| S.No | Question | Option A | Option B | Option C | Option D | Answer | Solution | Comments | Status | Action |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Newton’s ________ is also known as the law of inertia | First law of motion | Zeroth law of motion | Second law of motion | Third law of motion | a | Newton's first law of motion, often called the law of inertia, states that an object at rest will stay at rest, and an object in motion will stay in motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced external force. The concept of inertia, which is the resistance of an object to a change in its state of motion, is the core principle of this law. | Comments | Active | |
| 2 | The addition of ________ increases the melting point temperature of the tungsten electrode. | Copper | Aluminium | Iron | Thorium | d | The addition of thorium, or other rare earth oxides like lanthanum or cerium, to a tungsten electrode significantly increases its electron emissivity, which in turn improves arc starting and stability. This increased electron emission also allows the electrode to operate at a lower temperature for the same current, which prevents premature melting and increases the life of the electrode. | Comments | Active | |
| 3 | ________ is chemically active at soldering temperatures and promotes the wetting action required for successful joining. | Tin | Phosphorous | Gold | Silver | a | Tin is the chemically active metal that readily interacts with other metals at soldering temperatures, allowing the solder to "wet" the surfaces and create a strong joint. | Comments | Active | |
| 4 | The weld area formed by the resistance spot welding process is called ________. | Leg | Toe | Nugget | Finger | c | The weld area formed by the resistance spot welding process is called a "nugget." This is the localized volume of metal that has been heated to its plastic or molten state and then solidified to form the weld joint. The nugget is the key characteristic of a spot weld. | Comments | Active | |
| 5 | Ultrasonic testing is carried out to evaluate ________. | Toughness | Yield strength | Hardness | Cracks in the surface | d | Ultrasonic testing is a non-destructive testing (NDT) method used to detect internal and surface-breaking defects in materials. It uses high-frequency sound waves to identify discontinuities such as cracks, voids, and flaws by analyzing the reflected sound signals. This makes it a primary method for quality control and integrity assessment, not for evaluating mechanical properties like toughness, yield strength, or hardness. | Comments | Active | |
| 6 | Compared to venturimeters, orifice meters have ________ head loss. | Medium | Large | The same | Small | b | Compared to venturimeters, orifice meters have a significantly larger head loss. This is because the abrupt change in geometry in an orifice meter creates considerable turbulence and energy dissipation, leading to a much higher permanent pressure loss than the smooth, gradual expansion in a venturimeter. | Comments | Active | |
| 7 | The expression F = μ A (du/dy) denotes ________. | Newton’s law of momentum | Newton’s law of viscosity | Newton’s law of motion | Newton’s law of force | b | The expression F = μ A (du/dy) denotes the viscous force (F) in a fluid, which is directly proportional to the fluid's dynamic viscosity (μ), the area (A) of the fluid layer, and the velocity gradient (du/dy) across the fluid. | Comments | Active | |
| 8 | Cemented carbides tools are normally manufactured via ________. | Forging | Powder metallurgy | Welding | Casting | b | Cemented carbide tools are manufactured using powder metallurgy. This process involves mixing fine powders of hard carbides (like tungsten carbide) and a binder metal (like cobalt), pressing them into a desired shape, and then heating the compacted part to a high temperature below its melting point in a process called sintering. This method is ideal for creating hard, brittle materials with high melting points. | Comments | Active | |
| 9 | A rod of length 150 cm and of diameter 2.0 cm is subjected to an axial pull of 20 kN. If the modulus of elasticity of the rod material is 2 × 105 N/mm2, determine the stress developed in the rod. | 30.65 N/mm2 | 10 N/mm2 | 15.25 N/mm2 | 63.662 N/mm2 | d | Based on the calculations, the stress developed in the rod is approximately \(63.662textN/mm^{2}.\) | Comments | Active | |
| 10 | ________ is removed from a boiler by the blow down valve. | Ash | Sludge | Flue gas | Smoke | b | A blow down valve is used to remove concentrated dissolved and suspended solids, often referred to as sludge, that have accumulated at the bottom of the boiler. This process helps to maintain the water quality and prevent scale formation on the heat transfer surfaces. | Comments | Active | |
| 11 | The flow is ________ during the opening of a valve in a pipeline. | Unsteady | Uniform | Laminar | Steady | a | The flow is unsteady because the velocity and pressure of the fluid are changing with respect to time as the valve is being opened. A steady flow would have constant properties at any given point over time, which is not the case during the opening of a valve. | Comments | Active | |
| 12 | According to ________, when a bullet is fired from a gun, the opposite reaction of the bullet is known as the recoil of gun. | Newton’s zeroth law of motion | Newton’s second law of motion | Newton’s first law of motion | Newton’s third law of motion | d | According to Newton's third law, for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. When a gun is fired, the gun applies a forward force on the bullet (the action), and in response, the bullet applies an equal and opposite backward force on the gun. This backward force is what causes the gun to recoil. | Comments | Active | |
| 13 | Jet engines employ ________ type of compressor. | Radial flow | Centrifugal | Rotary flow | Axial flow | d | Most modern jet engines, such as those used in commercial aircraft, employ multi-stage axial flow compressors. This type of compressor is highly efficient and capable of achieving the high pressure ratios and large air mass flow rates required for high-speed flight. While some smaller jet engines or APUs use centrifugal compressors, axial flow is the dominant type for major applications. | Comments | Active | |
