| S.No | Question | Option A | Option B | Option C | Option D | Answer | Solution | Comments | Status | Action |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Two shafts are connected by a belt and D1 is diameter of the pulley on shaft A, N1 is the speed (rpm) of shaft A, D2 is the diameter of the pulley on shaft B, and N2 is the speed (rpm) of shaft (B) which of the following is true | \(\frac{N_{2}}{N_{1}}=\frac{D_{1}}{D_{2}}\) | \(\frac{N_{2}}{N_{1}}=\frac{D_{2}}{D_{1}}\) | \(\frac{N_{2}}{D_{2}}=\frac{N_{1}}{D_{1}}\) | \(N_{2}D_{1}=N_{1}D_{2}\) | a | \(\frac{N_{2}}{N_{1}}=\frac{D_{1}}{D_{2}}\) | Comments | Active | |
| 2 | In a machine if ‘M’ is the mechanical advantage and ‘V’ is the velocity ratio, then the efficiency of the machine is given by: | \(\frac{V}{M}\) | \(MV^{2}\) | VM | \(\frac{M}{V}\) | d | \(η=\frac{Mechanical Advantage }{Velocity Ratio }\) | Comments | Active | |
| 3 | Maximum efficiency of a screw jack for angle of friction is \('∅'\) | \(\frac{1-sin∅}{1+sin∅}\) | \(sin∅\) | \(\frac{1-sin∅}{sin∅}\) | \(\frac{sin∅}{1+sin∅}\) | a | Maximum efficiency of screw jack \(η_{max}=\frac{1-sin∅}{1+sin∅}\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 4 | When a body slides down on an inclined surface, the acceleration of body is given by: | a = g | a = g sin \(θ\) | \(a=gcosθ\) | \(a=gtanθ\) | b |  You can see F = \(mgsinθ\) ma = mgsin \(θ\) \(a=gsinθ\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 5 | Moment of inertia of a circular area where diameter is ‘d’ , about an axis perpendicular to area passing through centre is given by: | \(\frac{πd^{4}}{64}\) | \(\frac{πd^{4}}{32}\) | \(\frac{πd^{4}}{16}\) | \(\frac{πd^{4}}{24}\) | b | it will be polar moment of inertia for given circle. \(Izz=\frac{πd^{4}}{32}\) \(I_{xx}+I_{yy}=I_{zz}, I_{xx}=I_{yy}=\frac{πd^{4}}{64}\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 6 | Ratio of limiting friction and normal reaction is known as: | Coefficient of friction | Angle of friction | Angle of repose | Sliding friction | a | Coefficient of friction (COF) is a dimensionless number that is defined as the ratio between friction force and normal force | Comments | Active | |
| 7 | The resultant of two forces P & Q inclined at an angle ‘ will be inclined at following angle with respect to P: \(θ'\) | \(tan^{-1}(\frac{Qsinθ}{P+Qcosθ}) \) | \(tan^{-1}(\frac{Psinθ}{Q+Pcosθ})\) | \(tan^{-1}(\frac{Qcosθ}{Q+Psinθ})\) | \(tan^{-1}(\frac{Pcosθ}{(Q+Psinθ)})\) | a | \(tanθ=\frac{Qsinθ }{P+Qcosθ}\) | Comments | Active | |
| 8 | The ratio of hoop stress to longitudinal stress in thin cylinder is: | 1 | 1/2 | 2 | 1/4 | c | Hoop stress = Pd/2t Longitudinal Stress = Pd/4t \(\frac{σ_{h}}{σ_{L}}=2:1 \) |
Comments | Active | |
| 9 | Mohr’s circle can be used to determine the following stress. | Normal stress | Principal stress | Tangential stress | all of the above | d | Mohr's circle is very useful in determining the relationships between normal and shear stresses acting on any inclined plane at a point in a stressed body. It is helpful in finding maximum and minimum principal stresses, maximum shear stress, normal stress etc. | Comments | Active | |
| 10 | The torque that a clutch can transmit depends on: | Contact surfaces | Friction force | Spring force | all of the above | d | The torque capacity of a clutch depends on a series of factors:i. Total area of the friction surfaceii. Friction coefficientiii. Normal force acting on the clutchiv. Number of friction elements | Comments | Active | |
| 11 | Which of the following is a lower pair? | Ball and socket | Piston and cylinder | Cam and follower | Both a and b | d | Lower pair: Ball and socket joint, piston and cylinder Higher pair: Cam and follower |
Comments | Active | |
| 12 | A slider crank chain consists of following numbers of turning and sliding pairs | 1, 3 | 2,2 | 3, 1 | 4, 0’ | c | A slider crank chain consists of 3 turning and 1 sliding pair. | Comments | Active | |
| 13 | To transmit from one rotating shaft to another whose axes are neither parallel nor intersecting, use? | Spur gear | Spiral gear | Bevel gear | Worm gear | d | Worm gears are power-transmission components primarily used as high-ratio reductions to change the direction of shaft rotation and to decrease speed and increase torque between non-parallel rotating shafts. They are used on shafts with non-intersecting, perpendicular axes. | Comments | Active | |
| 14 | Purpose of using differential gear in an automobile is to: | Control speed | Avoid jerks | Help in turning | Obtain from movement | c | As part of the front and/or rear axle assembly, the differential plays an integral role in how your car makes turns. The differential is designed to drive a pair of wheels while allowing them to rotate at different speeds. | Comments | Active | |
| 15 | In order to balance reciprocating masses: | Only primary forces must be balanced | Only secondary forces must be balanced | Both primary and secondary forces must be balanced | None of the above | d | For complete balancing of reciprocating mass primary and secondary forces and couples should be balanced In order to balance the reciprocating masses: - The unbalanced force due to reciprocating masses varies in magnitude but constant in direction while due to the revolving masses, the unbalanced force is constant in magnitude but varies in direction. |
Comments | Active | |
| 16 | The height of simple watt governor is proportional to | Speed N | \(\frac{1}{N}\) | \( N^{2}\) | \(\frac{1}{N^{2}}\) | d | Height of governor = \(\frac{895}{N^{2}}\) | Comments | Active | |
| 17 | The cams in which the follower reciprocates or oscillates in a plane parallel to the axis the cam, is known as: | Cylindrical cams | Radial cams | Reciprocating cams | Rotary cams | a | A cylindrical cam is a 3D cam which drives its follower in a groove cut on the periphery of a cylinder. The follower, which is either cylindrical or conical, may translate or oscillate. | Comments | Active | |
