| S.No | Question | Option A | Option B | Option C | Option D | Answer | Solution | Comments | Status | Action |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | The efficiency of a supercritical boiler is. | higher than subcritical boiler | equal to subcritical boiler | can be higher or lower than subcritical boiler | lower than subcritical boiler | a | The efficiency of power plants with supercritical steam generators is higher than with subcritical steam because thermodynamic efficiency is directly related to the magnitude of their temperature drop. | Comments | Active | |
| 2 | Work input required by a pump in the actual vapour cycle will be than the ideal vapour cycle. | equal | lesser | 0 | Greater | d | Comments | Active | ||
| 3 | Which of the following is an axial turbine? | Kaplan turbine | Pelton wheel | Francis Turbine | Parsons turbine | a | Kaplan turbine is a low head axial flow turbine with adjustable vane. | Comments | Active | |
| 4 | In vapour compression cycle, what will be the change in the refrigeration effect when the vapour is first superheated after compression and undercooled before throttling? | No change | Refrigeration effect may increase or decrease | Refrigeration effect decreases | Refrigeration effect increases | d | Comments | Active | ||
| 5 | What is the maximum working head for a low lift centrifugal pumps? | up to 20 meters | up to 5 meters | up to 10 meters | up to 15 meters | d | Low-Head Centrifugal Pumps: They can produce heads up to 15 m. | Comments | Active | |
| 6 | The heating arrangement for a medium capacity turbine in a regenerative Rankine cycle consist of. | not more than 3 heaters | not more than 12 heaters | not more than 7-9 heaters | not more than 5-7 heaters | a | The resulting cycle is known as regenerative or bleeding cycle. The heating arrangement comprises; (i) for medium capacity turbine — not more than 3 heaters; (ii) for high pressure high capacity turbines — not more than 5 to 7 heaters; and (iii) for turbines of supercritical parameters—8 to 9 heaters. |
Comments | Active | |
| 7 | Which of the following compressors is classified on the basis of method of compression? | Centrifugal compressor | Single acting compressor | Single stage compressor | Hermetic compressor | a | Comments | Active | ||
| 8 | Work done by an ideal nozzle is: | maybe high or low | cannot be determined | 0 | high | c | Nozzles are frequently used to control the rate of flow, speed, direction, mass, shape, and/or the pressure of the stream that emerges from them. In a nozzle, the velocity of fluid increases at the expense of its pressure energy. W = 0, no work is done by the nozzle, v1 <<< v2 and potential energy change is neglected. |
Comments | Active | |
| 9 | Resistance spot welding is used for sheets of thickness. | 3 mm or less | 10 mm or less | 5 mm or more | 6 mm to 10 mm | a | Comments | Active | ||
| 10 | In an open system: | Energy can cross the boundaries of the system but mass cannot. | Both mass and energy cannot cross the boundaries of the system. | Mass can cross the boundaries of the system but energy cannot. | Mass and energy can cross the boundaries of the system. | d | An open system is one in which there is an exchange of both matter and energy with its surroundings. Example: Water in an open beaker. |
Comments | Active | |
| 11 | In a centrifugal pump the vortex casing helps in conversion of. | kinetic energy into the potential energy. | kinetic energy into the mechanical energy. | kinetic energy into the pressure energy. | pressure energy into the kinetic energy. | c | Vortex Casing: This is a circular chamber between the impeller and the volute casing. The fluid first passes through the vortex casing and then through the volute casing. This helps in better conversion of the velocity energy into water pressure. | Comments | Active | |
| 12 | The cooling of air without any change in its specific humidity is called as: | cooling with adiabatic humidification | sensible cooling | sensible heating | Dehumidification | b | The removal of heat from the air while maintaining the same level of humidity is the definition of sensible cooling. | Comments | Active | |
| 13 | The mechanical loss in an engine is mainly constituted by: | Work of charging the cylinder with fresh charge | ventilating action of the flywheel | power absorbed by engine auxiliaries | frictional losses | d | Total engine friction, defined as the difference between indicated horse power and brake horse power, includes the power required to drive the compressor or a scavenging pump and the power required to drive engine auxiliaries such as oil pump, coolant pump and fan, etc. | Comments | Active | |
| 14 | For which of the following processes the internal energy becomes equal to the heat transferred (ΔU = Q)? | adiabatic process | isochoric process. | Isobaric process | Isothermal Process | b | Work done is zero for constant volume (isochoric) process. | Comments | Active | |
| 15 | Consider the following statements: | Neither A nor B is true | Only A is true | Both A and B is true | Only B is true | c | Their function is to seal off gases generated in the internal combustion process, help with transferring heat to the cylinder wall and then to both lubricate and scrape down oil from it. | Comments | Active | |
| 16 | What is the velocity ratio of the belt drive with the diameter of the follower is 400mm and the diameter of the driver is 150mm and the thickness of the belt being 50mm? | 0.4 | 2.6 | 2.25 | 3 | c | \(∆_{driver}=400 mm\) \(∆_{driver}=150 mm\) \(t=50 mm\) \(\frac{N_{driver}}{N_{driver}}=\frac{∆_{driver}+t}{∆_{driver}+t}\) \(=\frac{400+50}{150+50}=\frac{450}{200}\) V.R = 2.25 |
Comments | Active | |
| 17 | Which of the following is a graphitizing element? | Copper | Sodium | Magnesium | Silver | a | Copper is a graphitizing element and promotes formation of pearlite in a matrix, but increases stability of eutectoid cementite. The addition of copper increases tensile strength and hardness of nodular cast iron. | Comments | Active | |
| 18 | The mechanical efficiency of a 4-stroke single cylinder at full load is 60%. If the friction power is 47.5 kW, then calculate the brake power of the engine? | 73.45kW | 70.55 kW | 74.25kW | 71.25 kW | d | \(ƞ_{mech}=60%\) \(ƞ_{friction}=47.5 kW\) \(P_{B.P}=?\) \(ƞ_{mech}=\frac{P_{B.P}}{P_{I.P}}=\frac{P_{I.P}-P_{F.P}}{P_{I.P}}\) \(=1-\frac{P_{F.P}}{P_{I.P}}\) \(0.6=1-\frac{47.5}{P_{I.P}}\) \(P_{I.P}=\frac{47.5}{0.4}\) \(P_{I.P}=118.75 kW\) \(P_{B.P}=P_{I.P}-P_{friction}\) = 118.75-47.5 \(P_{B.P}=71.25 kW\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 19 | Hydrostatic Paradox is mathematically expressed as where P is the pressure at depth “h” from the surface of the liquid/fluid and h is the vertical height from the surface to the point. | P?h² | 1/P?h | P?1/h | P?h | d | Comments | Active | ||
| 20 | Find the COP of the refrigeration system if the work input is 40kJ/kg and the refrigeration effect produced is 160KJ/kg of refrigerant flowing? | 2 | 0.5 | 4 | 3 | c | Win = 40 KJ/kg R.E = 160 KJ/Kg COP = \(\frac{RE}{W_{in}}\) \(=\frac{160}{40}\) \(COP=4\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 21 | On which theory is the diameter of the shaft designed? | Maximum Shear stress Theory | Maximum principle strain theory | Maximum Principle stress theory | Energy distortion theory | a | When designing a shaft subjected to pure torsion, the maximum shear stress theory should be used to determine the largest diameter for the shaft. | Comments | Active | |
| 22 | What is the relation between the specific speed and the head under which the turbine is working? (Here N is the specific speed and H is the head) | Nα 1/H^(3/2) | Nα 1/H^(5/4) | Nα 1/H^(5/3) | Nα H^(5/2) | b | Specific speed of Turbine is \(N_{s}=\frac{NP}{H^{(\frac{5}{4})}}\) | Comments | Active | |