| 14 | ________ provides a clearance between the trailing edge of the tool and the newly generated work surface. | End relief angle | End cutting edge angle | Side relief angle | Side cutting edge angle | b | End cutting edge angle provides the clearance between the trailing edge of the tool and the workpiece. End cutting edge angle: It is the angle between the end cutting edge angle of the tool and a line perpendicular to its shank. It avoids rubbing between the trailing edge of the tool and the workpiece. It influences the direction of chip flow. |
Comments | Active | |
| 15 | ________ is/are caused due to the release of gases during pouring which consists of small gas cavities. | Sand wash | Pinholes | Hot tears | Sand blow | b | Pinholes are a type of casting defect that consists of small, rounded gas cavities. They are caused by the release of dissolved gases from the molten metal as it solidifies, which become trapped within the casting. | Comments | Active | |
| 16 | The force required to keep unit length of the surface film in equilibrium is called ________. | Viscosity force | Cohesion force | Friction force | Surface tension | d | Surface tension is defined as the force acting per unit length on the surface of a liquid, which is required to hold the surface film in equilibrium. It arises from the cohesive forces between the liquid molecules. | Comments | Active | |
| 17 | Identify the toe crack from the given figure.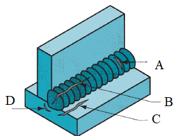 |
C | B | A | D | a | Comments | Active | ||
| 18 | A body of weight 300 N is lying on a rough horizontal plane having a coefficient of friction as 0.3. Find the magnitude of the force which can move the body while acting at an angle of 25° with the horizontal.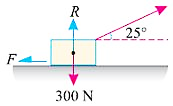 |
0.871 N | 8.71 N | 87.1 N | 871 N | c | On balancing forces in x-axis we get: Friction force \(F=μR\) \(F=F_{b}cos25^{°}⇒ μR=F_{b}cos25^{°}\) \(R=3.02 F_{b}\) On balancing forces in y-axis we get: \(R=F_{b}sin25^{°}=300\) \(3.02 F_{b}+F_{b}sin25^{°}=300\) \( F_{b}+(3.02+0.423)=300\) \( F_{b}=\frac{300}{3.44}=87.1 N\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 19 | Which cycle consists of two reversible isochores and two reversible adiabatics? | Otto cycle | Compression cycle | Air cycle | Diesel cycle | a | The Otto cycle is an idealized thermodynamic cycle that consists of two reversible adiabatic (isentropic) processes and two reversible isochoric (constant volume) processes. In contrast, the Diesel cycle consists of two reversible adiabatic processes, one reversible isobaric process, and one reversible isochoric process. | Comments | Active | |
| 20 | The definition of the compressible and incompressible fluid is defined according to the changes in ________. | Density | Temperature | Motion | Energy | a | The definition of a compressible and incompressible fluid is based on the changes in its density. An incompressible fluid is one whose density remains constant regardless of changes in pressure. A compressible fluid is one whose density changes significantly with changes in pressure. |
Comments | Active | |
| 21 | Shielding is done by ________ in gas welding process. | Outermost cone of the flame | External inert gas | Innermost cone of the flame | Flux | a | In the gas welding process (such as oxy-acetylene welding), the shielding of the molten weld pool is provided by the outermost cone of the flame. This part of the flame, also known as the envelope or oxidising cone, is where the hot gases (carbon dioxide and water vapor) from the primary combustion react with the surrounding atmosphere. This envelope of hot, inert gases acts as a shield to protect the molten metal from contamination by oxygen and nitrogen from the air. |
Comments | Active | |
| 22 | The area of the turning moment diagram represents the ________. | Work done per revolution | Energy consumed per revolution | Energy liberated per revolution | Motion proceeded per revolution | a | The area of the turning moment diagram represents the work done per revolution. This is because, in rotational motion, the work done () is the integral of the turning moment (torque, ) with respect to the crank angle (), which is mathematically represented as . The area under the curve of a graph with torque on the y-axis and angle on the x-axis corresponds to this integral. \(W\) \(T\) \(θ\) \(W=∫Tdθ\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 23 | ________ is a virtue by which moulding sand permits escape of gases formed during casting. | Shock resistance | Hardness | Grain size | Permeability | d | Permeability is the virtue by which moulding sand permits the escape of gases formed during casting. | Comments | Active | |
| 24 | The coefficient of discharge for venturimeters is in the range of ________. | 0.90 to 0.93 | 0.98 to 0.99 | 0.95 to 0.98 | 0.93 to 0.94 | c | The coefficient of discharge (Cd) for a venturimeter is a measure of its efficiency. Due to its streamlined, gradually converging and diverging cone shape, it minimizes energy losses from friction and turbulence. This results in a very high coefficient of discharge, close to unity. The typical range for the coefficient of discharge for a venturimeter is 0.95 to 0.98. |
Comments | Active | |
| 25 | Which of the following is NOT an obstruction type of flow meter? | Venturimeter | Pitot tube | Orifice meter | Nozzle meter | b | Pitot tube is not an obstruction type of flow meter. Venturimeter, Orifice meter, and Nozzle meter are all obstruction-type flow meters because they work by creating a constriction in the flow path, which causes a measurable pressure drop. A Pitot tube measures local fluid velocity at a single point by measuring the difference between stagnation and static pressure, without obstructing the main flow. |
Comments | Active | |
| 26 | Which of the following is NOT a type of rotary pump? | Centrifugal pump | Mixed flow pump | Impact pump | Axial flow pump | c | Based on the classification of pumps: Centrifugal pump, Mixed flow pump, and Axial flow pump are all types of rotary pumps (specifically, dynamic pumps) that use a rotating impeller to move fluid. Impact pump is not a standard or recognized type of rotary pump. |
Comments | Active | |
| 27 | Which of the following is NOT a direct task of flux in a welding arc? | Stabilise the arc | Reduce spattering | Reduce the welding time | Provide a protective atmosphere for welding | c | The direct tasks of flux in a welding arc are to stabilize the arc, provide a protective atmosphere, and reduce spattering. Reducing the welding time is not a direct function of the flux. It is a result of using an efficient welding process, not the flux itself. |
Comments | Active | |