| 18 | The term “effort of governor†refers to: | Centrifugal force of balls | Useful power developed | Force acting on sleeve for given percentage change of speed | Minimum force required on sleeve for percentage change of speed | c | The mean force exerted on the sleeve during the given change of speed is known as the effort of the governor | Comments | Active | |
| 19 | In a reverted gear train axis of shafts of both driver and driven gears are: | Intersecting at an angle | Intersecting at right angle | Coaxial and collinear | None of the above | c | Reverted gear train: When the axes of the first gear and the last gear are co-axial, then the gear train is known as reverted gear train and here the motion of the first gear and the last gear is like. | Comments | Active | |
| 20 | Flywheel maintains consistency of rpm due to: | Its light weight | Its high moment of inertia | Its high speed of rotation | It is rotated by wind power | b | Flywheel is a mechanical device which uses the conservation of angular momentum to store rotational energy; a form of kinetic energy proportional to the product of its moment of inertia and the square of its rotational spee(d) Flywheel maintains consistency of rpm due to its high speed of rotation | Comments | Active | |
| 21 | Which of the following should be inverted to have Whitworth quick return mechanism? | Four bar chain | Single slider crank chain | Both a and b | None of the above | b | Inversion of Single Slider Mechanism: i. Reciprocating Engine ii. Witworth QRMMiii. Crank and Slotted lever ORMMiv. Handpump |
Comments | Active | |
| 22 | Which of the following is true condition for uniform wear theory? (‘p’ is the pressure and ‘r’ is radius) | p constant | p/r = constant | pr = constant | None of the above | c | For uniform wear theory Pr = constant For uniform pressure theory constant \(\frac{P}{r}=\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 23 | Which of the following does not affect the balancing of rotating system? | Casting Defects like blow holes | Eccentricity | Keys and Keyways | Distortion (e) Clearance Tolerance (f) Corrosion (g) Wear etc |
d | Causes of unbalancing of a rotor | Comments | Active | |
| 24 | Automobile gears are generally made of | Brass | Cast iron | Stainless steel | Alloy steel | d | Automobile gears are generally made of alloy steel. | Comments | Active | |
| 25 | The clutch is mounted between the: | Engine and gear box | Gear box and propeller shaft | Propeller shaft and final drive | Final drive and differential | a | A clutch is used to connect and disconnect transmission of power from the engine flywheel to the transmission gearbox of drive shaft. | Comments | Active | |
| 26 | The King pin inclination is usually: | Less than \(\frac{1}{2}°\) | Between \(1° to 2°\) | Between \(2° to 5°\) | More than 7 \(°\) | c | Comments | Active | ||
| 27 | Which of the following is an inversion of double slider crank chain? | Coupling rod of a locomotive | Oscillating cylinder engine | Elliptical trammels | All of the above | c | Inversions of Double slider crank chain i. Elliptical Trammels ii. Scotch Yoke mechanism iii. Oldham’s coupling |
Comments | Active | |
| 28 | If two gear A and B are meshing with each other such that A rotates with 100 rpm. If module of A = 2mm, module of B = 4mm, no. of teeth of A = 50 and no. of teeth of B = 30, then revolution of gear B is: | 60 rpm | 100 rpm | 92 rpm | 83 rpm | d | Fundamentally this equation is wrong because meshing of two gear is only feasible only when module of both gear is same. But still solution is as follows: Module = Pitch dia/No of teeth For first gear \(D_{1}=2×50=100\) For second gear \(D_{2}=4×30=120\) Now velocity ratio \(\frac{D_{1}}{D_{2}}=\frac{N_{2}}{N_{1}}\) \(\frac{100}{120}=\frac{N_{2}}{100}\) \(N_{2}=83.333=83 RPM approx\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 29 | In a flywheel, the safe stress is 25.2 MN/m2 and the density is 7 g/cm3. What is the maximum peripheral velocity? | 30 m/s | 45 m/s | 60 m/s | 120 m/s | c | Given \(σ=25.2\frac{MN}{m^{2}}=25.2 ×10^{6}N/m^{2}\) \(Ï=\frac{7}{1000 ×10^{-6}} kg/m^{3}\) \(v=\frac{σ}{Ï}=\frac{25.2×10^{6}}{7/(1000×10^{-6})}\) \(v=60 m/s\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 30 | Which of the following is an absorption type dynamometer? | Prony brake dynamometer | Rope brake dynamometer | Torsion dynamometer | Both a and b | d | Example of absorption type dynamometer: i. Prony brake dynamometer ii. Rope brake dynamometer |
Comments | Active | |
| 31 | The partial balancing means | Balancing partially the revolving masses | Balancing partially the reciprocating masses | Best balancing of engines | All of the above | b | In the case of reciprocating masses, Primary forces are partially balanced because in the reciprocating masses "the resultant forces" will be completely balanced but "the resultant couple" won't be balanced, that is why we say that reciprocating masses are only partially balanced | Comments | Active | |
| 32 | The circular pitch of spur gear is the ratio of: | Number of teeth to the pitch diameter | Pitch diameter to the number of teeth | Circumference of pitch circle to number of teeth | Circumference of pitch circle to diameter of pitch circle | c | Circular Pitch = \(\frac{Ï€D}{T}\) Here circumference of pitch circle \(Ï€D=\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 33 | In automobiles, epicyclic gear train is used for | Clutch | Brakes | Steering | Differential | d | The epicyclic gear trains are used in the back gear of lathe, differential gears of the automobiles, hoists, pulley blocks, wrist watches, etc The epicyclic gear trains are useful for transmitting high-velocity ratios with gears of moderate size in a comparatively lesser space. | Comments | Active | |
| 34 | In a governor if the equilibrium speed is constant for all radii of rotation of balls, the governor is said to be: | Stable | Unstable | Inertia | Isochronous | d | Isochronous governor:i. A governor is said to be isochronous when the equilibrium speed is constant (i.e. range of speed is zero) for all radii of rotation of the balls within the working range, neglecting friction.ii. The isochronisms is the stage of infinite sensitivity.iii. A spring-loaded governor can only possibly be an Isochronous governor. | Comments | Active | |
