| S.No | Question | Option A | Option B | Option C | Option D | Answer | Solution | Comments | Status | Action |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | What does the process of Principle of Arc welding involve? | Supplying oxygen and acetylene between the electrodes to melt the metal | Creating flow of electric current in the air gap between the electrode and the workpiece to melt the metal | Creating a chemical reaction between the electrode and the workpiece to melt the metal | Creating friction between the electrode and the workpiece to melt the metal | b | Arc Welding: Electric discharge – Arc (charge flows from electrode to base metal), Ionised air gap is known as plasma or ARC requirement of welding Low Voltage and high current (20 to 80 V) \(→ \) |
Comments | Active | |
| 2 | Given an annual usage value of 400 units, the procurement cost is 20 per order, cost per piece is 100 and cost of carrying inventory is 10%. Calculate the EOQ | 50 | 30 | 40 | 60 | c | Cost of carrying inventory \(C_{h}=\frac{10×100}{100}=10\) \(EOQ=\frac{2DC_{o}}{C_{h}}=\frac{2×400×20}{10}=40\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 3 | What is a primary advantage of using an open impeller design? | Easier inspection and cleaning compared to closed impellers | Higher pressure generation compared to radial flow pumps | Improved efficiency due to reduced flow separation | Complete elimination of cavitation risks | a | Open impeller pump: The impeller is not provided with any shroud or Plate. Such pumps are used for handling mixtures of water, sand, pebbles and clay etc. Closed impeller pump: This type is meant to handle non-viscous liquid such as ordinary water, hot water and chemicals. Used when the liquid is free from debris. |
Comments | Active | |
| 4 | The power required to drive a pump is calculated by considering: | the pump's weight | only the hydraulic power output | only the mechanical friction in the pump | the work done in overcoming hydraulic losses and delivering the desired head | d | To determine the power required to drive a pump, we must consider: Hydraulic losses in the pump (due to turbulence, eddies, etc.) Mechanical losses (due to bearing friction, gland friction, etc.) Volumetric losses (due to leakage through clearances) So, the actual power required at the shaft of the pump (called shaft power or input power) is: Shaft Power (P) = \(\frac{ÏgQH}{overall efficiency} \) \(η_{overall}=η_{mech}×η_{volumetric}×η_{hydraulic}\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 5 | Which of the following wheels supports the workpiece in internal centreless grinding operation? | Pressure roller, supporting roller and regulating wheel | Only regulating wheel | Only pressure roller | Only supporting roller | a | Internal Centreless Grinding: Holes in ring type parts can be ground on internal centreless grinding machines. The work- piece 1 is loaded into the grinding zone where it is held between three steel rolls support 2, pressure 3 and regulating 4 - mounted in housing 5. The lever mounted pressure roll 3 exerts a preset force on the workpiece holding it against the support and regulating rolls. The regulating roll, linked to the workdrive, rotates the work piece at a peripheral speed of from about 0.7 to 1.0 m/s. An axial force acting on the workpiece, due to the fact that the regulating wheel axis is inclined to about 1/2°, holds the workpiece axially with one end face against a roller stop. The hole is ground with a wheel mounted on spindle 6. The rotation of the work on grinding is the result of the friction force between the work and the regulating roll. The workpiece is loaded and unloaded by moving the pressure roll outward. In internal centreless grinding, the workpiece is not held between centers or chucked. Instead, it is supported in a three-point contact system, which includes: Regulating wheel – controls the rotation and feed of the workpiece. Supporting roller – supports the workpiece from below. Pressure roller – presses the workpiece against the regulating wheel and supporting roller.  (Reference : A textbook of production Technology By P.C.Sharma – page no.-543 ) |
Comments | Active | |
| 6 | A symmetrical planar built-up section consists of two channel sections joined together at the tips of their flanges to form a closed rectangular area. The total width of each flange is ' B' Each web is 'w' units deep inside, D' units deep at its outside (longer) face, and 'b' units thick. The moment of inertia of the composite section about its centroidal axis perpendicular to the webs is given by: | \(\frac{BD^{3}}{12}+\frac{(B-b)w^{3}}{3}\) | \( \frac{BD^{3}}{12}-\frac{(B-b)w^{3}}{12}\) | \( \frac{BD^{3}}{12}+\frac{Bw^{3}}{3}\) | \( \frac{BD^{3}}{6}+\frac{(B-b)w^{3}}{6}\) | d | The section is a symmetrical rectangular box created by joining two channels at their flanges. We calculate the moment of inertia about the centroidal axis perpendicular to the webs (horizontal axis). Step 1: Moment of inertia of the full outer rectangle: Iouter = \(\frac{BD^{3}}{12}\) Step 2: Moment of inertia of the inner (hollow) void: Iinner = \(\frac{(B-b)w^{3}}{12}\) Step 3: Since the shape is symmetrical and built using two channels, we multiply the difference by 2: I = 2 \((\frac{BD^{3}}{12}-\frac{(B-b)w^{3}}{12})=\frac{BD^{3}}{6}-\frac{(B-b)w^{3}}{6}\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 7 | What is the function of shielding gas in Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW)? | Protects the tungsten electrode and the molten metal weld pool from the atmospheric contamination | Protects the consumable bare electrode and the molten metal weld pool from the atmospheric contamination | Protects the consumable coated electrode and the molten metal weld pool from the atmospheric contamination | Removes the slag by striking and conducts current to pass through it | a | Gas Tungsten Metal Arc Welding (GMAW or TIG): Non consumable electrode welding Straight polarity is used Penetration will be higher with DCEN compare to DCEP for Al and Mg sheet welding AC is suitable also used for cathode cleaning to remove oxide layer with Al welding with AC argon inert gas is used weakest part of weld setup is ceramic nozzle of torch which is connected to torch by threaded joint In Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW), also known as TIG welding, a non-consumable tungsten electrode is used to produce the weld. The shielding gas (usually argon or helium) serves two main functions: Protects the tungsten electrode from oxidation and contamination Shields the molten weld pool from atmospheric gases like oxygen, nitrogen, and hydrogen, which can cause porosity, oxidation, and other weld defects.  |
Comments | Active | |
| 8 | It is important for the piston to fit 'snugly' into the cylinder to: | both, allow for easy movement and provide a gas-tight space | allow for easy movement alone | provide a gas-tight space alone | neither allow for easy movement nor provide a gas-tight space | a | In an internal combustion engine, the piston moves up and down inside the cylinder. A snug fit is essential because: Gas-tight sealing is necessary to: Prevent leakage of combustion gases from the combustion chamber. Maintain compression and engine efficiency. Easy movement is also essential to: Allow the piston to reciprocate smoothly with minimal friction. Prevent excessive wear and seizure during thermal expansion. To achieve this balance: Piston rings are used to improve the gas seal. Clearance is maintained to allow for thermal expansion during operation. |
Comments | Active | |
| 9 | ______ is/are the most widely used material for the broaches in a broaching operation. | Copper | Metal matrix composites | Silver-copper combination | High speed steel | d | In broaching operations, the cutting tool is the broach, which is subjected to: High cutting forces Continuous contact with the workpiece. Precise dimensional requirements High Speed Steel (HSS) is the most widely used material for broaches because it offers: Good wear resistance High toughness (less brittle than carbide) Good machinability Retains hardness at high temperatures |
Comments | Active | |