| 28 | In a ________ flow, the fluid layers do not mix macroscopically. | Constant | Laminar | Turbulent | Steady | b | In a laminar flow, the fluid layers move smoothly past one another without significant macroscopic mixing. This type of flow is characterized by orderly, parallel fluid layers or streamlines. The opposite of this is turbulent flow, where fluid layers mix chaotically. |
Comments | Active | |
| 29 | Identify the odd one out of the following options. | Metal active gas welding | Metal inert gas welding | Submerged arc welding | Gas metal arc welding | c | Submerged arc welding is the odd one out. Metal active gas welding (MAG), Metal inert gas welding (MIG), and Gas metal arc welding (GMAW) are all variations of the same welding process. |
Comments | Active | |
| 30 | Typical heat factor for TIG welding is taken as ________. | 0.7 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.4 | a | The typical heat factor for TIG welding is in the range of 0.6 to 0.7. Among the given options, 0.7 is the most representative value. | Comments | Active | |
| 31 | Identify the odd one out of the following processes. | Submerged arc welding | Manual metal arc welding | Shielding metal arc welding | Stick welding | a | Submerged arc welding is the odd one out. Manual metal arc welding (MMAW), Shielded metal arc welding (SMAW), and Stick welding are all different names for the same welding process. Submerged arc welding (SAW) is a distinct process. |
Comments | Active | |
| 32 | Parting line is between ________. | Riser and pouring basin | Cope and drag | Flask and runner | Runner and riser | b | A parting line in a sand mold is the line or plane that separates the two halves of the mold. The two main sections of a two-part sand mold are the cope (the top half) and the drag (the bottom half). Therefore, the parting line is between the cope and the drag. |
Comments | Active | |
| 33 | Identify the odd one out of the following options. | Lost pattern process | Evaporative-foam process | Lost-foam process | Predictive-foam process | d | The other three options (Lost pattern process, Evaporative-foam process, and Lost-foam process) are all standard and related terms for a type of casting where a foam pattern is vaporized by molten metal. | Comments | Active | |
| 34 | Which process uses a molten metal bath for brazing? | Furnace brazing | Infrared brazing | Dip brazing | Torch brazing | c | Dip brazing is the process that uses a molten metal or flux bath for brazing. The parts are immersed in the bath, which heats them and melts the filler metal. | Comments | Active | |
| 35 | If in a double helical gear, the right and left inclinations meet at a common apex and there is no groove in between, the gear is known as ________. | Herringbone gear | Crossed helical gear | Helical spur gear | Spiral bevel gear | a | A double helical gear with right and left inclinations meeting at a common apex and no groove in between is known as a herringbone gear. | Comments | Active | |
| 36 | The smaller version of the Lancashire boiler is the ________. | Stirling boiler | Cornish boiler | Thimble boiler | Cochran boiler | b | The smaller version of the Lancashire boiler is the Cornish boiler. The Cornish boiler has a single internal flue, whereas the Lancashire boiler has two. |
Comments | Active | |
| 37 | The sensitivity of simple manometers can be improved by ________. | Glass bulb | Perpendicular tubes | Inverted tubes | Inclined tubes | d | An inclined manometer is a type of differential manometer where one leg is inclined at a small angle. This design increases the length of the fluid column's movement (L) for a given vertical height change (h), making small pressure differences easier to measure and thus increasing the overall sensitivity of the device. | Comments | Active | |
| 38 | Which of the following techniques is NOT a type of magnetic particle testing method | Prod technique | Coil technique | Plate technique | Yoke technique | c | Plate technique is NOT a type of magnetic particle testing method. The prod, coil, and yoke techniques are all standard methods used to magnetize a material for magnetic particle testing. |
Comments | Active | |
| 39 | Tap water if used in boilers could directly promote ________. | Scaling | Loss of mechanical property | Corrosion | Loss of hardness | a | The dissolved minerals and salts present in tap water, which are responsible for its hardness, tend to precipitate out when the water is heated and converted into steam in a boiler. This precipitation forms a hard, insulating layer on the boiler's internal surfaces. This process is called scaling. | Comments | Active | |
| 40 | The process where the carbon from outside is introduced in the surface of steel by keeping charcoal at higher temperatures is called ________. | Case hardening | Nitriding | Tempering | Quenching | a | Case hardening is a heat treatment process that hardens the surface of a metal part while leaving the core softer and tougher. One common method of achieving case hardening is carburizing, which involves diffusing carbon into the surface of the steel. The use of charcoal as a source of carbon at high temperatures is a classic example of this. | Comments | Active | |
| 41 | During the analysis of bars of composite sections as shown in the given figure. The modular ratio is defined as ________.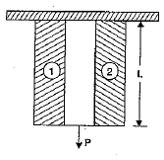 |
Shear modulus of Bar 1 / Shear modulus of Bar 2 | Young modulus of Bar 1 / Young modulus of Bar 2 | Shear modulus of Bar 2 / Shear modulus of Bar 1 | Young modulus of Bar 2 / Shear modulus of Bar 1 | b | The modular ratio () is a dimensionless quantity used in the analysis of composite sections to relate the elastic properties of the different materials. It is defined as the ratio of the Young's Modulus (Modulus of Elasticity) of the two materials. \(m\) \(m=\frac{Young’s modulus of Bar 1}{Young’s modulus of Bar 2}\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 42 | Which of the following elements does NOT form carbides in ferrous steels? | Chromium | Vanadium | Cobalt | Molybdenum | c | Cobalt does NOT form carbides in ferrous steels. Chromium, Vanadium, and Molybdenum are all strong carbide-forming elements used in steels. |
Comments | Active | |
| 43 | Flat pivot bearing is also known as ________. | Collar bearing | Truncated bearing | Foot step bearing | Conical bearing | c | A flat pivot bearing is a type of thrust bearing used to support an axial load at the end of a vertical shaft. It is also commonly known as a foot step bearing. | Comments | Active | |