| 35 | In a Watt governor, if ‘A’ is angular velocity of the balls and arms about the spindle axis in rad/s, then the height of the governor is given by: | A/g | g/A2 | gA2 | g/A3 | b | For watt governor \(h=\frac{g}{A^{2}}\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 36 | In a simple gear train, if there is odd number of idlers, the direction of rotation of the driver and driven gear will be: | Opposite | Same | Depends on the number of teeth of gears | Depends on the relative size of idlers | b | We know that the even number gears have same direction and odd number gears have same direction. So in question let us assume the total no. gears are seven so the direction of 1st and the 7th gear have same direction. | Comments | Active | |
| 37 | ABCD is a mechanism with link lengths AB = 200 mm, BC = 300 mm, CD = 400 mm, DA = 350 mm. Which of the following links should be fixed for the resulting mechanism to be a double crank mechanism? | AB | BC | CD | DA | a | For Double crank mechanism, we always fixed the crank is the smallest among the other links i.e; A(B) | Comments | Active | |
| 38 | The function of a distributor in an automobile is: | To distribute fuel to all cylinders | To regulate powers | To distribute to all moving parts | To time the spark | d | The distributor's main function is to route high voltage, current from the ignition coil to the spark plugs in the correct firing order, and for the correct amount of time. | Comments | Active | |
| 39 | A system of masses rotating in different parallel planes is in dynamic balance if the resultant: | Force is equal to zero | Couple is equal to zero | Force and couple both equal to zero | Force in numerical equal to the resultant couple but neither of them need to be zero | c | Dynamic Balancing: Dynamic balance is a balance due to the action of inertia forces.A body is said to be in dynamic balance when the resultant moments or couples, which involved in the acceleration of different parts is equal to zero. | Comments | Active | |
| 40 | In a flat belt drive, the belt can be subjected to a maximum tension ‘T’ and centrifugal tension ‘Tc’. What will be the condition for transmission of maximum power? | T = Tc | \(T=3T_{c}\) | \(T=2T_{c}\) | \(T=3T_{c}\) | d | Condition for transmission of max power \(T_{C}=\frac{T_{max}}{3}\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 41 | Sensitiveness of a governor is defined as | \(\frac{Range of speed }{Mean speed }\) | Mean speed Range of speed \(×\) | \(\frac{Mean speed }{Range of speed }\) | Mean speed + Range of speed | a | Sensitiveness of governor = \(\frac{Range of speed}{Mean speed}\) | Comments | Active | |
| 42 | Number of degree of freedom of an epicyclic gear train is: | Zero | One | Two | Three | c | 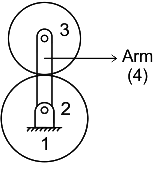 L = 4 j = 3 Between (1 and 2, 1 and 4, 3 and 4)h = 1 (between 2 and 3) DOF = \(3 ×(4-1)-2×3-1=2\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 43 | What is the maximum acceleration of a cam follower undergoing simple harmonic motion? | \(\frac{h}{2}(\frac{πw}{∅})^{2}\) | \(4h(\frac{w^{2}}{∅^{2}})\) | \(4h(\frac{w^{2}}{∅})\) | \(\frac{2hπw^{2}}{∅^{2}}\) | a | \(a_{max}=\frac{h}{2}(\frac{πw}{∅})^{2}\) | Comments | Active | |
| 44 | Total number of instantaneous centers of rotation for a mechanism having ‘n’ link is | \(\frac{n(n-1)}{2}\) | \(\frac{n}{2}\) | \(n-1 \) | n | a | I-centre = \(\frac{n(n-1)}{2}\) | Comments | Active | |
| 45 | Euler’s formula is applicable to | Short column | Medium column | Long column | None of the above | c | Euler's formula gives correct results only for very long columns. For short or long columns Rankine's Formula is used. | Comments | Active | |
| 46 | The slenderness ratio for long column is | Less than 32 | 50-60 | 80-100 | More than 120 | d | Short columns have a slenderness ratio of less than 32. Such columns are always subjected to direct compressive stress only. The medium column slenderness ratio is between 32 to 120. Long columns have a slenderness ratio of more than 120. | Comments | Active | |
| 47 | Value of longitudinal stress for the thin cylinder, d = diameter of thin cylinder, P = Pressure, t = thickness | \(\frac{Pd}{2t}\) | \(\frac{Pd}{4t}\) | \(\frac{2Pd}{t}\) | None of the above | b | Longitudinal stress = \(\frac{Pd}{4t}\) Hoop stress = \(\frac{Pd}{2t}\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 48 | Two shafts, one hollow and other solid have the same material length and mass. The inner diameter of hollow shaft is half the outside diameter. The ratio of torque that can be transmitted by these two shafts is: | \(\frac{15}{16}\) | \(\frac{5}{23}\) | \(\frac{7}{33}\) | \(\frac{1}{32}\) | b | Let \(D_{h}=outer dia of Hollow shaft\) \(d_{h}=inner dia of hollow shaft\) \(D=dia of solid shaft\) Given \(l_{h}=l_{s}& m_{h}=m_{s}\) And \(d_{h}=\frac{D_{h}}{2}\) \(k=\frac{inner dia}{outer dia}=\frac{d_{h}}{D_{h}}=\frac{1}{2}=0.5\) As given in the question \(m_{h}=m_{s}\) \(⇒(ÏgV)_{h}=(ÏgV)_{s} \) same material \([Ï_{h}=Ï_{s}\)] \(⇒A_{h}l_{h}=A_{s}l_{s}\) \(\frac{Ï€}{4}(Dh2-dh2)=\frac{Ï€}{4}D^{2}\) \(⇒Dh2-\frac{Dh2}{4}=D^{2}\) \(⇒3DH2=D^{2}\) \(D=\frac{3}{2} D_{h}\) Now, \(\frac{Ï„_{s}}{Ï„_{h}}=\frac{(16T_{s})Ï€D^{3}}{16T_{H}/Ï€Dh3(1-k^{4})}\) \((Ï„_{s}=Ï„_{h})\) \(∴same material\) \(⇒\frac{Ï„_{s}}{Ï„h}=\frac{D^{3}}{Dh3(1-\frac{1}{16})}\) \((∴k=\frac{1}{2}=\frac{d_{h}}{D_{h}})\) \(=\frac{(\frac{3}{2})^{3}Dh3}{Dh3×\frac{15}{16}}\) \(\frac{T_{s}}{T_{h}}=\frac{33}{8}×\frac{16}{15}=\frac{23}{5}\) \(\frac{T_{h}}{T_{s}}=\frac{5}{23}\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 49 | Which of the following material is most elastic? | Rubber | Plastic | Steel | Glass | c | Steel is the most elastic material. If the object is elastic, the body regains its original shape when the pressure is removed. | Comments | Active | |
| 50 | Relation between E (Modulus of Elasticity) and K (Bulk modulus of Electricity) is given by | E = \(2K(1-\frac{2}{m})\) | \(E=K(1-\frac{2}{m})\) | \(E=3K(1-\frac{2}{m})\) | \(E=4K(1-\frac{1}{m})\) | c | \(E=3K(1-2μ)\) | Comments | Active | |