| 23 | Consider the following statements: | Only A is true | Both A and B is true | Only B is true | Neither A or B is true. | b | For isentropic flow the gain of kinetic energy is equal to the enthalpy drop of the steam in a steam nozzle. Velocity of the steam leaving the steam nozzle is given by 4(d)72 √(kH) m/sec. Where K is the friction factor and H is the enthalpy drop. |
Comments | Active | |
| 24 | The Reynolds number for a flow in a pipe is given by 1278. What is the Darcy- Weisbach friction factor for the pipe? | 0.06 | 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.04 | c | \(R_{e}=1278\) \(f=\frac{64}{R_{e}}\) \(=\frac{64}{1278}\) \(f=0.05\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 25 | In the expression of capillary rise, the angle of contact between water and clean glass tube is approximately equal to_____. | 0° | 45° | 130° | 90° | a | The angle of contact between water and clean glass tube is approximately equal to 0. | Comments | Active | |
| 26 | The major losses in a pipe is calculated by using which of the following equations? (a) Navier Stokes Equation | Bernoulli's Equation | Euler's Equation | Darcy Weisbach Equation | d | The Darcy Weisbach Equation relates the loss of pressure or head loss due to friction along the given length of pipe to the average velocity of the fluid flow for an incompressible fluid. | Comments | Active | ||
| 27 | The condensing process in a theoretical vapour compression cycle with dry saturated vapour after compression takes place at: | only at constant entropy | only at constant temperature | only at constant pressure | constant temperature and pressure | d | The condensing process in a theoretical vapour compression cycle with dry saturated vapour after compression takes place at constant temperature and pressure. | Comments | Active | |
| 28 | Consider a body of weight 'A' resting on a horizontal plane. What will be the least force that will move the body if the angle of friction is "x"? | Acosx | Atanx | Asinx | Acotx | b | Body of weight = ? Normal reaction (since plane is horizontal). \(N=A\) Limiting friction \(F=μN=μA.\) We know: \(μ = tan x\) where x = angle of friction. So \(F = A tan x\) That is the least horizontal force required to just move the body. |
Comments | Active | |
| 29 | Which of the following loss of energy in a pipe is a major loss? | Loss of head due to friction | Loss of head due to sudden enlargement | Loss of head at the entrance | Loss of head due to bend | a | Head loss is potential energy that is converted to kinetic energy. Head losses are due to the frictional resistance of the piping system (pipe, valves, fittings, entrance, and exit losses). | Comments | Active | |
| 30 | Which of the following is an example of Pressure compounded impulse turbine? | Zoelly Turbine | Parson turbine | Propeller Turbine | Hero's Turbine | a | A pressure-compounded impulse stage is a row of fixed nozzles followed by a row of moving blades, with multiple stages for compounding. In this type, the total pressure drop of the steam does not take place in the first nozzle ring but is divided up between all the nozzle rings. This method of pressure compounding is used in Rateau and Zoelly turbines, but such turbines are bigger and bulkier in size. | Comments | Active | |
| 31 | Consider the following statements: | Both A and B is true | Neither A nor B is true | Only B is true | Only A is true | b | Horizontal line in the Mollier diagram represents isenthalpic process. Vertical line in the Mollier diagram represents isentropic process. |
Comments | Active | |
| 32 | The draught in which pressure difference is created between the base of chimney and the air inlet point of boiler because of density difference between hot flue gases inside the chimney and fresh colder air outside the chimney is a________. | Steam Jet Draught | Mechanical Draught | Forced Draught | Natural Draught | d | Natural Draught created between the base of chimney and the air inlet point of boiler because of density difference between hot flue gases inside the chimney and fresh colder air outside the chimney. | Comments | Active | |
| 33 | Consider the following statements: | The expansion of steam through a nozzle is not a free expansion, and the steam is not throttled, because it has a large velocity at the end of the expansion. | Neither A or B is true | Only A is true | Only B is true | d | The expansion of steam through a nozzle is an adiabatic, and the flow of steam through nozzle is regarded as an adiabatic flow. | Comments | Active | |
| 34 | Which of the following is not an intensive property? | velocity | Temperature | Pressure | energy | d | Properties which are independent of the amount of substance (or substances) present in the system are called intensive properties, e.g. pressure, density, temperature, viscosity, surface tension, refractive index, emf, chemical potential, sp. heat etc, These are intensive properties. | Comments | Active | |
| 35 | Consider a rod of 390mm long. Two like parallel forces of 50 N and 80 N act at the either end of the rod. Find the magnitude of the resultant force and the distance between the resultant and the smaller force. | 130 N and 120 mm | 130 N and 185 mm | 130 N and 240 mm | 30 N and 240 mm | c | 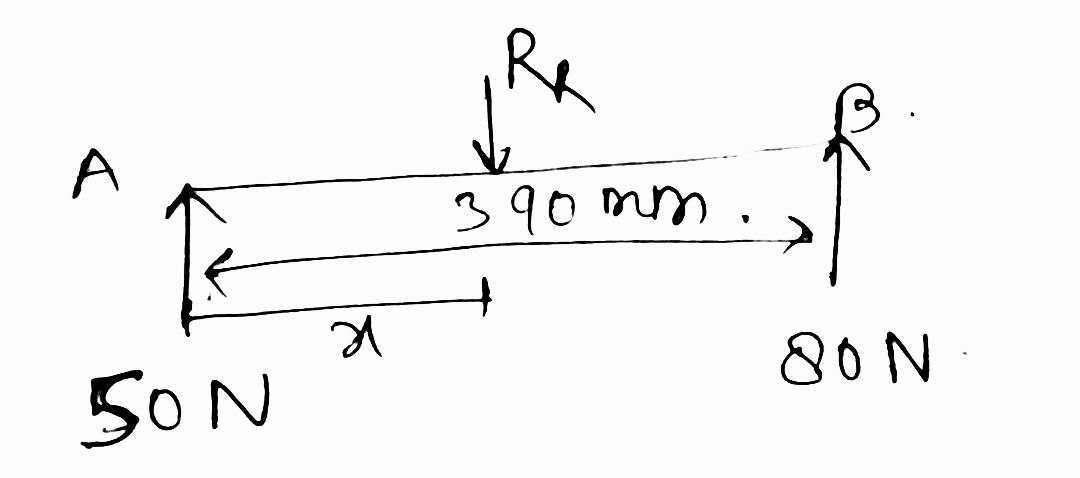 \(R_{A}+R_{B}=R_{R}\) \(R_{R}=50+80\) \(R_{R}=130 N\) \(R_{B}×390-R_{R}×x=0\) \(80×390-130×x=0\) \(\frac{80×390}{130}=x\) \(x=240 mm.\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 36 | The right limb of a simple U-Tube manometer containing mercury is open to the atmosphere while the left limb is connected to a pipe in which a liquid of specific gravity 0.5 is flowing. The centre of the pipe is 10 cm below the level of mercury in the right limb. Find the pressure of fluid in the pipe if the difference of mercury level in the two limbs is 20 cm. | 3.5 N/cm2 | 3.8 N/cm2 c) 2.3 N/cm2 |
2.6 N/cm2 | d | 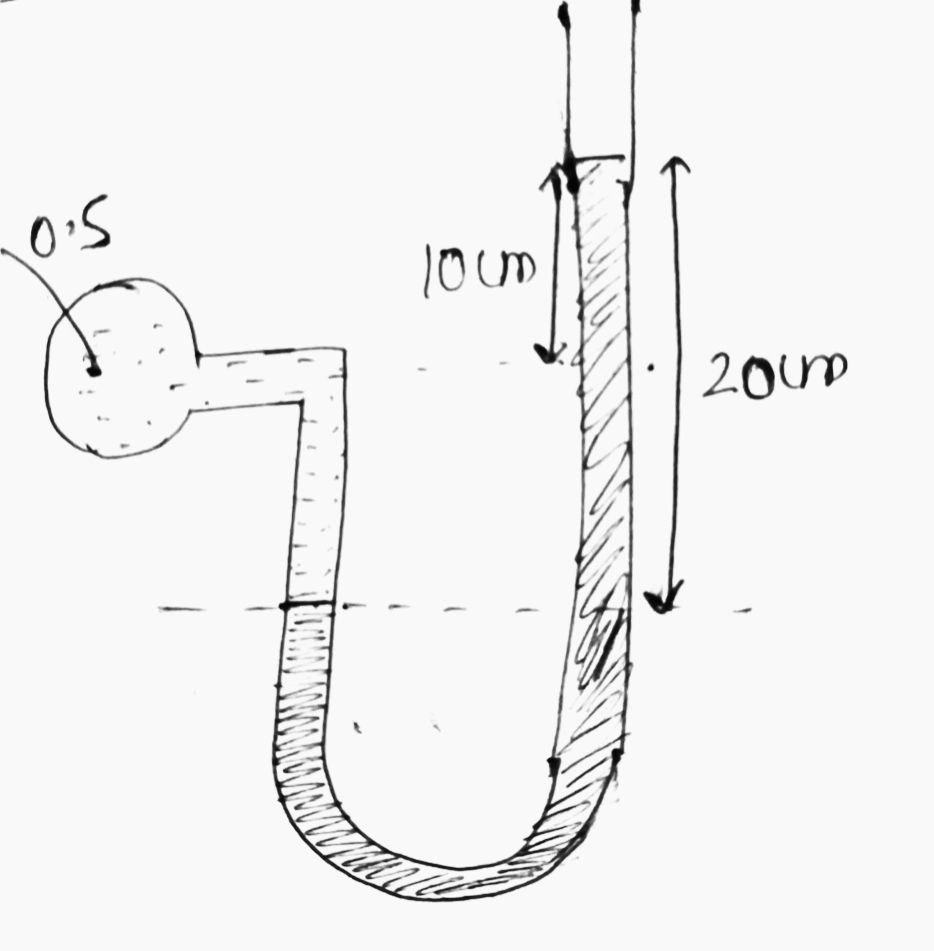 For fluid S1 = 0.5 e1 = 0.51000 \(×\) = 500 kg/m3 For mercury, S2 = 13.6, e2 = 13.61000 \(×\) =13600 kg/m3 Equating pressure above A-A: \(P_{pipe}+P_{left lump}=P_{right lumb}\) \(P_{pipe}+500×9.81×0.10=13600×9.81×0.20\) \(=26,192.7 N/m^{2}\) \(P_{pipe}=2.61927 N/cm^{2}\) |
Comments | Active | ||
| 37 | Consider the following statements: | Both A and B are true | Only A is true | Neither A or B are true | Only B is true | b | According to torsion equation, twisting moment is inversely proportional to the length. | Comments | Active | |
| 38 | The rate of shear strain between a fixed plate and a moving plate is 24000 sec-1 The viscosity of the fluid between the two plates is 5 × 10-4 poise. Find the force per unit area to maintain the speed of the moving plate. | 1.4 N/m2 | 1.6 N/m2 | 1 N/m2 | 1.22 N/m2 | d | \(\frac{du}{dy}=24000 s^{-1}\) \(μ=5×10^{-4} poise\) \(=5×10^{-5}Ns/m^{2}\) \(F= μ\frac{du}{dy}\) \(=5×10^{-5}×24000\) \(F=1.22 N/m^{2}\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 39 | Which of the following components is not a part of simple air cooling system for aircrafts? | gas turbine | cooling turbine | evaporator | Heat exchanger | c | The main components of simple air cooling system are the main compressor driven by the gas turbine, a cooling fan, heat exchanger and a cooling turbine. | Comments | Active | |
| 40 | A device which increases the velocity at the expense of pressure is: | Turbine | Diffusers | Pump | Nozzles | d | A nozzle is a device that increases the velocity of a fluid at the expense of pressure. A diffuser is a device that increases the pressure of a fluid by slowing it down. The cross sectional area of a nozzle decreases in the flow direction for subsonic flows and increase for supersonic flows. | Comments | Active | |
| 41 | Consider the following statements: | Both A and B are true | Neither A or B are true | Only B is true | Only A is true | a | Poisson's ratio (nu) is correlated to Cg and typically varies from 0.15 for glasses. | Comments | Active | |