| 44 | The entropy of an isolated system _______. | Can never decrease | Can never increase | Always remains constant | Can never be zero | a | According to the Second Law of Thermodynamics, specifically the principle of increase in entropy, the entropy of an isolated system can never decrease. It will either increase during an irreversible process or remain constant during a reversible process. | Comments | Active | |
| 45 | A balloon-shaped gas cavity caused by the release of mold gases during pouring is called ________. | Sand blow | Sand wash | Misrun | Pin holes | a | A balloon-shaped gas cavity caused by the release of mold gases during pouring is called a Sand blow. | Comments | Active | |
| 46 | In which of the following water tube boilers are water tubes inclined at a certain angle? | Locomotive boiler | Cornish boiler | Babcock and Wilcox boiler | Lancashire boiler | c | The Babcock and Wilcox boiler is a type of water-tube boiler where the water tubes are inclined at a certain angle (typically 15 degrees to the horizontal) to promote natural circulation of water. The other options are all types of fire-tube boilers. | Comments | Active | |
| 47 | The force of friction always acts in a direction ________ to that in which the body tends to move the body. | Inclined | Perpendicular | Opposite | Similar | c | Based on the principles of physics and mechanics, the force of friction always acts in a direction that opposes motion or the tendency of motion between two surfaces in contact. Therefore, the force of friction always acts in a direction opposite to that in which the body tends to move. |
Comments | Active | |
| 48 | For irrotational flow, the Bernoulli constant is ________. | Zero | Different everywhere | Constant | The same everywhere | d | For a steady, inviscid, and incompressible fluid flow, the Bernoulli constant is constant along a streamline. | Comments | Active | |
| 49 | Which of the following is NOT a type of beam? | Continuous beam | Continuum beam | Fixed beam | Overhanging beam | b | Continuum beam is NOT a standard type of beam. Continuous, fixed, and overhanging are all recognized classifications of beams based on their support conditions. |
Comments | Active | |
| 50 | The line of action of concurrent forces meet at ________. | Two points | A plane | Perpendicular planes | A single point | d | The line of action of concurrent forces meet at a single point. This is the definition of concurrent forces in engineering mechanics. Their lines of action all pass through a common point of intersection. |
Comments | Active | |
| 51 | The quantitative statement of entropy principle is denoted by the ________. | zeroth law of thermodynamics | 2nd law of thermodynamics | 3rd law of thermodynamics | 1st law of thermodynamics | b | Comments | Active | ||
| 52 | A gas tungsten arc-welding operation is performed at a current of 300 A and voltage of 20 V. The power applied in the operation is ________. | 1.5 kW | 60 kW | 6 kW | 15 kW | c | The electrical power (P) applied in a welding operation is calculated by multiplying the current (I) and the voltage (V). \(P=I×V\) Given: Current \((I) = 300 A\) Voltage \((V) = 20 V\) \(P=300 A×20 V=6000 W\) To convert this value to kilowatts (kW), divide by 1000: \(P=\frac{6000}{1000}kW=6 kW\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 53 | Heavy trucks use the ________ cooling system. | Thermo siphon | Forced-circulation | Evaporative | Air | b | Heavy trucks use a forced-circulation cooling system. In this system, a pump (typically a water pump) actively circulates the coolant through the engine block and radiator. This ensures a consistent and high rate of heat removal, which is essential for the large, high-power engines found in heavy trucks. |
Comments | Active | |
| 54 | The flow is observed to be laminar till a Reynolds number value of about ________. | 5000 | 7000 | 2300 | 1000 | c | The flow is generally considered to be laminar until a Reynolds number value of about 2300 for internal flow in pipes. | Comments | Active | |
| 55 | Orifices are used to measure ________. | Pressure | Flow rate | Density | Velocity | b | Based on standard fluid mechanics principles, orifices are used to measure the flow rate of a fluid. An orifice plate is a device used to measure flow rate. It works on the principle of a pressure differential. When a fluid passes through the constricted opening of the orifice, its velocity increases, and its pressure decreases. The pressure difference is measured, and this measurement is used to calculate the flow rate. |
Comments | Active | |
| 56 | The probe of ultrasonic flaw detector contains ________. | Trducer | Copper balls | Plastic plugs | Polystyrene fibers | a | The key component inside a probe for an ultrasonic flaw detector is a transducer. A transducer is a device that converts one form of energy into another. In this case, it converts electrical energy into high-frequency sound waves (ultrasound) to be sent into the material being tested. When these sound waves reflect off a flaw, the transducer receives the echoes and converts them back into electrical signals that can be displayed on the detector's screen. The term "Trducer" in the options is a misspelling of "Transducer." |
Comments | Active | |
| 57 | If N1 = Minimum equilibrium speed, N2 = Maximum equilibrium speed, N = Mean equilibrium speed | (N2 + N1) / N | (N2 + N1) / (N2 − N1) | (N2 - N1) / (NZ + N1) | (N2 − N1) / N | d | The formula for the coefficient of fluctuation of speed is: \(C_{s}=\frac{N_{2}-N_{1}}{N}\) Sensitiveness is the inverse of the coefficient of fluctuation of speed. However, the formula provided in option (d) is the one commonly used and is likely the intended answer. |
Comments | Active | |
| 58 | Sensitiveness of the governor is denoted as ________. | Comments | Active | |||||||
| 59 | The angle between the normal to the cam profile and the axis of the follower is called the ________. | Origin angle | Contact angle | Pressure angle | Inclination angle | c | The angle between the normal to the cam profile and the axis of the follower is called the pressure angle. The pressure angle is a critical parameter in cam design because it determines the side thrust exerted on the follower. A larger pressure angle leads to higher side thrust, which can cause increased friction and potential jamming of the follower. |
Comments | Active | |
| 60 | ________ stress is defined as the maximum value of the stress levels which a material can withstand before fracture. | Proof | Ultimate | Yield | Working | b | Ultimate stress is the maximum stress a material can withstand before fracture. | Comments | Active | |