| 51 | A vertical hanging bar of length weighs ‘w’ kg/unit length and carries a load ‘W’ at bottom. The tensile force at a distance ‘y’ from support in the bar will be: \('l'\) | W + w \((l-y)\) | W | W + w \(l\) | \((W+w)y/l\) | a |  |
Comments | Active | |
| 52 | Volumetric strain of a regular body subjected to an axial force, in terms of linear strain ‘e’ and Poisson’s ratio ‘ is equal to \(μ'\) | \(e(1-2μ)\) | \(e(1+2μ)\) | \(e(1-μ)\) | \(e(1+μ)\) | a | Volumetric strain = linear strain \(×(1-2μ)\) | Comments | Active | |
| 53 | A beam of length ‘l’ having uniform load of w kg per unit length is supported freely at the ends. The bending moment at mid span will be: | \(wl/4\) | \(wl^{2}/2\) | \(wl^{2}/4\) | \(wl^{2}/8\) | d | The maximum bending moment for the mention case: \(B.M=\frac{wl^{2}}{8}\) Where w = load per unit length |
Comments | Active | |
| 54 | The moment diagram for a cantilever beam carrying concentrated load at the end of the beam will be: | Rectangular | Triangular | Parabola | Ellipse | b | The BMD for a cantilever beam carrying concentrated load at the end of the beam will be triangular and for SFD it will be rectangular. | Comments | Active | |
| 55 | The slenderness ratio of a vertical column of square cross section of 2.5 cm on edge and 3 m long is: | 120 | 240 | 416 | 550 | c | Given b = = 300cm \(2.5 cm\) \(l\) \(k=\frac{I}{A}=\frac{b^{4}/12}{b^{2}} \) \(k=\frac{b^{2}}{12}=\frac{b}{23}=0.72\) 416 \(Se=\frac{l}{k}=\frac{300}{0.72}=\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 56 | A circular shaft with diameter ‘D’, the modulus of the section is: | \(πD^{3}/64\) | \(πD^{3}/32\) | \(πD^{3}/16\) | \(πD^{4}/64\) | b | The modulus of section is \(Z=\frac{πD^{3}}{32}\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 57 | A point of contraflexure occurs on a loaded beam where: | Bending moment is maximum | Bending moment changes sign and it is zero | Thickness of beam is least | Maximum load is focused | b | The point of contraflexure (PoC) occurs where bending is zero and at the point of change between positive and negative (or between compression and tension) | Comments | Active | |
| 58 | If ‘ be the proof stress or maximum stress to which the bar is stressed upto the elastic limit, then modulus of resilience is equal to : \(σ_{p}'\) | \(σ_{p}/2E\) | \(\frac{σp2}{2E}\) | \(\frac{σ_{p}}{4E}\) | \(\frac{σp2}{4E}\) | b | The modulus of resilience is defined as the maximum energy that can be absorbed per unit volume without creating a permanent distortion. \(\frac{U}{Vol}=\frac{σp2}{2E}\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 59 | In 2-D, stress system, the co-ordinates of the centre of Mohr’s circle are: | \((\frac{σ_{x}-σ_{y}}{2},0)\) | \((0, \frac{σ_{x}+σ_{y}}{2})\) | \((\frac{σ_{x}+σ_{y}}{2},0)\) | \((0,\frac{σ_{x}-σ_{y}}{2})\) | c | In 2-D, stress system, the co-ordinates of the centre of Mohr’s circle are \((\frac{σ_{x}+σ_{y}}{2},0)\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 60 | Neutral axis of beam is the axis at which: | The shear stress is zero | The moment of inertia is zero | The bending stress is maximum | The bending stress is zero | d | The layer of fibers in between in which is neither in tension or compression is called the neutral surface. Bending stress on the neutral axis is zero. | Comments | Active | |
| 61 | The radius of gyration of a circular cross section column of diameter‘d’ is: | d/4 | d/2 | \(d^{2}/16\) | \(d^{2}/4\) | a | Given \(I=\frac{π}{64}d^{4}\) \(A=\frac{πd^{2}}{4}\) Radius of gyration (k) = \(\frac{I}{A}\) \(k=\frac{\frac{π}{64}d^{4}}{\frac{π}{4}d^{2}}\) \(k=\frac{d}{4}\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 62 | Two springs of stiffness and respectively are connected in series, the stiffness of composite spring is : \(k_{1}\) \(k_{2}\) | \(K=k_{1}+k_{2}\) | \(K=k_{1}×k_{2}\) | \(K=\frac{k_{1}k_{2}}{k_{1}+k_{2}}\) | \(K=\frac{k_{1}+k_{2}}{k_{1}k_{2}}\) | c | In series \(\frac{1}{k_{eq}}=\frac{1}{k_{1}}+\frac{1}{k_{2}}\) \(k_{eq}=\frac{k_{1}k_{2}}{k_{1}+k_{2}}\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 63 | The maximum bending stress in a flat spring of rectangular cross section b under bending moment ‘M’ is: \(×d\) | \(M/bd^{2}\) | \(6M/bd^{2}\) | \(12M/bd^{2}\) | \(16M/bd^{2}\) | b | \(σ_{b}=\frac{6M}{bd^{2}}\) | Comments | Active | |
| 64 | In a simply supported of length ‘L’ with a uniform load of ‘W’ per unit length, the maximum bending moment will be: | \(\frac{WL^{2}}{8}\) | \(\frac{WL^{2}}{4}\) | \(\frac{WL^{2}}{2}\) | \(\frac{WL}{8}\) | a | The maximum bending moment for the mention case: \(B.M=\frac{WL^{2}}{8}\) Where W = load per unit length |
Comments | Active | |
| 65 | In a simply supported beam of length ‘L’ with a point load at ‘L/2’ from left support, the maximum bending moment will occur at a length: | L/4 from left support | 2L/3 from left support | 3L/4 from left support | None of the above | d | For the case which is mention in the question, the maximum bending moment will be on the midpoint of the beam i.e from left or right support. \(L/2\) | Comments | Active | |
| 66 | For a power transmission shaft transmitting power ‘P’ at ‘N’ rpm, its diameter is proportional to: | \((\frac{P}{N})^{\frac{1}{3}}\) | \((\frac{P}{N})^{\frac{1}{2}}\) | \((\frac{P}{N})^{\frac{2}{3}}\) | \((\frac{P}{N})\) | a | We know \(P=T.ω\) \(P=(\frac{πD^{3}}{16}.τ)×\frac{2πN}{60}\) \(D=(\frac{P}{N})^{\frac{1}{3}}\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 67 | If ‘d’ is density of the material in kg/m3, ‘E’ is Young’s modulus , is length of the bar and ‘g’ is acceleration due to gravity , then the total elongation produced in bar due to self-weight is given by \('l'\) | \(dgl^{2}/E\) | \(dgl^{2}/2E\) | \(dg/E\) | \(d^{2}gl/2E\) | b | We know that \(δl=\frac{Ïgl^{2}}{2E}\) According to question \(δl=\frac{dgl^{2}}{2E}\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 68 | If ‘D’ is the diameter of coil of a close coiled helical spring and total angle of twist in full length is ‘A’, then the deflection of the spring will be: | DA | DA/2 | 2DA | D2A/2 | b | Deflection of spring = \(Rθ\) According to question it will be \(δ=\frac{DA}{2}\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 69 | The ratio of shear modulus to modulus of elasticity, if Poisson’s ratio is 0.25, will be: | 0.4 | 0.25 | 4 | 0.5 | a | Given \(μ=0.25\) \(E=2C(1+μ)\) \(\frac{C}{E}=\frac{1}{2(1+.25)}=0.4\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 70 | The effective length of a column with one end fixed and other end free is | Its own length | Twice the length | Half the length | \(\frac{1}{2}×its length \) | b | Effective length of a column with one end fixed and other end free is twice the length. If it asked about the Euler’s load then it will be of the original loa(d) \(\frac{1}{4}th \) | Comments | Active | |