| 42 | The hoop stress of a thin cylindrical shell is 45.76N/mm². Find the longitudinal stress of the same cylinder? | 45.76N/mm² | 11.4 N/mm² | 22.88 N/mm² | 91.52 N/mm² | c | \(σ_{h}=45.76\frac{N}{mm^{2}}\) \(σ_{l}=?\) \(σ_{l}=\frac{σ_{n}}{2}\) \(=\frac{45.76}{2}\) \(σ_{l}=22.88 N/mm^{2}\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 43 | Consider the following statements: | Only A is true | Both A and B is true | Neither A nor B is true | Only B is true | a | air-cooled chiller advantages include lower maintenance costs, a prepackaged system for easier design and installation, and better performance in freezing temperature. Water-cooled chiller advantages include greater energy efficiency, larger capacities, and longer equipment life. | Comments | Active | |
| 44 | COP of a heat pump is equal to. | COP of refrigerator | COP of refrigerator +1 | 1- COP of refrigerator | COP of refrigerator -1 | b | For a refrigeration system: \(COP_{refrigerator} =\frac{QL}{W}\) \(COP_{heat pump} =\frac{QH}{W}\) But \( Q_{H}=Q_{L}+W.\) So, \(COP_{heat pump} =\frac{Q_{L}+W}{W}=\frac{Q_{L}}{W}+1=COP_{refrigerator}+1\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 45 | In the performance map of an SI engine, moving from the region of highest efficiency along a line of constant bmep the brake specific fuel consumption. | decreases due to increased friction at higher piston speeds. | decreases due to decreased friction at higher piston speeds. | increases due to decreased friction at higher piston speeds. | increases due to increased friction at higher piston speeds. | d | In a performance map of an SI (spark ignition) engine, the region of highest efficiency typically occurs at a specific combination of engine speed and brake mean effective pressure (bmep). The brake specific fuel consumption (bsfc) is a measure of an engine's fuel efficiency. When you move from this point of highest efficiency along a line of constant bmep, you are essentially increasing the engine's speed while keeping the output work per cycle the same. As the engine speed increases, the friction losses within the engine also increase significantly. These losses are due to the movement of internal components such as the piston rings, bearings, and valve train. Since the bmep (and thus the work done per cycle) is held constant, the increased friction requires more fuel to maintain the same power output. This leads to a higher rate of fuel consumption for the same amount of brake power, causing the brake specific fuel consumption (bsfc) to increase. |
Comments | Active | |
| 46 | Consider the following statements: | All statements are true | A and C is true | A and B is true | B and C is true | a | Reaction turbines are the turbines that use the pressure as well as the velocity of the moving water to rotate. Reaction turbines are placed in the water stream where the water enters the casing tangentially. After rotating the blades the water axially leaves the casing of the turbine. | Comments | Active | |
| 47 | Indian standard metric thread has an included angle of. | 60° | 40° | 55° | 50° | a | ISO metric threads consist of a symmetric V-shaped thread. In the plane of the thread axis, the flanks of the V have an angle of 60° to each other. | Comments | Active | |
| 48 | Consider the two statements assuming the conditions of a rigid body which is not moving at all to be in equilibrium. The sum of external forces on the rigid object must be equal to zero. Sum of external torques on a rigid object must be equal to zero. |
Both A and B are true | Only A is true | Only B is true | Neither A nor B is true | a | For a rigid body to be in equilibrium, the net force as well as the net moment about any arbitrary point O must be equal to zero. | Comments | Active | |
| 49 | Which of the following statements is the true purpose of a boiler trial? | A,C | B,C | A,B,C | A,B | a | The objectives of a boiler trial are: a. To determine the steam generation capacity of the boiler. b. To determine the thermal efficiency of the plant while working at a certain pressure. c. To prepare the heat balance sheet for the boiler. |
Comments | Active | |
| 50 | Calculate density of 1 litre of fluid which is of weight 5N? Take g as 10 m/sec2 | 500kg/m3 | 600kg/m3 | 700kg/m3 | 400 Kg/m3 | a | V = 1 letre = 10-3 m3 W = 5 N g = 10 m/s2 m = \(\frac{W}{g}= \frac{5}{10}=0.5 kg\) \(e=\frac{m}{v}=\frac{0.5}{10^{-3}}\) \(e=500 kg/m^{3}\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 51 | Consider the following statements related to IC engines: A) If the fuel air mixture is made lean it will result in lower specific heat. B) As the fuel air mixture gets richer both the efficiency and power output keeps on increasing. |
Only B is true | Only A is true | Both A and B is true | Neither A nor B is true | b | Fuel efficiency or combustion quality matter matter most. Petrol engines produced more power when they are running a slightly rich mixture, not because of combustion ratio but due to the reduction in heat. A cooler running tempeture equates to a more efficient combustion, and in turn more power. | Comments | Active | |
| 52 | A flywheel has a mass of 289 kg rotating at 6 rad/s. What would be its rotational kinetic energy if the radius of gyration is 1/17 m? | 15 J | 24 J | 18 J | 9 J | c | m = 289 kg W = 6 rad/s. K = 1/17 m K.E. = \(\frac{1}{2}Iw^{2}\) \(=\frac{1}{2}mk^{2}w^{2}\) \(=\frac{1}{2}×289×\frac{1}{17}×\frac{1}{17}×6×6\) K.E = 18 J |
Comments | Active | |
| 53 | Which of the following defines the compression ratio of an internal combustion engine? Here "Vs" is the stroke volume and "Vc" is the clearance volume. | Vs/Vc | (Vc+Vs)/Vc | Vc/Vs | Vs/(Vs+Vc) | b | Compression Ratio = (Swept volume + Clearance Volume)/ Clearance Volume | Comments | Active | |
| 54 | A spur gear has 30 teeth which are rotating at 300 rpm. Determine the circular pitch of the gear if the module of the gear is 4? | 6.28 | 9.42 | 7.51 | 12.56 | d | T = 30 N = 300 rpm P = ? m = 4 P = m \(π\) = 3.14 4 \(×\) P = 12.56 |
Comments | Active | |
| 55 | The speed of a flywheel is 420 rpm. Find the approximate radius of a flywheel whose peripheral velocity is 22 m/s. | 0.8 m | 0.6 m | 0.2 m | 0.5 m | d | N = 420 rpm R = ? V = 22 m/s \(V=\frac{π∆N}{60}\) \(22=\frac{22}{7}×\frac{∆×420}{60}\) \(∆ =1m\) r = 0.5m |
Comments | Active | |
| 56 | Which of the following equations is used to calculate absolute pressure? | absolute pressure = gauge pressure- atmospheric pressure | absolute pressure = atmospheric pressure - gauge pressure | absolute pressure = gauge pressure- vacuum pressure | absolute pressure = atmospheric pressure + gauge pressure | d | absolute pressure = atmospheric pressure + gauge pressure | Comments | Active | |
| 57 | Which of the following processes are involved in Rankine cycle? | Two reversible adiabatic process, constant pressure process., one constant volume process. (b) Two isothermal process and two constant pressure process. | Two reversible adiabatic process and two constant volume process. | Two reversible adiabatic process and two constant pressure process. | d | Thermal power plant works on principle of the Rankine Cycle shown in Fig. 2[5]The cycle consists of four processes: (1-2) Isentropic compression on pump; (2-3) Constant pressure heat addition in a boiler; (3-4) Isentropic expansion in a turbine; (4-1) Constant pressure heat rejection in a condenser. | Comments | Active | ||
| 58 | Consider the following statements: A) For a given compression ratio the Otto cycle is more efficient that diesel cycle. B) For an Otto cycle an increase in the compression ratio leads to an increase in the mean effective pressure but decrease in thermal efficiency. |