| 61 | ________ violates both the statements (Kelvin-Planck and Clausius statements). | PMM2 | PMM3 | PMM1 | PMM4 | a | A PMM2 (Perpetual Motion Machine of the Second Kind) violates the second law of thermodynamics. Since the Kelvin-Planck and Clausius statements are both equivalent formulations of the second law, a PMM2 violates both. | Comments | Active | |
| 62 | Which of the following is NOT a type of SMAW process electrode coating? | Basic | Martensitic | Rutile | Acidic | b | Basic, Rutile, and Acidic are all standard classifications for the chemical composition of the flux coating on SMAW electrodes. Martensitic refers to a specific type of hard, brittle microstructure that can be formed in steel after rapid cooling. It describes a metallurgical property of the weld metal, not the type of electrode coating. |
Comments | Active | |
| 63 | For an exothermic reaction the change in enthalpy is ________. | Negative | Constant | Positive | Neutral | a | In an exothermic reaction, heat is released from the system into the surroundings. By thermodynamic convention, when a system loses energy in the form of heat, the change in enthalpy (ΔH) is considered negative. Conversely, for an endothermic reaction, which absorbs heat, the change in enthalpy is positive. |
Comments | Active | |
| 64 | The equation 2() represents the _________. \(ω_{1} - ω_{2}) / (ω_{1} + ω_{2}\) | Maximum fluctuation | Coefficient of friction for flywheel | Mean speed of the flywheel | Coefficient of fluctuation of speed | d | The equation provided, 2(), is used to calculate the coefficient of fluctuation of speed for a flywheel. \(ω_{1} - ω_{2})/(ω_{1} + ω_{2}\) Here: is the maximum angular speed. \(ω_{1}\) is the minimum angular speed. \(ω_{2}\) The term (represents the maximum fluctuation of speed. \(ω_{1} - ω_{2}) \) The term ( represents the mean speed. \(ω_{1} – ω_{2})/2\) The coefficient of fluctuation of speed () is defined as the ratio of the maximum fluctuation of speed to the mean speed. \(C_{s}\) \(C_{s}=\frac{ω_{1}-ω_{2}}{(ω_{1}+ ω_{2})/2}=\frac{2(ω_{1}- ω_{2})}{ω_{1}+ω_{2}} \) |
Comments | Active | |
| 65 | Between two concentrated loads, the shear force diagram for any part of the beam, is a ________. | Line inclined to axis | Horizontal straight line | Vertical straight line | Parabola | b | When a beam is subjected to concentrated loads, the shear force remains constant in any section of the beam between two consecutive concentrated loads. Therefore, the shear force diagram between two concentrated loads is a horizontal straight line. The shear force changes abruptly only at the points where the concentrated loads are applied. |
Comments | Active | |
| 66 | Rivets are specified by their length, ________ head and type. | Weight | Diameter | Colour | Strength | b | Rivets are commonly specified by their diameter, head type, and length. The diameter is a crucial dimension as it determines the size of the hole required and the strength of the joint. | Comments | Active | |
| 67 | The addition of CO2 with shielding gas is applied in the ________ process. | Submerged arc welding | Shielded metal arc welding | Metal active gas welding | Tungsten inert gas welding | c | The addition of with shielding gas is applied in the Metal active gas welding process, as is an active gas. \(CO_{2}\) \(CO_{2}\) | Comments | Active | |
| 68 | Which of the following statements is correct regarding the metal inert gas welding process? (l) Spatter is a problem. (ll) Electrode is in the form of a wire. (lll) Tungsten inclusion is a rampant defect. |
I, II and III | Only I and II | Only I and III | Only II and III | b | Based on the characteristics of the Metal Inert Gas (MIG) welding process: Statement (I): Spatter is a problem. This is correct. Spatter, which refers to small particles of molten metal that fly off the weld, is a very common issue in MIG welding, especially with certain settings and gas types. Statement (II): Electrode is in the form of a wire. This is correct. MIG welding uses a continuous solid wire electrode that is fed from a spool through the welding gun. Statement (III): Tungsten inclusion is a rampant defect. This is incorrect. Tungsten inclusion is a common defect in TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) welding, not MIG welding. TIG welding uses a non-consumable tungsten electrode, and if it is touched to the weld puddle, it can contaminate the weld. MIG welding uses a consumable wire electrode, so tungsten is not involved. |
Comments | Active | |
| 69 | The compression ratio of the diesel engine is in the range of ________. | 6-10 | 16-20 | 25-40 | 1-5 | b | The compression ratio of a diesel engine is significantly higher than that of a gasoline engine because diesel engines rely on the heat generated from compressing the air to ignite the fuel. The typical compression ratio for a diesel engine is in the range of 16:1 to 20:1. |
Comments | Active | |
| 70 | The ratio of change in the internal energy of a substance from 4°C to T and from T to 10°C is 2. What is T? | 6° | 8° | 7° | 5° | b | \(Case-I:T_{intital}=4^{°}C , T_{final}=T^{°}C\) \(Case-II:T_{intital}=TC , T_{final}=10^{°}C\) Case-I: Change in Internal Energy: \(⇒∆U_{I}=mC_{v}(T_{final}-T_{intial})\) \(⇒∆U_{I}=mC_{v}(T-4)\) Case-II: Change in Internal Energy: \(⇒∆U_{II}=mC_{v}(10-T)\) \(⇒∆U_{II}=mC_{v}(10-T)\) The ratio between and is given as 2. \( ∆U_{I}\) \(∆U_{II}\) \(\frac{∆U_{I}}{∆U_{II}}=2\) \(\frac{mC_{v}(T-4)}{mC_{v}(10-T)}=2\) \(T-4=20-2T\) \(3T=24\) \(T=8^{°}C\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 71 | For a refrigeration system, if the work input is 40 kJ/kg and the refrigeration effect produced is 130 kJ/kg of refrigerant flowing, COP is ________. | 3 | 3.50 | 3.25 | 2.75 | c | The Coefficient of Performance (COP) of a refrigeration system is calculated as the ratio of the refrigeration effect to the work input. \(COP=\frac{Refrigeration Effect}{Work Input}\) Given: Refrigeration Effect = 130 kJ/kg Work Input = 40 kJ/kg \(COP=\frac{130}{40}=3.25\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 72 | Forces meeting at one point but having lines of action, not in one plane are called ________. | Coplanar concurrent forces | Coplanar non-concurrent forces | Non-coplanar concurrent forces | Non-coplanar non-concurrent forces | c | Based on the classification of force systems: Concurrent forces are forces whose lines of action all pass through a single point. Non-coplanar forces are forces whose lines of action do not lie in the same plane. The question describes forces that meet at one point (concurrent) but whose lines of action are not in one plane (non-coplanar). |