| 10 | What defines a black body in the context of thermal radiation? | A material that only emits visible light | A surface that reflects all incident radiation without absorption | An object with perfect thermal insulation | An idealised object that absorbs all incident radiation and emits the maximum possible radiation at a given temperature | d | In the context of thermal radiation, a black body is a theoretical or ideal object with the following properties: Absorbs all incident radiation, regardless of wavelength or direction Emits the maximum possible radiation at a given temperature (as described by Planck’s law) Its emission is only a function of temperature and wavelength, not material or surface finish |
Comments | Active | |
| 11 | Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW) is also called _______. | Manual Metal Arc Welding | Metal Inert Gas Welding | Tungsten Inert Gas Welding | Gas Tungsten Arc Welding | a | Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW). Also known as Manual metal arc welding (MMAW), Stick Welding. Arc temperature ranges from 5000°C to 6800°C. Arc heat is directly proportional to current supplied. Heat first melts electrode rod then coating is melted. Arc length should be equal to 1 to 1.5 times of electrode diameter. Too short arc causes electrode gets stick with work and too long arc causes spatter, undercut, porosity and arc gets distinguish. If Low current supplied Low depth of penetration, unfused toes of weld, excess reinforcement. If High current supplied Undercut, Crater at the end of weld and excessive arc force. |
Comments | Active | |
| 12 | Which of the following does a cascade refrigeration system use? | Two or more refrigerants with different boiling points | A single refrigerant in both cycles | Only air as a working fluid | Only ammonia as a refrigerant | a | A cascade refrigeration system is used for achieving very low temperatures, typically below –40°C, where a single refrigerant system becomes inefficient or impractical. Using two or more vapor-compression refrigeration cycles, each operating with a different refrigerant. These refrigerants are selected based on their boiling points suited to the temperature levels in each stage: The low-temperature cycle uses a refrigerant with a very low boiling point. The high-temperature cycle uses a refrigerant with a higher boiling point. A cascade heat exchanger connects the two cycles, where the condenser of the low-temp cycle is cooled by the evaporator of the high-temp cycle. This allows the system to operate efficiently at ultra-low temperatures. |
Comments | Active | |
| 13 | In torch brazing, heat is produced by burning a mixture of ______ . | oxy-hydrogen gas | oxy-neon gas | oxy-nitrogen gas | oxy-acetylene gas | d | In torch brazing, the required heat to melt the filler metal (but not the base metal) is provided by a gas flame, typically generated by burning a fuel gas in oxygen. The most commonly used fuel in torch brazing is acetylene, because: It produces a very high flame temperature when combined with oxygen (up to ~3200°C) The flame is easily controlled and concentrated, suitable for precision work in brazing Thus, the oxy-acetylene flame is the standard heat source in torch brazing. |
Comments | Active | |
| 14 | What is the complete form of 'LVDT', one of the most popular electromechanical comparators? | Linear versatile differential transformer | Linear variable differential transformer | Longitudinal variable differential transformer | Linear variable dimensional transformer | b | LVDT stands for Linear Variable Differential Transformer, and it is a highly accurate and widely used electromechanical comparator for measuring small linear displacements. Linear: Measures displacement in a straight line Variable: Output voltage changes with position Differential: Based on the difference in voltage between two secondary coils Transformer: Works on electromagnetic induction principle The core movement changes the voltage induced in two secondary windings, giving a differential AC output proportional to the displacement. |
Comments | Active | |
| 15 | For machining yellow metals and free-cutting steels, ______ is/are used as cutting fluids. | water soluble oils | insoluble oils | germicides and water | water | a | For machining yellow metals (like brass and bronze) and free-cutting steels, the preferred cutting fluids are: Water-soluble oils (also called emulsifiable oils) because they: Provide good cooling properties due to water content. Offer adequate lubrication from the oil phase. Prevent staining and corrosion on non-ferrous metals. Reduce tool wear and improve surface finish. These oils form an emulsion with water, combining the cooling effect of water with the lubricating properties of oil, which is ideal for high-speed machining of such materials. |
Comments | Active | |
| 16 | In Submerged Arc Welding, _______ electrode is used in combination with a flux feeder tube. | non-consumable baked carbon | non-consumable tungsten | consumable bare | non-consumable graphite | c | Submerged Arc Welding, (SAW). In this, coalescence is produced by heating with an arc between a bare wire electrode and the work. The weld zone is shielded by a blanket of fusible granular flux material supplied directly on the weld seam ahead of the electrode to shield the arc. Pressure is not used and molten filler metal is obtained from the electrode. Electrode is in form of wire and Granular flux is used. |
Comments | Active | |
| 17 | Two shafts, A and B, are of the same material. If the diameter of A is thrice the diameter of B, then the torque that can be transmitted by A will be: | 64 times that of B | 9 times that of B | 16 times that of B | 27 times that of B | d | \( T=\frac{Ï€d^{3}}{16}Ï„, Tâˆd^{3},\) times that of B. \( T_{A}=(3d)^{3}=27\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 18 | Identify the milling cutter used for parting off operations or cutting thin slots. | Angle milling cutter | Metal slitting cutter | Plain milling cutter | Fly milling cutter | b | A metal slitting cutter is a thin, circular milling cutter specifically designed for: Parting off operations Cutting very narrow slots or grooves These cutters resemble thin circular saw blades and are used when precision and fine-width cuts are required. They are often made of high-speed steel (HSS) and can be used in both horizontal and vertical milling machines. |
Comments | Active | |
| 19 | What is the impact of effective preplanning on the economic efficiency of a manufacturing operation? | Increase in the complexity of the production process | Elimination of the need for any forecasting | Focus on the design of jigs and tools | Prevention of the production of large uneconomic output | d | Effective preplanning creats positive impact in manufacturing operation . As option d says prevention of production of large uneconomic output is correct . Effective preplanning can reduce the losses. | Comments | Active | |
| 20 | Which of the following is the function of hose pipes in the gas welding process? | Removes the oxide film and maintains a clean surface | Supplies the gases from the pressure regulators | Mixes oxygen and acetylene in the correct proportion | Protects the eyes from harmful heat and ultraviolet rays | b | In the gas welding process (e.g., oxy-acetylene welding), hose pipes serve a very specific and essential function: They transport gases (oxygen and acetylene) from the pressure regulators on the gas cylinders to the welding torch. They are typically color-coded for safety: Red hose for acetylene Blue or black hose for oxygen These hoses are made of reinforced rubber or other flexible materials to handle low-pressure gas flow safely. |
Comments | Active | |
| 21 | While measuring surface texture, the part of the profilometer that makes contact with the workpiece surface is ______. | a finely pointed stylus | an electrical pickup | a recording unit | a motorised mechanism | a | In surface texture measurement using a profilometer, the component that directly contacts the work piece surface is: A finely pointed stylus, typically made of diamond or other hard material It traces the surface irregularities (peaks and valleys) as it moves across the surface The vertical movements of the stylus are converted into electrical signals, which are then amplified and recorded to produce a profile of the surface texture. |
Comments | Active | |