Neither A nor B is true | Both A and B is true | Only A is true | Only B is true | c | Q1 = 1000 J T1= 327 + 273 = 600 K Q2 = 700 J \(Ƞ_{C}=ƞ_{E}\) \(1-\frac{T_{2}}{T_{1}}=1-\frac{Q_{2}}{Q_{1}}\) \(\frac{T_{2}}{600}=\frac{700}{1000}\) \(T_{2}=420 K\) \(T_{2}=147℃\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 59 | A Carnot engine absorbs 1000 J of heat from a reservoir at 327 C and rejects 700 J of heat during each cycle. Calculate the temperature of the sink. | 180°C | 420°C | 147°C | 600°C | d | The boiler water level indicator ensures that there is enough water in the tubes to sufficiently cool them in operation while making steam; otherwise the flames could overheat the tubes, softening the metal & permitting bursting due to pressure. | Comments | Active | |
| 60 | Which of the following is a boiler mounting? | Air preheater | Economiser | Superheater | Water level indicator | c | Comments | Active | ||
| 61 | Consider the following statements: | Only A is true | Only B is true | Both A and B is true | Neither A or B is true | c | Statement (A) is true because a draft tube is a diverging tube placed at the exit of a reaction turbine. It allows the turbine to be installed above the tail race level without losing the available head. By creating a negative pressure (or vacuum) at the runner's outlet, it effectively recovers the kinetic energy of the water leaving the runner, converting it into pressure energy. This increases the pressure difference across the turbine, thereby increasing the net head and the overall efficiency of the turbine. Statement (B) is also true. A Francis turbine is a type of reaction turbine in which water enters the runner radially inwards and leaves axially. The term "reaction" refers to the fact that the pressure energy of the water changes as it flows through the runner, with the reaction force of the flowing fluid providing the torque on the runner. Its inward flow design is a key characteristic that distinguishes it from other turbines. |
Comments | Active | |
| 62 | Which of the following turbine does not have a nozzle? | Reaction Turbine | Da-Laval turbine | Impulse turbine | Francis turbine | a | The stationary & rotating blades of reaction turbine are actually part impulse & part reaction. A fully reaction blade is very difficult to manufacture, hence such construction as impulse blades are relatively easy to manufacture. There are two components in a reaction turbine. One is the static part - gives direction to incoming steam towards the rotating part - uses kinetic energy & enthalpy of steam to convert the same into rotating energy of turbine shaft/rotor. | Comments | Active | |
| 63 | Consider the following statements: | A and C is true | All statements are true | A and B is true | B and C is true | d | Critical pressure ratio is the pressure ratio where the flow is accelerated to a velocity equal to the local velocity of sound in the fluid. The critical pressure ratio is also defined as the ratio of pressure at the throat to the inlet pressure, for checked flow when Ma = 1. | Comments | Active | |
| 64 | Consider the following statements: | Neither A nor B is true | Only B is true | Both A and B are true | Only A is true | c | Aluminium has a high thermal conductivity. The cold areas of the metal are continually trying to pull the heat away from the welding area. This makes it hard for the weld to penetrate. Opting for higher heat inputs will help to attain the critical temperature for the weld to penetrate. | Comments | Active | |
| 65 | Which of the following casing allows water to enter into the pump without shock? (a) Single casing | Diffuser casing | Vortex casing | Volute casing | b | A diffuser is a set of stationary vanes that surround the impeller. The purpose of the diffuser is to increase the efficiency centrifugal pump by allowing a more gradual expansion and less turbulent area for the liquid to reduce in velocity. | Comments | Active | ||
| 66 | Vapour Absorption System uses which energy compared to Vapour Compression system? | Neither uses heat or mechanical energy | heat energy instead of mechanical energy | Both heat and mechanical energy | mechanical energy instead of heat energy | b | In the vapor absorption system, the energy input is given in the form of the heat. While in the vapour compression system the energy input is given in the form of the mechanical work from the electric motor run by the electricity. | Comments | Active | |
| 67 | For which of the following system internal energy is used exclusively for doing work as per the first law of thermodynamics? | Isochoric System | Isothermal System | Adiabatic system | Isolated system | c | In an adiabatic process the internal energy is used to do work where as in an isothermal process it remains constant and is not reduced. Hence internal energy is greater for an isothermal process. | Comments | Active | |
| 68 | Which of the following will improve thermal efficiency of the Rankine cycle? | A,B,D | A,B,C | B,C,D | A,B,C,D | a | The thermal efficiency of the Rankine cycle can be improved by increasing the average temperature at which heat is added or decreasing the average temperature at which it's rejected. Regenerative feed heating (A): This increases the average temperature of heat addition by preheating the water before it enters the boiler. Reheating of steam (B): This increases the average temperature of heat addition and the turbine's work output. Increasing condenser pressure (C): This increases the temperature at which heat is rejected, which decreases the efficiency. Superheating the steam (D): This increases the average temperature of heat addition, leading to higher efficiency. |
Comments | Active | |
| 69 | Which of the following statements is/are true? | Only B is true | Both A and B are not True | Both A and B is true | Only A is true | b | Hydrostatic force is the resultant force acting on a submerged surface due to the pressure loading of the fluid into which the surface is submerged. The center of pressure is the point at which the hydrostatic force act. | Comments | Active | |
| 70 | The slope of an isobar on the h-s coordinate in a mollies chart is equal to the. | absolute volume | absolute pressure | absolute temperature. | absolute entropy | c | The slope of an isobar on the h-s coordinates is equal to the absolute temperature. If the temperature remains constant the slope will remain constant. If the temperature increases the slope of the isobar will increase. | Comments | Active | |
| 71 | Surging in centrifugal compressors occurs when the refrigeration load decreases to . | 50 % below the rated capacity. | 25 % below the rated capacity. | 35 % below the rated capacity. | 40 % below the rated capacity. | c | The main disadvantage in centrifugal compressors is *surging. It occurs when the refrigeration load decreases to below 35 percent of the rated capacity and causes severe stress conditions in the compressor. | Comments | Active | |
| 72 | Grain size obtained in normalizing are. | can be big or small than that obtained in annealing. | bigger than that obtained in annealing. | equal to the ones obtained in annealing. | smaller than that obtained in annealing. | d | Normalizing is a heat treatment used on steel so as to refine its crystal structure and produces a more uniform and desired grain size distribution. | Comments | Active | |
| 73 | Consider the following statements: | Only A is true | Only B is true | Both A and B is true | Neither A nor B is true | c | The vapour expands as a superheated vapour up to the point at which condensation takes place suddenly and irreversibly. The state of steam at this point is neither stable nor unstable. The steam in this state is said to be in a supersaturated state or metastable state. | Comments | Active | |
| 74 | Consider the following statements: | Only B is true | Only A is true | Both A and B are true | Neither A nor B is true | b | The specific work output for the Rankine cycle is more than the Carnot cycle for the same maximum and minimum temperature. | Comments | Active | |