Comments | Active | |
| 73 | Which of the following is NOT a section of the single screw extruder? | Feed section | Metering section | Cooling section | Compression section | c | A single-screw extruder is typically composed of three main sections: 1. Feed section 2. Compression section 3. Metering section The Cooling section is not one of the standard primary sections of a single-screw extruder. |
Comments | Active | |
| 74 | Which of following is true for a laminar flow? | f = 62/ Re | f = 66/ Re | f = 60/ Re | f = 64/ Re | d | For fully developed laminar flow in a circular pipe, the friction factor (f) is directly related to the Reynolds number (Re) by the following formula, which is derived from the Hagen-Poiseuille equation: \(f=\frac{64}{Re}\) This relationship is a fundamental principle in fluid dynamics for the calculation of head loss due to friction in laminar flow. |
Comments | Active | |
| 75 | Governors are used in power plants to directly ________. | Control the flow of working fluids | Generate the working fluids | Reduce carbon emissions | Decrease the power consumption | a | Governors in power plants are used to directly control the speed of the turbine by regulating the flow of the working fluid (such as steam, water, or fuel) into the turbine. | Comments | Active | |
| 76 | Identify the defect from the given figure. |
Undercut | Underfill | Underpass | Overlap | b | Comments | Active | ||
| 77 | Arrange the processes in increasing order of the strength of their joint. | Soldering – Welding – Brazing | Brazing – Welding – Soldering | Brazing – Soldering – Welding | Soldering – Brazing – Welding | d | The correct order of processes in increasing order of joint strength is: Soldering < Brazing < Welding |
Comments | Active | |
| 78 | Identify the defect in the given figure. |
Shrinkage cavity | Hot tears | Cold shut | Misrun | b | Comments | Active | ||
| 79 | _______ forces are acting on a rope in a tug of war. | Parallel | Non-concurrent | Colinear | Non-collinear | c | In a tug of war, the forces exerted by the teams on the rope are directed along the same straight line. Forces that act along the same straight line are called collinear forces. |
Comments | Active | |
| 80 | ________ is used to minimise splash and turbulence when metal is flown into a down sprue. | Riser | Runner | Pattern | Pouring cup | d | The pouring cup (or pouring basin) is the funnel-shaped opening at the top of the mold. Its primary purpose is to receive the molten metal from the ladle and guide it smoothly into the down sprue, minimizing turbulence, splashing, and the entrapment of air. | Comments | Active | |
| 81 | ________ occur between the impeller surfaces and the fluid. | Leakage losses | Recirculation losses | Disc friction losses | Mechanical losses | c | Disc friction losses occur due to the friction between the outer surfaces of the rotating impeller and the surrounding fluid within the pump casing. The fluid is dragged along by the impeller, leading to a loss of energy. This is a common form of hydraulic loss in centrifugal pumps. | Comments | Active | |
| 82 | A ton of refrigeration or air conditioning is the amount of heat that must be removed from 1 ton (2000 lbm) of water in ________ to freeze it at 32°F at 1 atmosphere pressure. | 365 days | 24 hours | 60 seconds | 60 minutes | b | A ton of refrigeration (TR) is a unit of power used to describe the heat removal capacity of refrigeration and air conditioning systems. By definition, one ton of refrigeration is the amount of heat that must be removed from 1 ton ) of water at 32°F to freeze it into ice in 24 hours. \((2000 lbm\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 83 | Which of the following is NOT a type of riveted joint? | Compression riveted joint | Tension riveted joint | Solid riveted joint | Tubular riveted joint | b | Comments | Active | ||
| 84 | ________ serves as storage of liquid metal for compensating for the shrinkage during solidification of casting. | Pouring basin | Runner | Core | Riser | d | A riser is a reservoir of liquid metal provided in a mold to compensate for the volumetric shrinkage of the casting as it solidifies. As the casting cools and shrinks, the liquid metal from the riser flows into the mold to fill the voids and prevent defects. | Comments | Active | |
| 85 | The turning moment diagram is also designated as a ________. | crank-lever diagram | lever-crank effort diagram | lever-effort diagram | crank-effort diagram | d | The turning moment diagram is a graph that plots the turning moment (or torque) against the crank angle. The turning moment is also commonly referred to as crank effort. Therefore, the turning moment diagram is also designated as a crank-effort diagram. |
Comments | Active | |
| 86 | A/An ________ measures the velocity indirectly by measuring the difference between the stagnation and static pressures. | Hot wire anemometer | Orifice meter | Breezometer | Pitot tube | d | A Pitot tube measures velocity by determining the difference between stagnation and static pressures. | Comments | Active | |
| 87 | Identify the odd one out of the following options with respect to the position of the boiler. | Cochran boiler | Lancashire boiler | Locomotive boiler | Cornish boiler | a | Based on their physical orientation, boilers are classified as either vertical or horizontal. Cochran boiler: This is a vertical fire-tube boiler. Lancashire boiler: This is a horizontal fire-tube boiler. Locomotive boiler: This is a horizontal fire-tube boiler. Cornish boiler: This is a horizontal fire-tube boiler. The Cochran boiler is the only one in the list with a vertical orientation. Therefore, it is the odd one out. |
Comments | Active | |
| 88 | Which of following statements is/are true for manometers? (l) Manometers are easy to operate. (ll) Manometers do not require frequent calibration. (lll) Manometers are made of steel. |
I, II and III | Only I and III | Only II and III | Only I and II | d | Statement (I): Manometers are easy to operate. This is true. They are simple devices that require a direct reading of a fluid column height. Statement (II): Manometers do not require frequent calibration. This is true. Their measurement is based on the fluid's density and gravity, which are stable, unlike mechanical or electronic gauges that can drift over time. Statement (III): Manometers are made of steel. This is false. The measuring part of a manometer (the tube) is typically made of a transparent material like glass or plastic to allow the fluid level to be seen. |