| 22 | Which of the following does NOT belong to assumptions in calculating EOQ in the basic inventory model? | Material cannot be supplied in variable quantities | Lead time is constant | Delivery of all items are instantaneous | Demand is continuous | a | The Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) model is a basic inventory control model that helps determine the optimal order quantity to minimize total inventory costs (ordering cost + holding cost). Key assumptions of the basic EOQ model: Demand is constant and known Lead time is constant and known Entire order is delivered instantaneously No stockouts are allowed Ordering cost and holding cost are constant Price per unit is fixed (no quantity discounts) |
Comments | Active | |
| 23 | The key step in making a dimensional measurement using a tool maker's microscope is ______. | aligning the cross-wires with the measurement points | changing the objective lens power | adjusting the focus on the workpiece | viewing the magnified image | a | Positioning of the workpiece on the table is extremely important to ensure accuracy in measurement. The measuring direction of the workpiece should be aligned with the traversing direction of the table. While looking into the eyepiece, the position of the eyepiece mount should be adjusted so that the horizontal cross-wire is oriented to coincide with the direction of the table movement. Now, the eyepiece mount is firmly secured by tightening the fixing screws. The workpiece is placed/clamped on the table and the micrometer head turned to align an edge of the workpiece with the centre of the cross-wires. Then, the micrometer is operated and the moving image is observed to verify whether the workpiece pavement is parallel to the measuring direction. By trial and error, the user should ensure that the two match perfectly. Most tool maker's microscopes are provided with a surface illuminator. This enables the creation of a clear and sharp image. Out of the following three types of illumination modes that are available, an appropriate mode can be selected based on the application. (Reference: -Book- Engineering Metrology and Measurements textbook by N.V. Raghavendra & I. Krishnamurthy Page no. - 170 ) |
Comments | Active | |
| 24 | The Vickers hardness number (VHN) for a material with a 20 kg load and an average indentation diagonal of 0.3 mm is: | 115 | 78 | 324 | 412 | d | \( VHN=\frac{1.854×P}{d^{2}}=\frac{1.854×20}{0.3×0.3}=\frac{37.08}{0.009}=412\) | Comments | Active | |
| 25 | In an air standard cycle, heat addition is assumed to occur ______. | through internal combustion of fuel | from an external constant high-temperature source | by direct contact with a flame | from a combination of chemical reactions and external sources | b | Assumptions of Air Standard Cycle: The working fluid is air, which behaves as an ideal gas throughout the cycle. The heat addition and heat rejection processes are idealized as occurring at constant temperatures. The specific heats of air are assumed to be constant. All processes are internally reversible. There are no changes in kinetic or potential energy of the working fluid |
Comments | Active | |
| 26 | In a 'spirit-level device', to which point of the glass vial does the bubble always move? | Highest point | Lowest point | Random point | Middle point | a | A spirit level device (commonly called a bubble level) is used to check the levelness or flatness of a surface. The vial is a slightly curved glass tube, partially filled with a liquid (like alcohol or ether), leaving a bubble inside. When the vial is tilted, gravity causes the liquid to flow to the lower side. Consequently, the bubble, being lighter than the liquid, moves to the highest point of the vial. This behavior is consistent due to the buoyant force and the shape of the tube. |
Comments | Active | |
| 27 | The overall efficiency of a pump is calculated by comparing: | the volumetric flow rate to the pump casing size | the hydraulic power output to the mechanical power input | the pump speed to the impeller diameter | the manometric head to the fluid velocity | b | Overall efficiency: Is defined as the ratio of the power output from the pump (WHP) to the power input from prime mover (SP) or (BHP). \(η_{0}=\frac{γQH_{m}}{SP}\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 28 | What is the basic essential condition for coating material in hot dipping? | It should have a higher melting point than the base metal. | It should form an alloy at the interface with the base metal. | It should have lower wettability. | It should completely evaporate during the process. | b | In hot dipping, the coating material is melted and the base metal is dipped into it, allowing them to mix and form an alloy at the interface, ensuring proper adhesion and bonding between the two metals. | Comments | Active | |
| 29 | Which of the following movements of the grinding wheel is possible in a chucking-type internal grinder? | Only reciprocating movement | Only rotational movement | Only vibrational movement | Both rotational and reciprocating movement | d | In a chucking-type internal grinder, the grinding wheel must perform two key motions to effectively grind the internal surface of a work piece: Rotational Movement: The grinding wheel rotates at high speed to carry out the cutting or abrasive action. Reciprocating Movement: The grinding wheel also moves back and forth along the axis of the bore to ensure the entire inner surface is ground evenly. These combined motions are essential for: Achieving a uniform surface finish Covering the entire length of the bore Maintaining dimensional accuracy |
Comments | Active | |
| 30 | How is thermal efficiency defined in the context of internal combustion engines? | The ratio of exhaust gas temperature to the intake air temperature | The ratio of the engine displacement to the fuel mass used | The ratio of indicated power to frictional power losses | The ratio of useful work output to the total chemical energy input from fuel | d | \( η_{thermal}=\frac{useful work output(brake or indicated power)}{total heat energy supplied from fuel}\) | Comments | Active | |
| 31 | Which area under the stress-strain curve represents the toughness of a material? | Area of elastic region | Total area under the curve | Slope of the elastic region | Area of plastic region | b | Toughness is the property of a material which enables it to absorb energy without fracture. This property is very desirable in components subject to cyclic or shock loading. Toughness is measured in terms of energy required per unit volume of the material, to cause rupture under the action of gradually increasing tensile load. This energy includes the work done upto the elastic limit which is small in comparison with the energy subsequently expanded. Below Fig. shows the stress-strain curves, both for mild steel as well as high carbon steel. The toughness is represented by the area under the stress-strain curve for the material. Area up to fracture point is considered as total area so here option B will be correct answer.  (Reference:- Mechanics of material by B.C.Punmia – chapter-1-Page no.-3) |
Comments | Active | |
| 32 | What will be the value of the maximum absolute shear stress produced in a thin cylinder if hoop stress = 40 MPa and longitudinal stress = 20 MPa? | 20 MPa | 10 MPa | 30 MPa | 60 MPa | a | \( σ_{h}=40Mpa, σ_{l}=20Mpa, \) Radial stress in thin cylinder is negligible, \(σ_{r}=0\) \(τ_{max}=\frac{σ_{max}-σ_{min}}{2}=\frac{40-0}{2}=20Mpa \) Note: in Plane stress condition, max shear stress is , . \(\frac{σ_{x}-σ_{y}}{2}\) \(σ_{z} not considerd\) But in condition of maximum absolute shear stress, \(σ_{z} is considerd\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 33 | The work done by the load in stretching the bar is known as: | Strain Energy | Dislocation Energy | Potential Energy | Kinetic Energy | a | When an elastic material is deformed under load, work is done by the applied load against the internal resisting forces induced in the material. The work done by the load in straining the body is stored within the strained material in the form of strain energy. (Reference: Mechanics of material by B.C.Punmia – chapter-6-Page no.-201) |
Comments | Active | |
| 34 | According to the Principle of Resolution, the algebraic sum of the resolved parts of multiple forces in a given direction is equal to: | the difference between the largest and smallest force | the resolved part of their resultant in the same direction | the total magnitude of all forces combined | the sum of all forces acting in that direction | b | Principal of Resolution: It states, "The algebraic sum of the resolved parts of a number of forces in a given direction is equal to the resolved part of their resultant in the same direction." | Comments | Active | |