| 75 | The head loss due to exit from a pipe is given by H. What will be the head loss due to entrance of the same pipe? | H² | H | 2H | H/2 | d | The head loss due to exit from a pipe is given by H. The head loss due to entrance of the same pipe will be H/2. | Comments | Active | |
| 76 | Consider the following statements: | Only A is true | Only B is true | Both A and B is true | Neither A nor B is true | c | Statement (A) is true. Knocking in a spark ignition (SI) engine is caused by the spontaneous and uncontrolled combustion of the end-gas before the flame front arrives. Reducing the inlet air-fuel mixture temperature lowers the overall temperature and pressure inside the cylinder during compression. This increases the ignition delay of the fuel, making it less likely to self-ignite and cause knocking. Statement (B) is also true. Knocking in a compression ignition (CI) engine, or diesel knock, is caused by the ignition delay of the injected fuel. A longer delay allows more fuel to accumulate, leading to a rapid, explosive combustion once ignition occurs. Increasing the compression ratio raises the temperature and pressure in the cylinder at the end of the compression stroke. This reduces the ignition delay of the injected fuel, allowing it to ignite more smoothly and preventing the explosive combustion that causes knocking. |
Comments | Active | |
| 77 | A hydraulic press has a ram of 40 cm diameter and a plunger of 4 cm diameter. Find the weight applied to operate the press if it has to lift a weight of 100 N. | 1N | 2N | 4N | 3N | a | \(D_{R}=40 cm\) \(D_{p}=4 cm\) \(W=100 N\) \(\frac{π}{4}×\frac{F}{D^{2}P}=\frac{W}{\frac{π}{4}×D^{2}R}\) \(\frac{F}{4^{2}}=\frac{100}{40}\) \(=\frac{100×16}{16×100}\) \(F=1N\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 78 | Viscosity of liquids: | increases with the decrease in temperature. | decreases with the increase in temperature. | decreases with the decrease in temperature. | increases with the increase in temperature. | b | Viscosity of liquids decreases with the increase in temperature. | Comments | Active | |
| 79 | If the speed is kept constant, the variation in manometric head power and efficiency with respect to discharge: | gives the constant head and constant discharge curves for centrifugal pump. | gives the efficiency curves for centrifugal pump. | gives the main characteristic curves for centrifugal pump. | gives the operating characteristic curves for centrifugal pump. | d | If the speed is kept constant , the variation of manometric head , power and efficiency with respect to discharge gives the operating characteristic curves of the pump. The input power curve shall not pass through the origin. | Comments | Active | |
| 80 | A pitot tube works on the principle if velocity of flow at a point becomes zero then the pressure is. | decreased due to conversion of kinetic energy into pressure energy. | decreased due to conversion of kinetic energy into heat energy. | pressure is the same. | increased due to conversion of kinetic energy into pressure energy. | d | Stagnation pressure head is used to calculate the velocity at a point. It is based on the principle that if the velocity of flow at a point becomes zero, the pressure there is increased due to the conversion of the kinetic energy into pressure energy. | Comments | Active | |
| 81 | If high head is to be developed in a centrifugal pump then the impeller is to: | high head cannot be developed | can be connected in series or on same shaft | connected in parallel | can be connected in series as well as parallel | b | For developing a high head, a number of impellers are mounted in series or on the same shaft. The discharge passing through each impeller is the same. | Comments | Active | |
| 82 | Which of the following is a 50% reaction turbine? | Francis turbine | Da-Laval Turbine | Parson Turbine | Turgo Turbine | c | A blade having a 50 percent degree of reaction, or a 50 percent reaction stage, is one in which half the enthalpy drop of the stage occurs in the fixed blades and half in the moving blades. However, the pressure drops will not be equal. A widely used 50% reaction is known as Parson's Turbine. | Comments | Active | |
| 83 | Which of the following is an heat exchanger which feed water is heated from heat available with exhaust gases? | Air preheater | Feed pump | Superheater | Economiser | d | An economizer is a heat exchanger used for heating the feed water before it enters the boilers. The economizer recovers some of waste heat of hot flue gases going to the chemistry and thus it helps in improving the boiler efficiency. | Comments | Active | |
| 84 | Consider the following statements: | Neither A or B is true | Only A is true | Only B is true | Both A and B is true | d | Stirling cycle - two isothermal and two constant volume process. Otto cycle - two isentropic processes and two constant volume processes. |
Comments | Active | |
| 85 | Determine the pressure increase (in Pascal) required to reduce the volume of water by | 3.5 x 107 Pa | 4 x 107 Pa | 7.5 x 106 Pa | 3.3 x 107 Pa | d | K \(=2.2×10^{9}Pa\) \(\frac{∆V}{V}=0.015\) \(K=\frac{dp}{(\frac{dv}{v})}\) \(dp=K×\frac{dv}{v}\) \(=2.2×10^{9}×0.015\) \(=3.3×10^{7}Pa\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 86 | Which of the following welding processes use a non consumable electrode? | Shielded Metal Arc welding | Flux-cored arc welding | Carbon arc welding | Gas Metal Arc welding | c | Carbon arc welding (CAW) is a process which produces coalescence of metals by heating them with an arc between a non-consumable carbon (graphite) electrode and the work-piece. | Comments | Active | |
| 87 | Time loss factor in an IC engine is: | loss of work on expansion stroke | Leakage of fuels. | loss of heat from gases to cylinder walls. | time required for mixing of fuel and air. | d | Time loss factor: loss due to time required for mixing of fuel and air and also for combustion. | Comments | Active | |
| 88 | The main characteristic curves of a centrifugal pump is obtained by keeping the pump at. | constant speed and varying the temperature of over desired range. | constant discharge and varying the speed over desired range. | constant speed and varying the pressure over desired range. | constant speed and varying the discharge over desired range. | d | The operating characteristic curve of a turbine means a curve drawn at a constant speed. The curves that make up a hydraulic turbine's characteristic curves can be used to determine the turbine's precise behaviour and performance under various operating situations. | Comments | Active | |
| 89 | The masses of vapour and liquid is are 6 kg and 9 kg respectively. Find the dryness fraction of the liquid vapour mixture. | 0.667 | 0.4 | 0.8 | 0.6 | b | mv = 6kg M = 9 kg \(l\) X = \(\frac{6}{9+6}=\frac{6}{15}=\frac{3}{5}\) \(=0.6\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 90 | A steel rod of 20 mm diameter and 3.14m long is subjected to an axial pull of 2000N.Determine the elongation of the rod if the elastic modulus is 2 x 10⁵ N/mm². | 10mm | 1mm | 0.1mm | 0.01mm | c | d = 20 mm L = 3140 mm P = 2000 N E = 2105N/mm2 \(×\) SL = \(\frac{PL}{AE}\) \(=\frac{2000×3140×4}{3.14×20^{2}×2×10.5}\) SL = 0.1 mm |
Comments | Active | |
| 91 | The inward force acting on the rotating balls of a governor running at steady speed is known as. | Shear force | Controlling force | Tension | Frictional force | b | In a governor, the controlling force is the central, inward force that acts on the rotating balls, pulling them towards the axis of rotation. This force balances the outward centrifugal force produced by the rotation. The controlling force is provided by a spring, gravity, or a combination of both, and it is responsible for maintaining the governor's equilibrium position at a given speed. This balance of forces allows the governor to sense changes in engine speed and adjust the throttle accordingly. | Comments | Active | |