Comments | Active | |
| 89 | Which of the following processes solves the problem of discontinuous filler metal addition of the SMAW process? | Metal inert gas welding | Stick welding | Manual metal arc welding process | Gas welding process | a | The problem of discontinuous filler metal addition in the SMAW process is solved by using a continuous wire feed. Metal Inert Gas (MIG) welding uses a continuously fed solid wire electrode from a spool, which allows for an uninterrupted weld. Stick welding and Manual Metal Arc Welding are other names for SMAW, which has this discontinuity issue. Gas welding also typically involves discontinuous filler metal addition. |
Comments | Active | |
| 90 | A beam engine works on a ________. | Crank and lever mechanism | Single slider crank chain | Double lever mechanism | Double crank mechanism | a | A beam engine is a classic reciprocating steam engine. The mechanism consists of a large, rigid beam that is pivoted at its center. One end of the beam is connected to the piston rod (via a parallel motion linkage), and the other end is connected to a connecting rod. The connecting rod then drives a crankshaft. This configuration is a direct application of a crank and lever mechanism. The beam acts as the lever, and the crankshaft provides the rotary motion. The piston's reciprocating motion is converted into rotary motion through the combined action of the lever (the beam) and the crank. |
Comments | Active | |
| 91 | Identify the odd one out of the following options. | Pumps | Baffles | Retarders | Turbulators | a | Based on the function of each component: Baffles, Retarders, and Turbulators are all passive devices used to modify the flow of a fluid, often to increase turbulence or residence time for better heat transfer or mixing. They do not add energy to the fluid. Pumps are active machines that add mechanical energy to a fluid to increase its pressure or velocity. |
Comments | Active | |
| 92 | Which of the following statements is/are correct regarding a flywheel? (I) Flywheel acts as a reservoir of energy. (II) Flywheel maintains a constant speed. (III) Flywheel reduces fluctuation of speed. |
II and III | I and II | I and III | Only I | c | Based on the principles of machine design and the function of a flywheel: Statement (I): Flywheel acts as a reservoir of energy. This is correct. A flywheel stores rotational kinetic energy during the part of a cycle when there is an excess of energy and releases it when there is a deficit. Statement (II): Flywheel maintains a constant speed. This is incorrect. A flywheel does not maintain a perfectly constant speed. Its speed fluctuates as it absorbs and releases energy. The purpose of the flywheel is to reduce these fluctuations, not eliminate them. A governor, not a flywheel, is used to maintain a constant mean speed against changes in load. Statement (III): Flywheel reduces fluctuation of speed. This is correct. By absorbing and releasing energy, the flywheel smooths out the cyclical variations in speed that occur in a system (like an internal combustion engine) with an uneven power output. |
Comments | Active | |
| 93 | Determine the fluid pressure at a tapping connected with an inclined manometer if the rise in fluid level is 10 cm along the inclined tube above the reservoir level. The tube is inclined at 20° to horizontal as shown in the figure. The density of the manometric fluid is 800 kg/m3.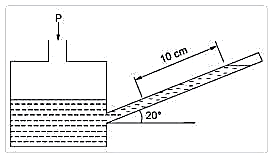 |
268.42 N/m2 | 26.842 N/m2 | 2.6842 N/m2 | 0.268 N/m2 | a | The pressure () is calculated using the formula, where the vertical height () is found from the inclined length () and angle (). \(P\) \( P=ρgh\) \(h\) \(L\) \(θ\) 1. Calculate the vertical height: \(h=L sin(θ)=0.1 m×sin(20°)≈0.0342 m\) Calculate the pressure: \(P=(800 kg/m^{3})×(9.81 m/s^{2})×(0.0342 m)≈268.42 N/m^{2}\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 94 | What is the maximum efficiency of a series of vertical plates? | 50% | 66.67% | 100% | 33.34% | a | The theoretical maximum efficiency is achieved when the velocity of the plates is exactly half the velocity of the fluid jet. Under this condition, the maximum efficiency is calculated to be 50% | Comments | Active | |
| 95 | A manometer is generally used to measure ________. | High pressure | Atmospheric pressure | Low pressure | Moderate pressure | d | A manometer is a device used to measure pressure by balancing a column of liquid against the unknown pressure. It is most effective and accurate for measuring moderate pressures, as these pressures are high enough to cause a measurable fluid displacement but low enough not to require an excessively tall or complex device. Atmospheric pressure is typically measured using a barometer. High pressures are usually measured with mechanical gauges like a Bourdon gauge, which are more robust and can handle much higher pressures than a liquid-column manometer. Very low pressures (vacuum) are measured with specialized gauges like McLeod gauges or Pirani gauges. |
Comments | Active | |
| 96 | In which of the following heat treatments is the cooling carried out only in the furnace where it is heated? | Hardening | Quenching | Annealing | Normalizing | c | Based on the principles of heat treatment processes: Hardening and Quenching involve heating the material and then cooling it rapidly in a medium like water, oil, or forced air, not by leaving it in the furnace. Normalizing involves heating the material and then cooling it in still air at room temperature, outside the furnace. Annealing involves heating the material to a specific temperature and then allowing it to cool very slowly, typically by shutting off the furnace and letting both the furnace and the part cool together. This ensures the cooling is carried out only in the furnace. |
Comments | Active | |
| 97 | Quality of the petrol used is expressed as ________. | Octane number | Calorific value | Cetane number | Petro number | a | The quality of petrol (gasoline) is expressed by its Octane number. This number indicates the fuel's resistance to premature combustion (engine knocking or detonation). A higher octane number means greater resistance to knocking. | Comments | Active | |