| 35 | In a four-stroke cycle diesel engine, the intake valve starts to open at | 10 - 25 before TDC \(°\) \(°\) | 25°- 40° before BDC | 25 - 40 after BDC \(°\) \(°\) | 10 - 15 after TDC \(°\) \(°\) | a | (Reference : Ic engine by m. L. Mathur and r. P. Sharma -dhanpat rai publication -25 edition - page -25) The typical valve timing diagram for a four-stroke CI engine is as follows: IVO up to 30° before TDC IVO up to 50° after BDC EVO about 45° before BDC EVO about 30° after TDC Injection about 15° before TDC |
Comments | Active | |
| 36 | What does the Polygon Law of Forces describe? | The force required to balance a single force | The interaction between two perpendicular forces | The method to find the resultant of multiple forces | The equilibrium condition of multiple forces | c | Polygon Law: - If any number of forces, acting at a point, be represented in magnitude and direction by the sides of a polygon, taken in order, then the closing side of the polygon taken in opposite order will represent the resultant both in magnitude and direction. Here multiple forces P,Q,R,S,T and polygon law is used to find resultant of these multiple forces. |
Comments | Active | |
| 37 | Which type of steel would be best suited for applications requiring both high strength and good corrosion resistance? | Stainless steel | High-carbon steel | Low-alloy steel | Mild steel | a | Stainless steel contains chromium (usually above 11%) which forms a passive oxide layer, providing excellent corrosion resistance. It can also be alloyed and heat treated to achieve high strength. High-carbon steel offers strength but poor corrosion resistance. Low-alloy and mild steels have limited corrosion resistance and strength compared to stainless steel. |
Comments | Active | |
| 38 | What is the typical behavior of creep deformation in materials at very high temperatures (above 0.5 times the melting temperature)? | Rapid deformation and fractures | Material exhibits significant plastic deformation | Deformation in material is negligible | Material becomes more brittle and fails instantly | b | At very high temperatures (above about 0.5 times the melting temperature in Kelvin), materials show significant creep deformation. The material undergoes time-dependent plastic deformation even under constant stress. This happens due to increased atomic diffusion and dislocation movement. It is not an instant fracture but gradual deformation that can lead to failure over time. |
Comments | Active | |
| 39 | Determine the minimum thickness of the rectangular axial bar shown against yielding. Given Factor of Safety (FOS) = 2 and Yield stress = 310 MPa. |
25 mm | 19.4 mm | 155 mm | 60 mm | b | Axial load, P = 120 kN = 120000 N Width of bar, b = 40 mm Yield stress, = 310 MPa \(σ_{yield}\) Factor of Safety, FOS = 2 Step 1: Allowable Stress \(σ_{allowable }=\frac{310}{2}=155 MPa\) Step 2: Use axial stress formula \(σ=\frac{P}{A}=\frac{P}{bt}⟶t=\frac{P}{b-σ_{allowable }}\) t = \(\frac{120000}{40-155}=\frac{120000}{6200}=19.35≈19.4 mm\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 40 | A symmetrical T-section has its flange horizontal on top. Its dimensions are: Flange: Width = 100 mm, thickness = 24mm ; Web: Height = 84 mm, thickness = 20 mm. Its moment of inertia about a vertical axis through its centroid parallel to the web is (in mm4) | 431 104 \(×\) | 2056 103 \(×\) | 384,0000 | 451 104 \(×\) | b | The section is divided into: 1. Flange (top part): Width = 100mm , Thickness = 24mm 2. Web (vertical part): Height = 84mm . Thickness = 20mm Step 2: Calculate moment of inertia for each part The moment of inertia for a rectangle about its centroidal axis is: I = \(\frac{bh^{3}}{12} \) Flange: Iflange = = 2,000,000 mm4 \(\frac{24 ×100^{3}}{12}\) Web: Iweb = = 56,000 mm4 \(\frac{84 ×20^{3}}{12}\) Step 3: Sum the contributions Since the centroids of both parts align with the global centroid (due to symmetry), their individual moments of inertia can be directly added: Iyy = Iflange + Iweb = 2,000,000 + 56, 000 = 2,056,000 mm4 Moment of inertia about the vertical centroidal axis = 2056 \(×10^{3}mm^{4}\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 41 | Impact strength is usually measured in units of: | Pascals | Newtons | Watts | Joules | d | Impact strength measures the energy absorbed by a material during fracture under sudden impact. Energy is measured in Joules (J). Pascals measure stress/pressure, Newtons measure force, Watts measure power. |
Comments | Active | |
| 42 | Which of the following is used in organic coating as catalysts that speed up the cure reaction? | Plasticisers | Cure additives | Colloidal stabilisers | UV stabilisers | b | Cure additives act as catalysts in organic coatings. They accelerate the chemical reaction (curing) that hardens the coating. Plasticisers make coatings more flexible but don’t speed up curing. Colloidal stabilisers prevent pigment settling. UV stabilisers protect coatings from ultraviolet light degradation. |
Comments | Active | |
| 43 | In a dry sump lubrication system, how is oil returned to the storage tank? | Oil remains in the engine block indefinitely. | Gravity drains oil directly to the crankcase. | A scavenge pump actively pumps oil back. | Centrifugal force separates oil from air. | c | In a dry sump lubrication system, oil does not just drain by gravity. Instead, scavenge pumps actively collect oil from the crankcase and return it to the external storage tank. This ensures continuous oil circulation and prevents oil starvation during high-speed. Unlike wet sump systems, oil is stored outside the engine. |
Comments | Active | |
| 44 | The creep rate in a material increases when: | stress is increased | alloying elements are removed | the material is stretched | the temperature is decreased | a | Creep is the time-dependent plastic deformation of a material under constant load or stress, typically at high temperature. Increasing the applied stress increases the creep rate because it promotes dislocation movement and diffusion mechanisms. Removing alloying elements usually decreases creep resistance, but the direct effect on creep rate depends on the alloy. Stretching the material is basically applying stress, but the key factor is stress itself. Creep rate increases with temperature, not decreases. |
Comments | Active | |
| 45 | Despite having the highest possible efficiency for Carnot cycle, it is not suitable for a practical engine using a gaseous working fluid as: | the work output from the cycle is quite low | it is easy to maintain isothermal processes in practice | it is impossible to achieve perfectly reversible processes | the cycle requires very high pressures that are hard to manage | c | The Carnot cycle assumes ideal, reversible processes, but in reality, perfect reversibility can’t be achieved because of friction, unrestrained heat transfer, and other irreversibilities. | Comments | Active | |
| 46 | Why is the concept of transmissibility of forces valid for a rigid body? | Because forces always act in the direction of motion | Because internal forces in a rigid body do not exist | Because a rigid body does not deform under applied forces | Because a rigid body always has an infinite number of forces acting on it | c | PRINCIPLE OF TRANSMISSIBILITY OF FORCES: It states, "If a force acts at any point on a rigid body, it may also be considered to act at any other point on its line of action, provided this point is rigidly connected with the body." Option c will be correct ans. Remid it: Rigid means – change in deformation is zero that means change in volume = 0 |
Comments | Active | |
| 47 | In which type of welding flame is oxygen proportion more compared to acetylene proportion? | Carburising welding flame | Reducing welding flame | Neutral welding flame | Oxidising welding flame | d | In oxidising flame, the oxygen-to-acetylene ratio is greater than 1, meaning excess oxygen is present. This flame has a short, sharp, and hissing inner cone. It burns at a higher temperature (~3500°C). Commonly used for welding brass, copper, and mild steel (when oxide formation is not an issue). |
Comments | Active | |