| 92 | Identify the CORRECT examples listed for the following types of boilers: | A) Cornish Boiler B) Lancashire Boiler | A) Lancashire Boiler B) Babcock and Wilcox boiler | A) Lancashire Boiler B) Cochran Boiler | A) Locomotive boiler B) Cornish Boiler | c | Lancashire Boiler is an internally fired and horizontal boiler because the furnace uses to present inside the boiler. This boiler generates low-pressure steam and it is a natural circulation boiler. Cochran boiler is a multi-tubular vertical fire tube boiler having numbers of horizontal fire tubes. It is the modification of a simple vertical boiler where the heating surface has been increased by means of numbers of fire tubes. |
Comments | Active | |
| 93 | Theworking compartment consists of special semi-circular shaped vanes cast into stainless steel rotor and stators. | hydraulic dynamometer | prony brake dynamometer | rope brake dynamometer | torsion dynamometer | a | A hydraulic dynamometer has semicircular vanes placed in a rotor and stator. Water flows in a toroidal vortex around the vanes and creates a torque reaction in the dynamometer casing that is resisted by the dynamometer and measured by a load cell. | Comments | Active | |
| 94 | The ratio of pressure energy change inside a runner of a reaction turbine to the total energy change inside a runner is called as. | Degree of reaction | Discharge of the turbine | Flow ratio | turbine efficiency | a | The Degree of reaction of a hydraulic turbine is defined as the ratio of change in pressure energy inside the runner per unit weight to the change of total energy inside the runner per unit weight. | Comments | Active | |
| 95 | The indicated power in KW is given by (where Pim is indicated mean effective pressure , n is the number of power strokes per min, k is the number of cylinders, L is the length of stroke, A is the area of the piston, Vs is the volume) | \(PimVsn/60000\) | \(PimAnk/60000\) | \(PimALnk/60000\) | \(PimVskL/60000\) | c | Indicated Power = PmLank/60000 kW | Comments | Active | |
| 96 | The forced circulation cooling system in an IC engine normally uses. | gear pump | piston pump | centrifugal pump | vane pump | c | The water flows from the lower portion of the radiator to the water jacket of the engine through the centrifugal pump. After the circulation water comes back to the radiator, it loses its heat by the process of radiation. This system is employed in cars, trucks, tractors, etc. | Comments | Active | |
| 97 | An IC engine has a brake power of 720 kW, with a fuel whose calorific value is 32 MJ/kg. The engine is expected to consume about 60 g/s. Calculate the brake thermal efficiency of the engine. | 0.375 | 0.395 | 0.25 | 0.32 | a | B.P = 720 KW C.V = 32 MJ/Kg Mf = 60 g/s = 60/1000kg/s \(ƞ_{B}=\frac{Brake power}{mf×Cv}\) \(ƞ_{B}=\frac{720}{\frac{60}{1000}×32×1000}\) \(\frac{720}{60×32}=0.375\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 98 | In velocity analysis of a Kaplan turbine the relation between the velocity of flow in the inlet (V₁) with the velocity of flow in the outlet (V₂) is. | V₁ = 2(V₂) | V₁ = V₂ | V₁ = (V₂)/2 | V₁ = V₂/4 | b | Kaplan turbine is axial flow reaction turbine as direction of flow of water is parallel to the axis of the rotating shaft. It differs from propeller turbine as the vanes of the hub are adjustable in Kaplan turbine. It differs from Francis turbine as the inlet and outlet peripheral velocity is equal in case of Kaplan turbine. | Comments | Active | |
| 99 | The point at which saturated vapour and saturated liquid coincide with each other is called as. | triple point | Critical point | boiling point | melting point | b | At critical point saturated liquid and saturated vapor point coincide. No distinct phase can be made in two phases. The latent heat of vaporization is zero at a critical point. | Comments | Active | |
| 100 | Consider the following statements: | Neither A nor B is true | Only A is true | Both A and B are true | Only B is true | b | Sand blow: This defect consists of a balloon-shaped gas cavity caused by the release of mold gases during pouring. It occurs at or below the casting surface near the top of the casting. A scab defect occurs by splash or boiling from teeming, casting, or conditioning. |
Comments | Active | |
| 101 | Reaction turbine means that the water at the inlet possesses. | kinetic and pressure energy | pressure energy | no energy | kinetic energy | a | If at the inlet of the turbine, the water possesses kinetic energy as well as pressure energy, the turbine is known as a reaction turbine. | Comments | Active | |
| 102 | Consider the following statements: | Neither A nor B is true | Only B is true | Both A and B is true | Only A is true | c | Statement (A) is true. Early Stirling engines struggled to compete with internal combustion engines partly due to the inability of materials and heat exchanger designs to handle the high temperatures required for high efficiency. Statement (B) is also true. For an Otto cycle, increasing the compression ratio improves the thermal efficiency, which means more work is done per cycle. Since mean effective pressure (MEP) is a measure of the net work done per unit displacement volume, a higher efficiency leads to a higher MEP. |
Comments | Active | |
| 103 | Which of the following is NOT a fusion welding process? | Thermit welding | Oxyacetylene welding | Electron-Beam Welding | Ultrasonic welding | d | Ultrasonic welding is an industrial process whereby high-frequency ultrasonic acoustic vibrations are locally applied to work pieces being held together under pressure to create a solid-state weld. It is commonly used for plastics and metals, and especially for joining dissimilar materials. | Comments | Active | |
| 104 | Consider the following statements: | Only A is true | Both A and B is true | Neither A nor B is true | Only B is true | a | Diesel cycle contains two isentropic process, 1 constant volume and 1 constant pressure process. | Comments | Active | |
| 105 | In case of mist lubricating system, the lubricating oil is mixed with the fuel the usual ratio being. | 3% | 5% to 9% | 1% to 3% | 7% to 9% | a | In a mist lubricating system, which is commonly used in small, two-stroke gasoline engines (like those found in scooters, chainsaws, or lawnmowers), the lubricating oil is mixed directly with the fuel. The oil is atomized into a fine mist and carried by the fuel-air mixture to lubricate the moving parts of the engine. The usual mixing ratio is a small percentage of oil to fuel, typically ranging from 1% to 3% by volume. This ratio is often specified by the engine manufacturer and is crucial for preventing excessive carbon buildup (from too much oil) or engine seizure (from too little oil). For example, a common ratio might be 1:50 or 1:40 (oil:fuel). |
Comments | Active | |
| 106 | The diverging angle of the venturimeter is less than the converging angle: | to avoid flow separation | To generate flow separation | to increase velocity in the direction of the diverging part | to decrease pressure in the direction of the diverging part | a | If divergence angle is very large, then back pressure will increase by great extent & eddies formation will take place resulting in flow separation. Thus, to avoid flow separation the divergence angle must not exceed more than 7° and range should be around 5 - 7°. | Comments | Active | |
| 107 | Consider the following statements: | Only B is true | Neither A or B is true | Only A is true | Both A and B are true | a | Like potential energy, the internal energy can be stored in the system. Notice, however, that heat and work can not be stored or conserved independently since they depend on the process. | Comments | Active | |
| 108 | Which of the following is increased due to friction in Nozzle? | A,C | B,D | B,C | A,B | a | Comments | Active | ||
| 109 | Which of the following is a method of steam turbine governing? | A,B,C | A,B,C, D © A,B,D |