| 98 | ________ is a similar type of valve as the steam stop valve used in a boiler. | Junction valve | Trient valve | Blow valve | Reverse valve | a | The steam stop valve, which is used to regulate the flow of steam from the boiler to the main steam pipe, is functionally a type of Junction valve. Both are used to control the flow of steam and are essential boiler mountings. In many contexts, the terms "steam stop valve" and "junction valve" are used interchangeably to describe this specific function of controlling the steam supply from the boiler. | Comments | Active | |
| 99 | The coefficient of fluctuation for a single cylinder, single acting, four stroke gas engine is ________. | 1.93 | 0.093 | 0.21 | 0.066 | a | The coefficient of fluctuation of energy, which is a key parameter for flywheel design, for a single cylinder, single-acting, four-stroke gas engine is typically very high due to the long period between power strokes. Based on standard engineering data, the coefficient of fluctuation for this specific type of engine is 1.93. |
Comments | Active | |
| 100 | Identify the type of bearing given in the figure.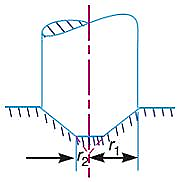 |
Conical pivot bearing | Trapezoidal pivot bearing | Flat pivot bearing | Collar bearing | b | A trapezoidal pivot bearing or Truncated pivot bearing has a frustum of a cone (a trapezoidal cross-section) as its contact surface. This design is specifically used to distribute the load over a larger area, which helps reduce the contact pressure and wear. This type of bearing can handle more significant loads than a flat or conical pivot bearing of a similar size. 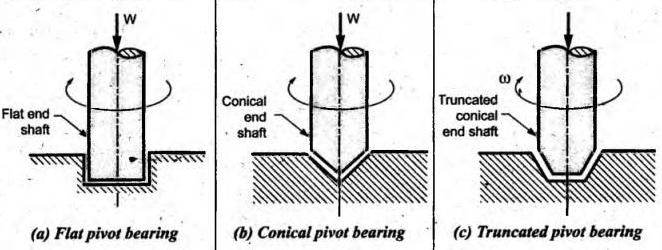 |
Comments | Active | |
| 101 | Which of the following is a permanent mold casting process? | Sand casting process | Investment casting process | Expanded polystyrene casting process | Slush casting process | d | Slush casting is a permanent mold casting process because it uses a reusable mold, typically made of metal. The other options, sand, investment, and expanded polystyrene casting, all use molds that are destroyed to remove the final cast part, making them expendable mold processes. | Comments | Active | |
| 102 | Identify the odd one out of the following options. | Bulk modulus | Modulus of elasticity | Modulus of rigidity | Modulus of viscosity | d | The other three options—Bulk modulus, Modulus of elasticity (Young's modulus), and Modulus of rigidity (Shear modulus)—are all properties related to the elastic behavior of solid materials, describing their resistance to deformation under stress. The Modulus of viscosity, however, is a property of fluids that describes their resistance to flow. Therefore, it is the odd one out. | Comments | Active | |
| 103 | A machine gun of mass 25 kg fires a bullet of mass 30 gram with a velocity of 250 m/s. Find the velocity with which the machine gun will recoil. | 0.9 m/s | 0.6 m/s | 0.3 m/s | 0.1 m/s | c | According to the law of conservation of momentum: Initial Momentum = Final Momentum \(0=M⋅V+m⋅v\) Rearranging the equation to solve for the recoil velocity (V): \(V=-\frac{m.v}{M}\) Substituting the given values: \(V=-\frac{(0.030kg).(\frac{250m}{s})}{25 kg}\) \(V=-\frac{7.5}{25 } m/s\) \(V=-0.3 m/s\) The negative sign indicates that the machine gun's velocity is in the opposite direction of the bullet's velocity. The magnitude of the recoil velocity is 0.3 m/s. |
Comments | Active | |
| 104 | The COP of component given in the figure is ________.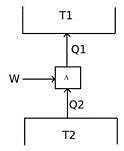 |
W/Q1 | W/Q2 | Q2/W | Q1/W | c | Comments | Active | ||
| 105 | Which of the following is a property of fluid which makes it suitable to be used in manometers? | High co-efficient of thermal expion | High viscosity | Higher surface density | Low viscosity | d | A low viscosity is a desirable property for a manometer fluid because it allows the fluid to respond quickly and accurately to changes in pressure, ensuring the fluid columns settle to their correct height without significant time lag. High viscosity would cause a slow, sluggish response. | Comments | Active | |
| 106 | Ideal fluids are ________. | Non-viscous and compressible | Viscous and compressible | Non-viscous and incompressible | Viscous and incompressible | c | Ideal fluids are a theoretical concept in fluid dynamics and are defined as being non-viscous (having no internal friction) and incompressible (having a constant density). | Comments | Active | |
| 107 | Which of the following is NOT a loaded type of governor? | Porter governor | Watt governor | Proell governor | Pickering governor | b | The question you've asked is a direct factual query. Based on the search results, the Watt governor is a simple, unloaded governor that operates based on the equilibrium of centrifugal and gravitational forces. The other governors listed—Porter, Proell, and Pickering—are all loaded types, meaning they have an additional weight or spring to increase their sensitivity. | Comments | Active | |
| 108 | Brake power is measured using a Prony brake for a ________ engine. | Variable speed | Low speed | Single cylinder | Low power | b | A Prony brake is a simple absorption dynamometer used to measure the brake power of an engine. It works by applying a braking force to a flywheel or a drum and measuring the torque developed. The Prony brake is most suitable for measuring the brake power of low-speed engines, as it can be difficult to manage the friction and heat generated at high rotational speeds. For high-speed or variable-speed engines, other dynamometers like hydraulic or eddy current dynamometers are preferred due to their greater accuracy and ease of operation. | Comments | Active | |
| 109 | Identify the type of fluid machine in the given figure.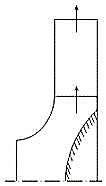 |
Radial flow | Axial flow | Inverted flow | Mixed flow | a | Comments | Active | ||
| 110 | Soldering fluxes perform which of the following tasks? | Decrease soldering time | Promote tarnishing of the surface | Promote oxidation of the surface | Promote wetting of the faying surfaces | d | Soldering fluxes are used to promote the wetting of the faying surfaces. They do this by cleaning the surfaces to be joined, removing any oxides or impurities that would prevent the solder from flowing and bonding properly. | Comments | Active | |
| 111 | Which of the following is true for TIG welding with DCEN polarity? | 30% heat is generated at the workpiece | 10% heat is generated at the workpiece | 90% heat is generated at the workpiece | 66% heat is generated at the workpiece | d | For TIG welding with DCEN (Direct Current Electrode Negative) polarity, 66% of the heat is generated at the workpiece. | Comments | Active |