| 48 | In a battery or coil ignition system, what is the role of the ignition coil? | To compress the air entering the combustion chamber | To regulate the fuel injection timing | To control the engine's exhaust temperature | To transform the low battery voltage into a high voltage required for spark generation | d | In a battery or coil ignition system, the ignition coil acts as a step-up transformer. Its function is to: Convert the 12V battery voltage Into a high voltage (typically 15,000 to 40,000 volts) Which is necessary to produce a spark across the spark plug gap That spark then ignites the air-fuel mixture in the combustion chamber |
Comments | Active | |
| 49 | Which of the following is the primary element that supports the workpiece in centerless grinding? | Work test blade | Pressure roller blade | Stationary table | Work rest blade | d | As you can observe in the below diagram that workblade is supporting to the workpiece as primary element.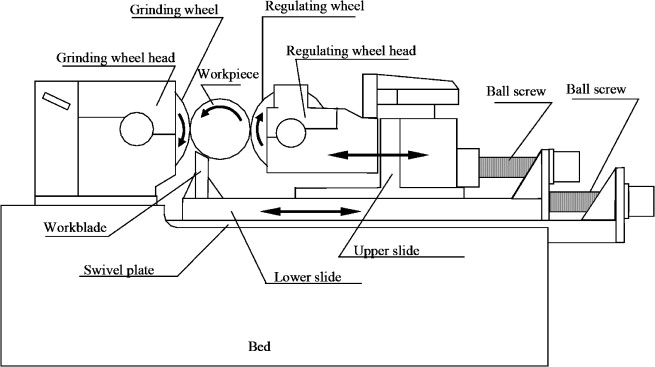 |
Comments | Active | |
| 50 | If two forces act at a right angle (90°), what will be the magnitude of their resultant force? | R = \(F12+F22\) | R = F1 + F2 | R = 2F1F2cos \(θ\) | R = F1 – F2 | a | R = \(F_{1}^{2}+F_{2}^{2}+2F_{1}F_{2} cosθ\) Given = 90 , = 0 \(θ\) \(°\) \(cos90\) R = \(F12+F22\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 51 | Which of the following is considered a primary output report from Material Requirements Planning? | Exception reports | Planning reports | Performance control reports | Planned order schedule | d | In Material Requirements Planning (MRP), the primary outputs are those that directly drive production and purchasing activities. The most important among them is the: Primary Outputs of MRP include: Planned Order Releases (Schedules) Order Rescheduling Notices Work Orders and Purchase Orders |
Comments | Active | |
| 52 | Specific volume of a fluid is the reciprocal of its ______. | mass density | viscosity | dynamic viscosity | surface tension | a | Density /mass density / specific mass ( ) = = = \(Ï\) \(\frac{mass}{volume}\) \(\frac{1}{\frac{volume}{mass}}\) \(\frac{1}{specific mass}\) So Specific volume of a fluid is the reciprocal of its mass density. |
Comments | Active | |
| 53 | Which welding process is NOT classified under arc welding processes? | Electroslag Welding | Stud Arc Welding | Tungsten Inert Gas Welding | Atomic Hydrogen Welding | * | No option is correct here (Reference: A textbook of production technology by P.C. Sharma –page no.-348) Types of Electric Arc Welding Processes. The common electric arc welding processes are: 1. Carbon Arc Welding 2. Shielded Metal Arc Welding 3. Flux Cored Arc Welding 4. Gas Metal Arc Welding 5. Gas Tungsten -Arc welding 6. Submerged Arc Welding 7. Atomic Hydrogen Welding 8. Plasma Arc welding 9. Stud welding 10. Electro Slag welding. |
Comments | Active | |
| 54 | What is the number of divisions on the Vernier scale of a Universal Bevel Protractor? | 60 | 70 | 24 | 46 | c | The Universal Bevel Protractor is a precision instrument used to measure angles very accurately. It has: A main scale graduated in degrees (usually 0° to 360°) A Vernier scale to allow readings with a least count of 5 minutes (5') The Vernier scale typically has 24 divisions, which span 23 degrees on the main scale. Each Vernier division = 23° / 24 = 57.5 minutes Since each main scale division = 1°, the difference between 1° and 57.5' gives a least count of 2.5' or 5', depending on the design. Thus, 24 divisions is standard for most bevel protractors used in precision work. |
Comments | Active | |
| 55 | What distinguishes a semi-open impeller from an open impeller? | A semi-open impeller is completely enclosed by a casing. | A semi-open impeller has vanes on both sides. | A semi-open impeller has a partial shroud on one side. | A semi-open impeller lacks any vanes. | c | Semi open impeller or non-clog pump: This pump is used for viscous liquids such as sewage water. In order to minimize the chance of impeller getting clogged, the number of varies is reduced and their height is increased. Open impeller pump: The impeller is not provided with any shroud or Plate. Such pumps are used for handling mixtures of water, sand, pebbles and clay etc. |
Comments | Active | |
| 56 | Which of the following is NOT a mechanical finishing process? | Pickling | Shot peening | Burnishing | Buffing | a | Pickling process is used to remove hard scale from the surface of the forgings. It consists of immersing the forgings in a tank filled with an acid solution, which is 12 to 15% concentrate of sulphuric acid in water. The solution acts to loosen the hard scale from the forging surface and remove it. The acid solution should not react with the clean metal while removing the scale. For this, an inhibitor agent is added to the acid solution. Remind It: Shot peening is a mechanical finishning process. ( Reference for shot peening :- DeGarmo's Materials and Processes in Manufacturing By J. t black & Ronald A. kohser -edition -2018- Chapter -34 - Page no.-723) Shot peening is mainly employed to increase the fatigue strength of work pieces subjected to impact and/or fatigue loads (parts made of steel and non-ferrous alloys), and also for strengthening welds. Typical applications include:- Coil springs, leaf springs, gear wheels and other complex parts. The other functions of shot peening are to prevent the cracking of work pieces in corrosive media and to improve the oil retaining properties of the processed surfaces. (Reference: A textbook of production technology by P.C. Sharma –page no.-313) |
Comments | Active | |
| 57 | A bench mounted drilling machine is of the same type as a _______. | deep hole drilling machine | gang drilling machine | radial drilling machine | sensitive drilling machine | d | A bench-mounted drilling machine is typically a small, manually operated machine used for light-duty drilling tasks. It is: Mounted on a workbench or table Operated by hand feed Used for small holes in light materials (e.g., in sheet metal or plastics) Requires the operator to "feel" the feed — hence the name "sensitive drilling machine" That’s why it is classified as a sensitive drilling machine. |
Comments | Active | |
| 58 | In drilling operations, a coolant is used to ______. | reduce durability of drill bit | heat the drill bit | cool down the drill bit | clean the drill bit | c | The primary work of coolant in drilling operation is to cool down the drill bit. It also fulfil the purpose of cleaning also but its secondary. Option c will be correct answer here. | Comments | Active | |
| 59 | What is meant by the resolution of a force? | Reducing the magnitude of a force in a given direction | Combining multiple forces to form a single resultant | Splitting a force into components without changing its effect | Changing the direction of a force without altering magnitude | c | Resolution of Forces: - Splitting a force into components without changing its effect.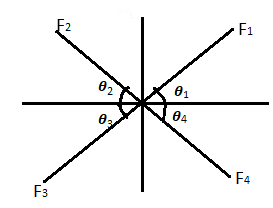 \(F_{H}=F_{1}Cosθ_{1}+F_{4}Cosθ_{4}-F_{2}Cosθ_{2}-F_{3}Cosθ_{3}\) \(F_{V}=F_{1}sinθ_{1}+F_{2}sinθ_{2}-F_{3}sinθ_{3}-F_{4}sinθ_{4}\) ; \(R=(F_{H})^{2}+(F_{V})^{2}\) \(tan∅=\frac{F_{V}}{F_{H}}\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 60 | Which cooling method is used in full annealing? | Cooling in an oil bath | Air cooling | Slow cooling inside a furnace | Quenching in water | c | Full annealing is a heat treatment process used to soften ferrous metals (typically steel), relieve internal stresses, and improve ductility and machinability. Heat the metal to above its upper critical temperature (for steel, typically 30–50°C above A₃ or A₠lines). Hold at that temperature to allow complete transformation. Cool slowly, typically inside the furnace — this is called furnace cooling. This very slow cooling allows the formation of coarse pearlite or ferrite-pearlite structure, resulting in a softer and more ductile material. |
Comments | Active | |
| 61 | Identify the class A items as per the ABC analysis in inventory. | The next 15-25% account for 10-20% of the consumption | The balance 65-75% account for 70-80% of the consumption | 10-20% of the items account for 70-80% of the consumption | The balance 65-75% account for 5-10% of the consumption | c | ABC Analysis: A Items =70-80% of the total inventory consumption, 10% of the total items. B Items =30-40% of the total inventory consumption, 30-40% of the total items. C Items =10-5% of the total inventory consumption, 70% of the total items. |
