and commonly used fluxes |
Comments | Active |