B,C,D | c | The objective of steam turbine governing is to keep turbine speed constant irrespective of the load on the turbine shaft. The performance of a steam turbine is affected when the load changes. Turbine governing is important because in practical conditions the load frequently varies. | Comments | Active | ||
| 110 | Which of the following is a disadvantage of steam injector in boiler? | Low thermal efficiency | Low pumping efficiency | Easy of operation | Presence of dynamic parts | b | The steam injector is a common device used for delivering water to steam boilers, especially in steam locomotives. It is a typical application of the injector principle used to deliver cold water to a boiler against its own pressure, using its own live or exhaust steam, replacing any mechanical pump. | Comments | Active | |
| 111 | The diverging part of the venturimeter is relatively: | longer than the converging section | shorter than the converging section | equal to the converging section | longer or shorter than the converging section | a | To avoid the possibility of flow separation and the consequent energy loss, the divergent cone of the venturi meter is made longer with a gradual divergence. | Comments | Active | |
| 112 | To find the velocity at any point in a pipe by a pitot tube the following arrangement is used: | Pitot tube along with a vertical piezometer tube. | Only A is true | Neither A nor B is true | Both A and B is true | d | The pitot tube extracts velocity after measuring total (stagnation) and static pressures. The difference between total and static pressures is the dynamic pressure which is a function of velocity at the measurement point. \(( ρV2 /2 )\) | Comments | Active | |
| 113 | Consider the following statements: | Only A is true | Only B is true | Neither A nor B is true | Both A and B is true | d | Boiler draught may be defined as the small difference between the pressure of outside air and that of gases within a furnace or chimney at the grate level, which causes the flow of air/hot flue gases to take place through the boiler. | Comments | Active | |
| 114 | Which of the following is A) Fire tube boiler B) Water Tube boiler? | A) Cochran boiler B) Lancashire boiler | A) Cornish boiler B) La-Mont boiler | A) Babcock-Wilcox boiler B) Stirling boiler | A) La-Mont boiler B) Benson boiler | b | Water Tube Boiler : Babcock –Wilcox, Stirling, La-mont, Loeffler,Velox, Benson Boiler. Fire tube Boiler : Lancashire , Cornish, locomotive, Cochran Boiler. |
Comments | Active | |
| 115 | A Carnot engine absorbs heat from a reservoir. It absorbs 473.15J of heat at the temperature of 200° C. The heat rejected at a reservoir which is maintained at the temperature of 0° C. Find the heat rejected and work done. | Heat rejected = 373.15J, Work done=100J | Heat rejected = 273.15J, Work done=200J | Heat rejected = 273.16J, Work done=50J | Heat rejected = 0J, Work done=100J | b | Q1 = 473.15J T1 = 200+ 273 = 473K \(℃ \) T2 = 0 + 273 = 273 K \(ƞ_{C}=ƞ_{E}\) \(1-\frac{T_{2}}{T_{1}}=1-\frac{Q_{2}}{Q_{1}}\) \(\frac{273}{473}=\frac{Q_{2}}{473.15}\) \(Q_{2}=273.086J\) \(W=Q_{1}-Q_{2}\) \(W=473.15-273.086\) \(W=200J\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 116 | Which of the following advantages of multi-stage compressions over single stage compression is/are true? | Neither A nor B is true | Both A and B is true | Only B is true | Only A is true | b | For multistage compression the pressure ratio ( Pd /Ps ) 1 N is less than the single stage compression for same Pd Ps . So, volumetric efficiency increases for multi stage compression. The operating cost reduces for multi stage compression. | Comments | Active | |
| 117 | Which of the following forces in Lami's Theorem is applicable to keep an object in static equilibrium? | Two coplanar and concurrent forces only | Three coplanar, non - collinear and concurrent forces | Two coplanar, non - collinear and concurrent forces | Three coplanar and concurrent forces | b | Lami's Theorem states that, 'When three forces acting at a point are in equilibrium, then each force is proportional to the sine of the angle between the other two forces'. | Comments | Active | |
| 118 | Which of the following test is easier to conduct comparatively in an IC engine ? | ip-bp method | Retardation test | Motoring test | Willian's Line test | d | The Willans line represents the relationship between fuel energy input and engine output. The test in which the engine runs at a constant speed using the motor and the engine is connected to the electric motor is called the Motoring test. |
Comments | Active | |
| 119 | Which of the following statement/s is/are true? | Neither A nor B is true | Only A is true | Both A and B is true | Only B is true | c | The Vapour absorption refrigeration systems include all processes in a vapor compression refrigeration system, such as compression, condensation, expansion, and evaporation—the refrigerant used in Vapour absorption systems as ammonia, water, or lithium bromide. | Comments | Active | |
| 120 | What is the standard feed temperature and working pressure adopted to compare two boilers ? | 100°C and 0.1 kg/cm² | 0°C and (a)033 kg/cm² | 100°C and (a)033 kg/cm² | 200°C and (a)033 kg/cm² | c | tandard feed temperature and working pressure adopted to compare two boilers are 100°C and 1.033 kg/cm². | Comments | Active | |
| 121 | Which of the following is a dynamic pressure pump? | Vane Pump | Gear Pump | Piston Pump | Centrifugal Pump | d | Centrifugal pump, diffuser pump and axial pump are Dynamic pumps. Dynamic pumps are also known as non-positive displacement pumps or roto-dynamic pumps. Reciprocating pump and rotary pumps are positive displacement pumps. | Comments | Active | |
| 122 | Which of the following is an incorrect assumption made in Bernoulli's equation? | Rotational flow | Steady flow | Incompressible flow | The viscosity of the fluid is zero | a | Bernoullis theorem is applicable for irrotational flow. | Comments | Active | |
| 123 | Consider the following statements: | Only A is true | Only B is true | Neither A or B is true | Both A and B is true | a | Carbon Loss results from the presence of unburned combustible materials: This statement is true. Carbon loss, or unburned carbon loss, is a form of heat loss in a boiler. It occurs when the fuel (e.g., coal) is not completely combusted, leaving unburned carbon in the ash (in the case of solid fuels) or flue gases (in the case of liquid/gaseous fuels). This represents a loss of potential heat that was not converted into useful energy, and it is a key factor in calculating a boiler's efficiency. The sensible loss is typically the largest single boiler loss component: This statement is false. The largest single loss component in a boiler is the dry flue gas loss, which is also a type of sensible heat loss. It's the heat carried away by the dry products of combustion (such as CO2, O2, and N2). While this is a sensible loss, the term "sensible loss" can also include other losses, but the specific loss from the dry flue gases is the largest and most significant component. The statement implies that "the sensible loss" as a general category is the largest, when it's the specific loss through the dry flue gases that holds this distinction. The heat loss due to incomplete combustion (carbon loss) or moisture in the flue gases can also be significant but is usually less than the dry flue gas loss. |
Comments | Active | |
| 124 | Consider the following statements: A- The point on the beam where the bending moment changes its sign is known as the point of contraflexure. B- If shear force is zero at a particular section bending moment will be at its peak in that particular section. |
Only A is true | Both A and B are true | Only B is true | Neither A or B are true | a | This means zero shear force will not produce maximum bending moments always. It is only possible in the case of a simply supported beam subjected to UDL. | Comments | Active | |