Comments | Active | |
| 62 | Soldering is a _______ temperature. similar or dissimilar metals by heating them to a required | method of joining | method of boring | method of cooling | method of cutting | a | Soldering is a low-temperature metal joining process used to bond similar or dissimilar metals by melting a filler metal (solder) which has a melting point below 450°C. The base metals are not melted; only the solder melts and flows into the joint by capillary action. It is commonly used in electronics, plumbing, and sheet metal work. |
Comments | Active | |
| 63 | A cantilever beam with a span length of L m carries a uniform moment of intensity 'M' N-m/m. Which of the following statements is correct? | Shear force throughout the length will be M/L. | Shear force throughout the length will be zero. | Shear force throughout the length will be ML/ (b) | Shear force throughout the length will be ML. | b | A uniform moment distributed along a beam does not cause any shear force. This is because shear force is caused by variations in bending moment along the length. |
Comments | Active | |
| 64 | In gas welding process, gas pressure regulators are employed for | increasing the oxygen and acetylene mixture pressure | igniting the welding torch | reducing the pressure of acetylene and oxygen gas from the cylinders to working pressure | mixing oxygen and acetylene thoroughly | c | In gas welding (like oxy-acetylene welding), gases are stored in cylinders under high pressure: Oxygen cylinders: up to 150–200 bar Acetylene cylinders: up to 15 bar These pressures are too high for direct use at the welding torch. Therefore, gas pressure regulators are used to: Reduce the high pressure of the gases from the cylinders Deliver the gases at safe and controllable working pressure (usually 0.1–2 bar depending on the process) |
Comments | Active | |
| 65 | Class ______ items are those that are 30-40% of all inventory items, and account for 30-40% of the total rupee consumption volume of the inventory. These are important, but not critical, and do NOT pose sourcing difficulties. | B | X | C | A | a | ABC Analysis: A Items =70-80% of the total inventory consumption, 10% of the total items. B Items =30-40% of the total inventory consumption, 30-40% of the total items. C Items =10-5% of the total inventory consumption, 70% of the total items. |
Comments | Active | |
| 66 | In four-stroke diesel engine, which valves are closed during the expansion stroke? | Only the inlet valve | Both inlet and exhaust valves | Only the exhaust valve | Neither inlet valve nor exhaust valve | b | In a four-stroke diesel engine, the expansion stroke (also called the power stroke) occurs after combustion, when the fuel-air mixture burns and forces the piston downward. During this stroke: The inlet valve is closed to prevent fresh air from entering. The exhaust valve is also closed to keep combustion gases inside until the stroke is complete. This ensures maximum pressure is applied to the piston for effective power output. |
Comments | Active | |
| 67 | If torsional rigidity increases in the torsion equation, then the: | angle of twist decreases | angle of twist first increases then decreases | angle of twist increases | angle of twist remains constant | a | TORSION EQUATION: \(\frac{T}{J}=\frac{τ}{R}=\frac{Cθ}{l}\) T = Twisting momentJ = Polar moment of Inertia = Shear stressR = Radius of shaft C = Modulus of Rigidity = Angle of twist l = length of shaft \(=\frac{πD^{4}}{32}\) \(τ\) \(θ\) : \(Torsional rigidity(CJ)\) \(Torsional rigidity=\frac{T×l}{θ}\) So, torsional rigidity increases in the torsion equation, then the angle of twist decreases |
Comments | Active | |
| 68 | Which of the following is NOT an angular measurement device? | Autocollimator | Sine Bar | Spirit Level | Digital Micrometer | d | Autocollimator: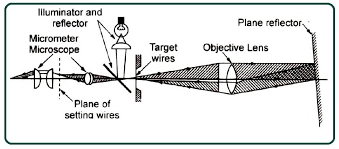 Optical precision instrument basically it measure small tilt angle also check angular deflection Measure flatness and straightness of surface Sine Bar:  Angle is measured indirectly = \(θ\) \(sin^{-1}\frac{h}{l}\) Spirit Level : Spirit levels are used for measuring small angle or inclinations and also enable the position of a surface to be determined with respect to the horizontal. A spirit level consists of a sealed glass tube, ground on its inside surface to a convex form with a large radius of curvature R. A scale is engraved on the glass at the top of the tube.  Digital Micrometer: It’s a linear measurement device not used for angular measurement. Digital Micrometer will be correct answer of this question.  |
Comments | Active | |
| 69 | In a two-stroke petrol engine, which of the following best describes the sequence of events during an exhaust stroke? | Both ports open simultaneously. | The exhaust port opens first, followed by the transfer port. | The exhaust port opens and closes before the transfer port opens. | The transfer port opens first, followed by the exhaust port. | b | In a two-stroke petrol engine, the sequence during the exhaust stroke is critical for efficient scavenging (removal of exhaust gases and filling with fresh charge). Exhaust port opens first: Exhaust gases start to leave the cylinder, reducing pressure inside. Transfer port opens next: Fresh air-fuel mixture from the crankcase enters the cylinder to push out remaining exhaust gases. This overlap helps in scavenging, but the exhaust port must open first to avoid pushing fresh charge directly out. |
Comments | Active | |
| 70 | In a profile projector, the magnified image of the workpiece is created by: | condenser lens | projection lens | mirrors | a Vernier micrometer | b | In a profile projector (optical comparator), the workpiece’s shadow or profile is magnified to allow precise measurement and inspection. The projection lens is responsible for forming the magnified image of the workpiece onto the viewing screen. The condenser lens illuminates the workpiece but does not form the image. Mirrors are generally used to direct light but do not magnify. Vernier micrometer is a measuring instrument, not part of the optical system creating the image. |
Comments | Active | |
| 71 | The structured list of components and sub-assemblies needed to manufacture a final product is represented by the: | lead time | bill of materials | components directory | master file | b | A Bill of Materials (BOM) is a structured list that details all the components, sub-assemblies, raw materials, and quantities required to manufacture a final product. It acts as a recipe or parts list for production and procurement. BOM is essential for inventory control, production planning, and cost estimation. |
Comments | Active | |
| 72 | Inventory control begins with ______ analysis, a fundamental supply chain activity frequently performed by inventory controllers and materials managers. | FSN | VED | ABC | ΧΥΖ | c | ABC Analysis: A Items =70-80% of the total inventory consumption, 10% of the total items. B Items =20-15% of the total inventory consumption, 15-20% of the total items. C Items =10-5% of the total inventory consumption, 70% of the total items. |
Comments | Active | |
| 73 | What is the primary function of the headstock in a lathe machine? | To provide support for cutting tools during operation | To control the movement of the carriage and tailstock | To hold and rotate the workpiece at different speeds | To adjust the feed mechanism for thread-cutting | c | the primary function of the headstock in a lathe machine is to hold and rotate the workpiece at different speeds. |
Comments | Active | |
| 74 | Intensity of radiation varies with the: | fourth power of the distance | cube of the distance | square of the distance | inverse square of the distance | d | The inverse square law is a physical principle that describes how the intensity of a physical quantity (such as radiation, light, sound, etc.) decreases as the distance from the source increases. According to this law, the intensity of radiation is inversely proportional to the square of the distance from the source. Mathematically, it can be expressed as: I \(âˆ1/d^{2}\) Where: I = Intensity of radiation d = Distance from the radiation source |
Comments | Active | |