| 71 | Maximum strain energy that can be stored in a body is known as | Impact energy | Resilience | Proof resilience | Modulus of resilience | c | Proof resilience is defined as the maximum energy that can be absorbed up to the elastic limit, without creating a permanent distortion | Comments | Active | |
| 72 | The point in the stress-strain curve at which the strain increases considerably without any significant increase in stress is called the: | Limit of proportionality | Elastic limit | Upper yield point | Lower yield point | c |  |
Comments | Active | |
| 73 | The materials having same elastic properties in all directions are called: | Ideal materials | Uniform materials | Elastic materials | Isotropic materials | c | Isotropic materials are those that have consistent and uniform properties throughout the material regardless of the orientation considered. | Comments | Active | |
| 74 | Maximum deflection in a cantilever beam due to pure bending moment “M†at its end is: | \(\frac{ML^{2}}{8EI}\) | \(\frac{ML^{2}}{6EI}\) | \(\frac{ML^{2}}{2EI}\) | \(\frac{ML^{2}}{4EI}\) | c | Maximum deflection in a cantilever beam = \(\frac{ML^{2}}{2EI}\) | Comments | Active | |
| 75 | Maximum principal stress theory is applicable for: | Ductile materials | Brittle materials | Elastic materials | None of the above | b | Maximum principal stress theory is also known as Rankine’s theory and it is applicable for brittle materials. | Comments | Active | |
| 76 | A steel bar 200 mm in diameter is turned at a feed rate of 0.25 mm/rev with a depth of cut of 4mm. Rotational speed is 16 rpm. The MRR in mm3/s is: | 160.6 | 167.4 | 1600.3 | 1675.5 | b | Given D = 4 mmd = 200 mmN = 16 rpm \(f=0.25 mm/rev\) MRR = \(fDV=fD×\frac{πdN}{60}\) MRR = \(0.25×4×\frac{π×200×16}{60}\) \(MRR=167.4 mm^{3}/s\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 77 | Two cutting tools are being compared for a machining operation. The tool life equations are: Carbide tool HSS tool \(VT^{1.6}=3000 and\) \(VT^{0.6}=200\) Where ‘V’ is in mpm; ‘T’ in minutes. The carbide tool will give higher tool life if cutting speed (mpm) exceeds: |
15 | 39.4 | 49.3 | 60.2 | b | Given For Carbide tool: For HSS tool \(VT^{1.6}=3000\) \(VT^{0.6}=200\) From HSS tool equation \(V=\frac{200}{T^{0.6}}\) Put value of V for Carbide tool and get the value of T T = 15 min \(\frac{200}{T^{0.6}}×T^{1.6}=3000\) Put this value of T for Carbide tool and get the velocity \(VT^{1.6}=3000\) \(V=\frac{3000}{(15)^{1.6}}\) \(V=39.4 mpm\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 78 | The metal lead and tin are normally hot worked at temperature approximately | \(500℃ to 600℃\) | At room temperature | Above 1000 \(℃\) | None of the above | b | The working of lead and tin at room temperature is called hot working as their recrystallization temperature is below the room temperature, but tungsten, when worked at 1200°C, is still called cold worked as its recrystallization temperature is higher than 1200°(C) | Comments | Active | |
| 79 | A key capable of tilting in a recess milled out in a shaft is known as | Woodruff key | Feather key | Flat saddle key | Gib headed key | a | A woodruff key, also known as a half‑moon key, is a semi-circular machine shaft key that prevents gears, hubs, or other components from moving independently of a rotating shaft or spindle. | Comments | Active | |
| 80 | If threads on a bolt are left handed, threads on nut will be: | Right handed with same pitch | Right handed with different pitch | Left handed with same pitch | Left handed with different pitch | c | Comments | Active | ||
| 81 | In a cotter joint, taper on the cotter and slot is provided: | On both the sides | On one side only | No taper is provided | None of the above | b | The taper in the cotter is provided to take advantage of wedging action (friction locking). Due to the tapered shape, it is easy to remove the cotter and dismantle the joint. The taper of the cotter, as well as slots, is on one side. | Comments | Active | |
| 82 | In a riveted joint design, diameter of rivet ‘d’ in terms of plate thickness ‘t’ is equal to : | \(1.2t\) | \(6t\) | \(1.9t\) | \(\frac{1}{1.2}t\) | b | Diameter of rivet‘d’ = 6 \(t\) | Comments | Active | |
| 83 | Anti-friction bearings are: | Sleeve bearings | Gas lubricated bearings | Ball and roller bearings | Plastic bearings | c | Anti-Friction Bearings – examples of these are ball bearings, roller bearings, and needle bearings. These would be used instead of a friction bearing when higher loads and higher speeds are needed for the application. | Comments | Active | |
| 84 | Maximum principal stress theory of failure of material at elastic point is known as: | Von-mises theory | Haig’s theory | Guest’s theory | Rankine theory | d | Maximum Principal Stress theory is known as Rankine’s theory. | Comments | Active | |
| 85 | The major factor considered for selecting the value of cutting velocity in a machining operation is: | Nature of cut | Type of work material | Cutting tool material | All of the above | d | Factors Affecting the Cutting Speed of the Tool: i. Tool Material ii. Workpiece Material iii. Tool life iv. Cutting Depth and Cutting Amountv. The Shape of the Toolvi. Use of Coolant |
Comments | Active | |
| 86 | Which of the following is a chip forming process? | Chamfering | Coining | Squeezing | Upsetting | a Solution Chamfering eases assembly, e.g. the insertion of bolts into holes, or nuts. Chamfering also removes sharp edges which reduces significantly the possibility of cuts, and injuries, to people handling the metal piece. |