| 125 | Moment of inertia of a solid sphere of radius R with the axis of rotation along it diameter is_________. | 2/3(MR²) | MR² | (MR²)/2 | 2/5 (MR²) | d | MOIsolid = 2/5 (MR²) | Comments | Active | |
| 126 | A gas tungsten arc-welding operation is performed at a current of 400A and voltage of 10V. The melting factor f2 = 0.5, and the unit melting energy for the metal 'Um' = 20 J/mm3. Determine the rate of heat generation at the weld. Heat transfer factor for gas tungsten arc welding is 0.7 |
2800 J/s | 1400 J/s | 700 J/s | 2100 J/s | b | The rate of heat absorbed by the workpiece (Qw) is the rate of heat generated by the arc multiplied by the heat transfer factor (f1). Qarc=V⋅I Qarc=10 V⋅400 A=4000 W=4000 J/s The rate of heat absorbed by the workpiece is: Qw=Qarc⋅f1 Qw=4000 J/s x 0.7=2800 J/s However, the rate of heat used for melting the metal is what is usually of interest. This is determined by the melting factor (f2). Qmelting = Qw⋅f2 Qmelting=2800 J/s x 0.5=1400 J/s The term "rate of heat generation at the weld" is often interpreted as the rate of heat effectively used for melting, which is a portion of the total heat generated by the arc. In this context, the total heat generated is 4000 J/s, the heat transferred to the workpiece is 2800 J/s, and the heat used for melting is 1400 J/s. |
Comments | Active | |
| 127 | Which of the following is used for periodical cleaning by discharging the water and sediments from bottom of boiler? | Blow off cock | safety valve | fusible plug | Feed check valve | a | To discharge mud and other sediments deposited in the bottom most part of the water space in the boiler, while boiler is in operation. | Comments | Active | |
| 128 | Match the correct pair of combustion chambers for SI engines: T-head Type: A) One valve in the cylinder head and the other in cylinder block. L-Head type: B) Used in early stage of engine development. I-Head type: C) Two valves on the same side of the cylinder and operated by single camshaft. F-head type: D) Also known as overhead valve. |
1-A, 2-D, 3-C, 4-B | 1-B, 2-C, 3-D, 4-A | 1-B, 2-D, 3-C, 4-A | 1-A, 2-C, 3-D, 4-B | b | T-head Type- Used in early stage of engine development. L-Head type - Two valves on the same side of the cylinder and operated by single camshaft. I-Head type - Also known as overhead valve. F-head type - One valve in the cylinder head and the other in cylinder block. |
Comments | Active | |
| 129 | Consider the following statements: | Only A is true | Only B is true | Neither A nor B is true | Both A and B is true | b | In the cylinder and valve timing diagram (Figure 1) note that the intake valve begins opening 30°, before T.D.C. (top dead center) or before the piston actually starts on the suction (intake) stroke. | Comments | Active | |
| 130 | A hydraulic press has a ram of 20 cm diameter and a plunger of 4 cm dia. Find the weight lifted by the hydraulic press when a force of 10 N is applied. | 100N | 0.4N | 50N | 250N | d | R = 20 cm \(∆\) P = 4 cm \(∆\) F = 10 N \(\frac{F}{\frac{π}{4}D^{2}P}=\frac{W}{\frac{π}{4}D^{2}R}\) \(\frac{10}{\frac{π}{4}(4)^{2}}=\frac{W}{\frac{π}{4}(20)^{2}}\) \(\frac{10×20×20}{4×4}=w\) W = 250 N |
Comments | Active | |
| 131 | The specific speed for a Francis Turbine in SI units is. | 51 to 225 | 30 to 51 | 255 to 860 | 8.5 to 30 | a | The specific speed of Francis turbine is in the range of 60-300. The specific speed of Kaplan/propeller turbine is greater than 300. | Comments | Active | |
| 132 | Which of the following type of impeller of a centrifugal pump is used for pumping highly contaminated slurry type liquids? |
Open Impeller | Closed Impeller | Semi-Open Impeller | Constricted Impeller | a | Open impellers are designed with vanes completely open on both sides, offering maximum passage for the fluid. These impellers are preferred for pumps that handle highly contaminated or viscous fluids and those containing solids. | Comments | Active | |
| 133 | Consider the following statements: | Both A and B is true | Neither A nor B is true | Only A is true | Only B is true | a | Heat VS. Work Both are recognized at the boundaries of a system as they cross the boundaries. That is, both heat and work are boundary phenomena. i. Systems possess energy, but not heat or work. ii. Both are associated with a process, not a state. iii. Unlike properties, heat or work has no meaning at a state. iv. Both are path functions (i.e., their magnitudes depend on the path followed during a process as well as the end states). |
Comments | Active | |
| 134 | You have given a liquid-vapour mixture where a and b are the masses of liquid and vapour respectively. What would be the dryness fraction(d) in the given scenario? | d = a / (a + b) | d = (a + b) / b | d = (a + b) / a | d = b / (a + b) | d | Dryness fraction is the ratio of mass of vapour to the total mass of mixture. | Comments | Active | |
| 135 | Friction power can be measured with high accuracy using which of the following methods? | Willian's Line | Morse test | measurement of brake and indicated power | motoring test | c | Friction power can be measured with high accuracy using measurement of brake and indicated power. F.P = I.P – B.P |
Comments | Active | |
| 136 | Super heating vapour after compression in a vapour compression cycle will: | increase the work done | have no effect. | increase the coefficient of performance | decrease the refrigerating effect | a | Superheating of Vapour increases both the refrigeration effect as well as the work of compression. COP (ratio of refrigeration effect and work of compression) may or may not increase with superheat, depending mainly upon the nature of the working fluid. | Comments | Active | |
| 137 | Which of the following is an advantage of rolling contact bearings over sliding contact bearing? | less initial cost | low starting friction | simple housing design | less noisy | b | It is an outstanding advantage of a rolling contact bearing over a sliding bearing that it has a low starting friction. Due to this low friction offered by rolling contact bearings, these are called antifriction bearings. | Comments | Active | |
| 138 | What will be the equation for the loss of head due to sudden enlargement if V₁ and V₂ are the velocities of the flow before and after the enlargement in a pipe? | \(\frac{(V12-V22)}{2g}\) | \(\frac{(V^{1}-V^{2})}{2g}\) | \(\frac{(V_{1}-V_{2})^{2}}{2g}\) | \(\frac{(V_{1}-v_{2})^{2}}{g}\) | c | The loss of head due to a sudden enlargement in a pipe is calculated using the Borda-Carnot equation. This equation accounts for the energy lost due to the eddies and turbulence created when the fluid's velocity abruptly decreases. The formula is: \(H_{L} =\frac{(V_{1} - V_{2})^{2}}{2g}\) Where: is the head loss due to sudden enlargement. \(h_{L}\) is the velocity in the smaller pipe before enlargement \(V_{1}\) is the velocity in the larger pipe after enlargement. \(V_{2}\) is the acceleration due to gravity. \(g\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 139 | At the critical point the latent heat of vaporization is. | maximum | negative | equal to pressure at (d)5 mm hg | 0 | d | At a critical point, latent heat of vaporization is zero because at critical point no energy is required to convert the liquid phase to the gaseous phase. | Comments | Active | |
| 140 | The acceleration and retardation of the follower at the beginning and at the end of each stroke when the follower moves with uniform velocity is. | negative | infinity | 0 | 0.5 | b | For a cam follower moving with uniform velocity, the velocity changes instantaneously at the beginning and end of the stroke. Since acceleration is the rate of change of velocity (a=dv/dt), an instantaneous change in velocity over a zero time interval results in infinite acceleration or retardation. | Comments | Active |