| 75 | A built-up section is made by joining two equal I-sections at the flanges at their outer faces so that the composite consists of one I-section above the other. The moment of inertia of each section through a centroidal axis parallel to the web is I yy The moment of inertia of the composite built-up section about a similar axis is: | \(\frac{I_{yy}}{2}\) | 2Iyy | Iyy | 4lyy | b | A built-up section formed by placing two equal I-sections one above the other has its moment of inertia about an axis parallel to the web calculated by summing the individual moments of inertia of the sections (when the axis remains unchanged). Given: Each section has a moment of inertia = lyy Axis of interest is parallel to the web (horizontal) Calculation: Since the axis is at the same level and passes through the centroid of each I-section in the same direction: Itotal = Iyy + Iyy = 2Iyy |
Comments | Active | |
| 76 | Which of the following is a key advantage of CNC lathes in turning operations? | They are less accurate than conventional chucking machines. | They rely mainly on mechanical devices for control. | They provide higher automation and complex machining cycles. | They are limited to simple machining operations. | c | CNC Lathes: Computer Numerical Control (CNC) lathes are advanced machine tools controlled by computer programs. They enable automation of machining processes. Capable of performing complex machining cycles with high precision and repeatability. Allow for multi-axis control and interpolation to create intricate shapes. Improve productivity by reducing manual intervention and setup times. |
Comments | Active | |
| 77 | What is the function of a shank in a broaching machine? | Removes chips and coolant from the cutting area | Breaks up the chips generated during the broaching process | Holds the broach in place and gives it a rotary motion | Guides the broach through the material and maintains tool alignment | d | Function of a shank in a broaching machine is to Guides the broach through the material and maintains tool alignment. |
Comments | Active | |
| 78 | The sensing element in the Tomlinson Surface Meter is _______. | rollers | springs | the stylus | the shoe | c | The sensing element in the Tomlinson Surface Meter is stylus. |
Comments | Active | |
| 79 | If a pump's theoretical manometric head is 30 metres and its measured head is 27 metres, what is its manometric efficiency? | 80% | 85% | 75% | 90% | d | Manometric Efficiency (ηm ): It is the ratio of the manometric head to head imparted by the impeller to the water. ηm = = 0.9 = 90 % \(\frac{27}{30}\)  |
Comments | Active | |
| 80 | Atmospheric pressure is: | the pressure exerted by the Earth's atmosphere at any given point | the pressure inside a fluid container | the pressure difference between two fluids | the pressure of a vacuum | a | Atmospheric pressure is the pressure exerted by the Earth's atmosphere at any given point | Comments | Active | |
| 81 | Which of the following is the correct sequence for the IS specification of any Grinding wheel? | Abrasive used - Structure - Grade - Grit number - Bond Type | Abrasive used - Grit number - Structure - Grade - Bond Type | Abrasive used - Grit number - Grade - Structure - Bond Type | Abrasive used - Grade - Structure - Grit number - Bond Type | c | Standard marking of Grinding Wheel: All grinding wheels are marked. Markings in the form of conventional designations are applied with an indelible paint to the wheel flat surface. The marking indicates the manufacturer, abrasive material, its grain size, grade, structure, bond type etc. (Reference : A Textbook of Production Technology by P.C.Sharma- page No.-536) |
Comments | Active | |
| 82 | A simply supported beam with a span length of 4 m carries a uniform load of intensity 5 N/m throughout its length. What will the value of the maximum bending moment (in N-m) in the beam be? | 20 | 4 | 0 | 10 | d | maximum bending moment for simply supported beam carrying udl, \(M_{max}=\frac{WL^{2}}{8}=\frac{5×4×4}{8}=10Nm\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 83 | Relative efficiency of an engine is defined as the ratio of: | actual thermal efficiency to Carnot efficiency | actual thermal efficiency to air-standard efficiency | mechanical efficiency to volumetric efficiency | brake thermal efficiency to indicated thermal efficiency | b | \( η_{rel} =\frac{actual thermal efficiency}{air standard efficiency}\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 84 | The main objective of the sequencing problem in production is to: | ignore the order of job processing | minimise the idle time of machines | maximise the number of jobs processed | increase the processing time of jobs | b | The main objective of the sequencing problem in production is to minimise the idle time of machines .When number of jobs are waiting in queue before an operational facility (such as, a milling machine), there is a need to decide the sequence of processing all the waiting jobs. Sequencing is basically an order in which the jobs, waiting before a operational facility, are processed. For this, priority rule, processing time, etc., are needed. | Comments | Active | |
| 85 | Which of the following expressions can determine the longitudinal feed rate in "Through Feed Centreless Grinding"? (If the diameter of the regulating wheel = D, r.p.m. of the regulating wheel = N, angle of inclination of the regulating wheel = 0) |
Longitudinal feed rate = [ D N] / Cos () \(π\) \(×\) \(×\) \(θ\) | Longitudinal feed rate = D N Sin () \(π×\) \(×\) \(×\) \(θ\) | Longitudinal feed rate = [ D N] / Sin () \(π\) \(×\) \(×\) \(θ\) | Longitudinal feed rate = D N Cos (θ) \(π× \) \(×\) \(×\) | b | In Through Feed Centreless Grinding, the longitudinal feed rate of the workpiece is controlled by the regulating wheel which is inclined at an angle θ to the axis of the workpiece. The regulating wheel rotates at speed N (rpm) with diameter D. The linear surface speed of the regulating wheel is: V=π×D×N Due to the inclination angle θ of the regulating wheel, the component of this speed along the axis (longitudinal feed direction) is: \(V_{feed}=V×sinθ=πDNsinθ\) Thus, the longitudinal feed rate is given by option (b). |
Comments | Active | |
| 86 | For a closed system undergoing a thermodynamic cycle, the first law states which of the following? | Net work done equals net heat transfer. | Pressure and temperature are inversely related. | Entropy always increases. | Internal energy remains constant | a | For a closed system undergoing a thermodynamic cycle, the first law of thermodynamics (energy conservation) states: ΔU=Q−W Where: ΔU = change in internal energy Q = heat added to the system W = work done by the system Since it’s a cycle, the system returns to its initial state, so: ΔU=0 Therefore, Q=W Which means the net heat transfer to the system equals the net work done by the system over a cycle. |
Comments | Active | |
| 87 | What should be the included angle of the cutting tool used for machining metric threads in a thread-cutting operation? | 60 degrees | 55 degrees | 45 degrees | 75 degrees | a | The Bureau of Indian Standards has adopted a unified screw thread profile based on the metric system as the standard thread profile for use in India and designated it as the Metric Screw Thread. It also recommends the pitch of the thread instead of threads per inch as one of the standard parameters in specifying a screw thread. Metric threads are specified in a drawing by the letter M followed by the nominal size (Basic Major Diameter) and pitch. both expressed in millimetres. The included angle of the cutting tool used for machining metric threads in a thread-cutting operation is 60°. |
Comments | Active | |
| 88 | One design advantage of a single volute casing is that: | it simplifies the manufacturing process | it allows for multiple impeller stages | it minimises hydraulic losses by equalising pressure distribution | it provides balanced radial forces | a | A single volute casing in a centrifugal pump is a spiral-shaped casing that collects fluid from the impeller and directs it to the discharge nozzle. It is the most basic and commonly used casing design, especially in low to medium duty pumps. Design Advantages of Single Volute Casing: Simple geometry: Easier to design and fabricate. Lower manufacturing cost: Due to single spiral passage and fewer components. Compact design: Suitable for smaller pumps. |
Comments | Active | |