Comments | Active | ||
| 87 | Coating material of welding electrode is used to provide: | Protective layer | Arc generator | Hardener | Flux | d | Basic functions of electrode coating: 1. To stabilize the arc2.To generate gases to act as a shield against the surrounding atmosphere.3. To control the rate at which the electrode melts. 4. To act as a flux to protect weld against formation of oxides, nitrides and other inclusions.5. To add alloying elements to the weld zone to enhance the properties of the joint. |
Comments | Active | |
| 88 | Total power required in a drilling operation does not depend on the following: | RPM of drill | Feed rate in mm/rev | Thrust force | All of the above | d | Power = \(T.ω\) Power depends on the rpm of drill and thrust force. |
Comments | Active | |
| 89 | In rolling operations the rolls rotate with a surface velocity: | Lower than speed of incoming metal | More than speed of incoming metal | Equal to speed of incoming metal | (a) & (c) both are correct | b | In rolling operations the rolls rotates with a speed more than the incoming metal. While the rolls rotates with a speed lower than the exiting metal. | Comments | Active | |
| 90 | Which of the following ropes will be more flexible? | \(6×7\) | \(6×19\) | \(6×37\) | None of the above | c | Comments | Active | ||
| 91 | Shape of woodruff key is like: | Cylinder | Semi-circle | Square | Rectangular | b |  |
Comments | Active | |
| 92 | Rankine’s formula is valid upto slenderness ratio | 60 | 120 | 180 | 240 | b | Rankine’s formula is valid upto slenderness ratio of 120. | Comments | Active | |
| 93 | Guest’s theory is used for | Brittle material | Ductile material | Elastic material | Plastic material | b | According to Guest's theory, the failure occurs at a point in a member when the maximum shear stress in a bi-axial stress system reaches the shear stress at elastic limit in simple tension test. This theory is suited for ductile material. | Comments | Active | |
| 94 | Factor of safety for fatigue loading is the ratio of: | Elastic limit to working stress | Young’s modulus to the ultimate tensile strength | Endurance limit to the working stress | Elastic limit to the yield point | c | Factor of safety = \(\frac{Ultimate Stress }{Working Stress}\) For fatigue loading the ultimate limit is fatigue limit So the factor of safety = \(\frac{endurance limit }{working stress}\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 95 | The strength of the unriveted or solid plate per pitch length is equal to: here p = pitch diameter, d = diameter of rivet, t = thickness of plate, \(σ_{t}=stress\) | \(p×d×σ_{t}\) | \(p×t×σ_{t}\) | \((p-t)×d×σ_{t}\) | \((p-d)×t×σ_{t}\) | b | Strength of the unriveted joint = \(p×t×σ_{T}\) | Comments | Active | |
| 96 | The cross-section of a flat key 16 . It is fitted on the shaft whose diameter is 50 mm.The key is to transmit a torque 400 N-m and crushing stress is 250 kN/mm2. The length of key is: \(×10mm\) | 18 mm | 17 mm | 16 mm | 15 mm | * | \( σ_{C}=\frac{4M_{t}}{dhl}\) \(l=\frac{4×400×1000}{50×10×250×1000}=0.0128 mm\) Which is impossible. That means data is given wrong. |
Comments | Active | |
| 97 | If the dynamic load carrying capacity of a ball bearing increased by 2 times without change in equivalent dynamic load, the life of bearing is increased: | 600% | 800% | 700% | 400% | c | As we know that \(L_{1}=(\frac{c}{p})^{3}\) \(L_{2}=(\frac{C}{P})^{3}=8\) \(% increase= \frac{L_{1}-L_{2}}{L_{1}} ×100\) \(=700% increment \) |
Comments | Active | |
| 98 | When the length of the journal is equal to the diameter of the journal, then the bearing is said to be a: | Short bearing | Long bearing | Medium bearing | Square bearing | d | For Long bearing: \(\frac{L}{D}>1\) For short bearing: \(\frac{L}{D}<1\) For square bearing: \(\frac{L}{D}=1\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 99 | Which type of loading is considered for designing the axle? | Bending moment only | Twisting moment only | Combined bending moment and torsion | Combined action of bending moment, twisting moment and axial thrust. | a | Axle is a non-rotating member used for supporting rotating wheels etc and do not transmit any torque. | Comments | Active | |
| 100 | An initial capital investment is and has a 6 year life and a salvage value. Working capital is Rs. 40,000. Total net profit after taxes over 6 year is estimated as Rs.1,67,000. Find the rate of return on investment. \(Rs.3,60,000\) \(Rs.60,000 \) | 0,05 | 0.07 | 0.08 | 0.03 | b | Given Annual profit ((A)P) = Rs. 1,67,000Capital investment ((C)I) = Rs. 3,60,000Working Capital (W.C) = Rs. 40, 000 \(Rate of return on investment (ROR)= \frac{AP/6}{C.I +W.C}\) \(ROR=\frac{1,67,000/6}{3,60,000+40,000}\) ROR = 0.07 |
Comments | Active | |
| 101 | The bottom of the threaded groove is called: | Crest | Root | Floor | End | b | 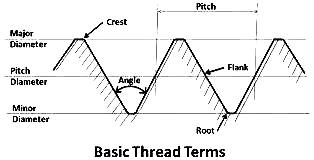 |
Comments | Active | |
| 102 | The aggregate of prime cost and factory overheads is given by: | Factory cost | Office cost | Total cost | Sales price | a | Factory cost is the summation of prime cost and factory overheads that includes indirect material, indirect labor and indirect expenses of factory. It is also known as work cost, manufacturing cost or production cost. | Comments | Active | |
| 103 | Which of the following welding processes uses non-consumable electrode? | MIG welding | Submerged arc welding | TIG welding | Manual arc welding | c | Tungsten Inert Gas (TIG) welding, also known as Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW) is an arc welding process that produces the weld with a non-consumable tungsten electrode. | Comments | Active | |
| 104 | The indirect cost of a plant is per year. The direct cost is Rs.20 per product. If average revenue per product is , the break even point is : \(Rs.4,00,000\) \(Rs.60\) | 60,000 products | 40,000 products | 20,000 products | 10,000 products | d | Given Fixed cost = Rs. 4,00,000Sales cost = Rs. 60Variable cost = Rs.20 BEP = \(\frac{F.C}{S.C-V.C}=\frac{4,00,000}{60-20}\) BEP = 10, 000 products |