| 89 | Brazing is a process of _______ metals without melting the base metal. | drilling | joining | cutting | melting | b | Joining Processes. Here, two or more components are joined together to produce the required product. The category includes : all the welding processes, brazing, soldering, diffusion bonding, riveting, bolting, adhesive bonding etc. ( Reference – A textbook of Production Technology by P.C.Sharma – Page No.-2) |
Comments | Active | |
| 90 | Which of the following best describes the strength of mild steel compared to alloy steel? | Alloy steel generally has higher strength than mild steel. | Mild steel is stronger in compression but weaker in tension than alloy steel. | Both mild steel and alloy steel have the same strength. | Mild steel generally has higher strength than alloy steel. | a | Mild Steel: Also called low carbon steel, typically contains 0.15–0.30% carbon. It is ductile, tough, weldable, and low in strength compared to alloy steels. Ultimate tensile strength (UTS): ~400–550 MPa Alloy Steel: Contains additional elements such as chromium, nickel, molybdenum, vanadium, etc. These elements improve strength, hardness, toughness, and resistance to wear and corrosion. Alloy steels are engineered for higher mechanical properties. UTS can exceed 700–2000+ MPa, depending on the type and treatment. |
Comments | Active | |
| 91 | In a modern optical measuring microscope, the 'cross-wires' are: | located on the surface of the workpiece | located on the objective lens | etched on glass within the eyepiece | located on the XY stage | c | In a modern optical measuring microscope, the 'cross-wires' are indeed etched on glass within the eyepiece. This design allows for precise and accurate measurement and alignment. The eyepiece, also known as the ocular lens, is the part of the microscope that you look through to see the magnified image of the specimen. Within the eyepiece, a reticle (or graticule) is etched on a piece of glass. This reticle usually consists of cross-wires or a grid, which helps in measuring and positioning the specimen accurately. Having the cross-wires etched on glass within the eyepiece offers several advantages: Precision: The etched reticle provides a fixed reference point, ensuring that measurements are consistent and precise every time. Durability: The reticle is protected within the eyepiece and is less prone to damage or wear compared to other locations. Ease of Use: The user can easily align and measure the specimen without any additional setup, as the cross-wires are always in view when looking through the eyepiece. The reticle's design can vary depending on the microscope's intended use. For instance, some reticles may feature a simple cross-hair design, while others might have a more complex grid or scale pattern for detailed measurements. |
Comments | Active | |
| 92 | For a thin planar ring of radius 'r' mm and thickness’t’ mm, its radius of gyration about the polar axis in mm is: | 2r | г | r/t | г/2 | b | For a thin planar ring (like a hoop) of radius r, the polar moment of inertia about the axis perpendicular to the plane of the ring and passing through its center (i.e., the polar axis) is: \(I=mr^{2}\) The radius of gyration k about this axis is defined as: \(I=mk^{2}, k=\frac{mr^{2}}{m}=r\) So, the radius of gyration is: k=r |
Comments | Active | |
| 93 | Among the following, which beam can be classified as a statically indeterminate beam? | Simply supported beam | Overhanging beam | Cantilever beam | Fixed beam | d | A statically indeterminate beam is one in which the number of unknown support reactions exceeds the number of independent equilibrium equations (which are 3 for a planar system: ∑Fx=0 ∑Fy​=0, ∑M=0 Statically indeterminate — has two fixed supports, resulting in 6 unknown reactions (3 at each support: vertical force, horizontal force, and moment). Only 3 equations of equilibrium are available ⇒ indeterminate to 3 degrees. |
Comments | Active | |
| 94 | The vaned diffuser in a centrifugal pump serves to: | accelerate the fluid | reduce cavitation by increasing turbulence | convert kinetic energy into pressure energy | control the pump's rotational speed | c | Diffuser pump or turbine pump: In this type of casing, there are guide blades surrounds the impeller. These guide blades are arranged at such an angle, so that the water enters without shock and forms a passage of increasing area, thus reducing the velocity of flow and consequently the pressure is built up. The ring of the guide blades is called diffuser and is very efficient. This type of pump is used in all multi-stage pump. |
Comments | Active | |
| 95 | Which of the following assumptions is essential for applying Bernoulli's theorem? | The flow is steady, incompressible and frictionless. | The flow is turbulent and rotational. | The fluid is viscous and incompressible. | The fluid has high compressibility | a |  |
Comments | Active | |
| 96 | Which of the following hardness scales uses a diamond cone indenter? | Vickers scale | Brinell scale | Mohs scale | Rockwell C scale | d | Rockwell hardness test: Rockwell hardness testers use a number of indenters in combination with a variety of loads. It has 1/16, 1/8, 1/4, 1/2 inch diameter spherical steel indenter as well as conical diamond indenter which is used for the hardest material. Each of the indenters can be used with a major load of 60, 100, or 150 kg, and a minor load of 10 kg. The hardness number is the difference between the penetrations caused by major and minor load applications. Based on these load and indenters scales are developed, Rockwell A scale, 60 kg with diamond indenter is used for steels and similar hard alloys. Rockwell B scale, 100 kg with 1/16 inch diameter sphere indenter are used for aluminum alloys/steel. Rockwell C scale, 150 kg with the diamond pyramid indenter are used for steel and similar hard alloys. Copper alloys are measured in k scales. Polymers are measured in the Rockwell E and M scales. M scales are used for hard polymers. |
Comments | Active | |
| 97 | Pressure head in a fluid system is best described as: | the kinetic energy per unit weight of the fluid | the rate of fluid flow per unit cross-sectional area | the difference between absolute and gauge pressure | the height of a fluid column equivalent to the pressure exerted | d | Pressure head is defined as the height of a column of fluid (usually in meters) that would produce a given pressure at its base due to the fluid’s weight. Pressure Head=P/Ï g ​ Where: P = Pressure (Pa or N/m²) Ï = Density of fluid (kg/m³) g = Acceleration due to gravity (9.81 m/s²) It represents the potential energy of the fluid due to pressure and is usually measured in meters of fluid. |
Comments | Active | |
| 98 | Which of the following is an example of forced convection? | Warm air naturally rising from a hot surface | Air blown over a car radiator by a fan | Thermal energy transmitted by electromagnetic waves | Heat transfer through a stationary fluid layer | b | Forced convection occurs when a fluid is made to flow over a surface or in a tube by external means such as a pump, fan, or blower, thereby enhancing heat transfer. In option (b), the fan forces the air to move over the radiator, thus clearly representing forced convection. |
Comments | Active | |
| 99 | Why does cast iron have high compressive strength but low tensile strength? | Due to its high malleability | Due to its ductile nature | Due to the presence of graphite flakes | Due to its elastic properties | c | Cast iron is a Brittle material and having good damping property due to which it is used as base structure in machine to damp vibration in ground .As we know that brittle material having good compressive strength and when we talk about brittleness of cast iron, it is due to presence of carbon that present in form of graphite flakes. So option c will be correct answer. | Comments | Active | |
| 100 | Which of the following is the correct rule when selecting a Grinding Wheel? | Fine finish needs open structure | Hard wheel for hard metal and soft wheel for soft metal | Close structure for ductile and soft material | Soft wheel for hard metal and hard wheel for soft metal | d | The harder the metal being ground, the softer the wheel should be, and vice versa, since in grinding a hard metal the grains will wear more intensively and be broken out of the wheel more readily to expose new sharp grains. So, choose a hard-grade wheel for soft materials and a soft grade wheel for hard materials. (Reference – A textbook of Production Technology by P.C.Sharma – Page No.-538) |
Comments | Active |