Comments | Active | |
| 105 | In welded joint, the throat of a weld as compared to size of weld is: | About 0.7 times | About same size | About 1.275 times | About 0.25 times | a | In a welded joint , the throat of a weld as compared to size of weld is about 0.7 times. | Comments | Active | |
| 106 | The usual ratio of forward and return stroke in shaper machine is | 1:2 | 3:2 | 2:3 | 2:1 | b | The Speed ratio is the ratio of Time taken in the forward stroke to the time taken in the return stroke which is usually taken as 3:2 (1.5:1). | Comments | Active | |
| 107 | In case of a riveted joint the maximum pitch in terms of diameter of rivet‘d’ is | 3d | d | d + 12 | 5d | a | Maximum pitch = 3d Where d = diameter of rivet |
Comments | Active | |
| 108 | The Piston rod and the cross head in a steam engine are usually connected by means of: | Knuckle joint | Ball joint | Cotter joint | Universal joint | c | Cotter joint is used to connect piston rods in a crosshead in a steam engine. It is used to connect the piston rod with its extension. It is also used in bicycles to connect pedals to sprocket wheels. Foundation Bolt. | Comments | Active | |
| 109 | A solid circular shaft is subjected to pure torsion. The ratio of maximum shear stress to maximum normal stress at any point would be: | 1:1 | 1:2 | 2:1 | 2:3 | a | For the case of pure torsion the maximum normal stress is equal to maximum shear stress. \(\frac{τ}{σ}=1:1 \) |
Comments | Active | |
| 110 | Which Class of fire extinguishers should have you use on electricity energized fires? | Class A | Class B | Class C | Class D | c | In the case of electrical fires, also known as energized electrical fires, a class C fire extinguisher is needed to put it out. | Comments | Active | |
| 111 | A normal conversation registers at about: | 0 to 10 decibels | 10 to 20 decibels | 30 to 40 decibels | 50 to 60 decibels | d | A normal conversation registers at about 50 to 60 decibels. | Comments | Active | |
| 112 | What does symbol ‘D’ imply in work study? | Inspection | Transport | Delay/temporary storage | Permanent storage | c | Delay occurs when something stops the process and a product waits for the next event | Comments | Active | |
| 113 | Workmen’s Compensation Act, 1923 applied to the persons employed in: | Mines | Plantations | Constructions | All of the above | d | Workmen’s Compensation Act 1923 is an act to provide for the payment by certain classes of employers to their workmen of compensation for injury by accident. | Comments | Active | |
| 114 | ABC analysis deals with: | Analysis of process chart | Flow of material | Ordering schedule of job | Controlling inventory cost money | d | ABC analysis is an inventory management technique that determines the value of inventory items based on their importance to the business. ABC ranks items on demand, cost and risk data, and inventory mangers group items into classes based on those criteria | Comments | Active | |
| 115 | Which of the following is independent of sales forecast? | Productivity | Inventory control | Production planning | Capital budgeting | a | Sales forecasting is the process of estimating future revenue by predicting the amount of product or services a sales unit (which can be an individual salesperson, a sales team, or a company) will sell in the next week, month, quarter, or year. Productivity is independent of sales forecast. | Comments | Active | |
| 116 | Preventive maintenance is also known as: | Breakdown maintenance | Corrective maintenance | Systematic maintenance | Real maintenance | c | Preventive maintenance (PM) is the regular and routine maintenance of equipment and assets in order to keep them running and prevent any costly unplanned downtime from unexpected equipment failure. | Comments | Active | |
| 117 | An chart is suited for following type of data: \(X\) | Count | Attribute | Measurement | None of the above | c |  |
Comments | Active | |
| 118 | Which of the following is not a tool of work study? | Process outline chart | SIMO chart | Control chart | String diagram | c | The control chart is a graph used to study how a process changes over time. Data are plotted in time order. | Comments | Active | |
| 119 | Identify the symbols for inspection & storage respectively as used in work study | b |  |
Comments | Active | |||||
| 120 | Which type of tolerance does a slip gauge have? | Bilateral tolerance | Zero tolerance | Unilateral tolerance | a and c both | a | Slip gauges have bilateral tolerance and they tend to cancel errors as they have tolerance on individual blocks. In bilateral tolerance variation is permitted in both directions. | Comments | Active | |
| 121 | Which of the following is true for calibration of equipment’s? | Calibration record should be documented | Ambient conditions should be maintained | Time of recalibration should be fixed | All of the above | d | Calibration is a comparison between a known measurement (the standard) and the measurement using your instrument. | Comments | Active | |
| 122 | Ergonomics factors are included in the product design to have | Comfort to user | Comfort to manufacturer | Comfort to tester | All of the above | d | Ergonomics defined as the science of fitting a workplace to the user's needs, ergonomics aims to increase efficiency and productivity and reduce discomfort. | Comments | Active | |
| 123 | Labour cost of 20 persons producing goods in 100 hours is . What is the cost of production per labour – hour? \(Rs 5 lakhs\) | Rs 250 per labour – hour | Rs. 25000 per labour- hour | Rs. 5000 per labour-hour | None of the above | a | You can calculate the cost of production per labour – hour Let x be the cost per labour-hour \(\frac{x}{500000}=\frac{1}{20}×\frac{1}{100}\) per labour-hour \(x=250 \) |
Comments | Active | |
| 124 | Which of the following is true in case of fixed position layout? | Work-piece does not move | Used to make heavy products | Machines move to work-piece | All of the above | d | In a fixed-position layout, the project remains in one place, and workers and equipment come to that one work are(a) Examples of this type of project are a ship, a highway, a bridge, a house, and an operating table in a hospital operating room. | Comments | Active | |
| 125 | Mostly the man machine systems are: | Open loop systems | Closed loop systems | (a) & (b) both | None of the above | b | At time a man can have feedback from machine so generally it is a closed loop system. The system which does not have feedback system is known as open loop system. | Comments | Active | |
| 126 | Routing prescribes the: | Flow of material in the plant | Proper utilization of man | Proper utilization of machine | None of the above | a | The routing decides the path and sequence of operations to be performed on the job from one machine to another. The purpose of routing is to establish the optimum sequence of operations so that the manufacture of the finished item is performed at the lowest cost and the fastest time. | Comments | Active | |
| 127 | If the forecast and actual demand for a month are 60 and 70 respectively. If then forecasted value of next month is: \(α=0.1, \) | 70 | 61 | 69 | 64 | b | Given \(F_{t-1}=60\) \(D_{t-1}=70\) \(α=0.1 \) Forecasted value for next month can be calculated as: \(F_{t}=F_{t-1}+α(D_{t-1}-F_{t-1})\) \(F_{t}=60+0.1(70-60)\) \(F_{t}=61\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 128 | An assembly activity is represented on an operation process chart by the symbol: | No symbol | A | D | O | d | The operation process defines the organization mode of the application task running process, system function running process, and resource running process. | Comments | Active | |
| 129 | Standard time is: | Normal time + allowances | (Normal time) + allowances \(×rating\) | (Normal time/rating) + allowances | Normal time + (allowances \(×rating)\) | a | Standard time = normal time allowances | Comments | Active | |
| 130 | Interchangeability can be achieved by: | Standardization | Better process planning | Bonus plan | Better product planning | a | Interchangeability or interchangeable manufacturer means that any standardized component will assemble correctly with a mating component, both being chosen at random. | Comments | Active | |
| 131 | Annual demand for a product costing per piece is 900 units. If ordering cost per order is and inventory holding cost is per unit per year, the economic lot size is: \(Rs.100\) \(Rs.100\) \(Rs.2\) | 200 | 300 | 400 | 500 | b | Given Demand (D) = 900 units Ordering Cost ( = 100 Rs. Holding Cost \(C_{o})\) \((C_{h})=2 Rs.\) Economic lot Size = \(\frac{2DC_{o}}{C_{h}}=\frac{2×900×100}{2}\) Economic Lot Size = 300 |
Comments | Active | |
| 132 | Control chart used for attributes is: | R-chart | chart \(X\) | p-chart | None of the above | c | An attribute chart is a type of control chart for measuring attribute data (vs. continuous data). There are four types of attribute charts: c chart, n chart, p chart, and u chart. The choice of charts depends on whether you have a problem with defects or defectives, and whether you have a fixed or varying sample size. | Comments | Active | |
| 133 | THERBLIGS are essential in | Flow process chart | Motion economy | Time study | Suggestion system | b | Therbligs are 18 kinds of elemental motions, used in the study of motion economy in the workplace. A workplace task is analyzed by recording each of the therblig units for a process, with the results used for optimization of manual labour by eliminating unneeded movements. | Comments | Active | |
| 134 | The layout suitable for the low demand and high variety product is: | Group product | Process layout | Product layout | Static layout | b | Fixed position layout (ship building, construction sector) Process oriented layout (low volume, high variety processes) Product oriented layout (high volume, low variety, best m/c util.)Retail/service layout, Warehouse layout | Comments | Active | |
| 135 | The full form of ISO is | International Organization for Standardization | International Standards Organization | Indian Standards Organization | International Standards Office | a | ISO (International Organization for Standardization) is an independent, non-governmental, international organization that develops standards to ensure the quality, safety, and efficiency of products, services, and systems. | Comments | Active | |
| 136 | In break-even-analysis, the total cost is equal to following: | Fixed cost | Variable cost | Fixed cost + variable cost | Fixed cost + sales revenue | c | The break-even point (BEP) or break-even level represents the sales amount—in either unit (quantity) or revenue (sales) terms—that is required to cover total costs, consisting of both fixed and variable costs to the company. Total profit at the break-even point is zero. | Comments | Active | |
| 137 | In the context of inspection, which of the following is true? | The GO gauge controls the upper limit of a hole | The NO-GO gauge controls the lower limit of a shaft | The NO-GO gauge controls the lower limit of hole | The GO gauge controls the lower limit of a hole | d | The 'GO' gage controls the lower limit of a hole and The 'NO GO' gage controls the upper limit of a hole. NO GO gages are designed for minimum material limit of component = upper limit of hole. | Comments | Active | |
| 138 | Which of the following factors affect the plant location decision? | Labour cost | Transportation cost of raw material | Transportation cost of finished goods | All of the above | d | Sol. Factors affecting the plant location: I. Primary Factor Availability of raw materials Nearness to the market Availability of labor Transport facilities Availability of fuel and power Availability of water II. Secondary factor Suitability of climate Government policies Availability of finance Competition between states Availability of facilities Disposal of waste |
Comments | Active | |
| 139 | An assembly line for producing cars is an example of | Process layout | Product layout | Fixed position layout | Group technology | b | Product Layout: It is also known as line layout. In implies that various operations on raw material are performed in a sequence and the machines are placed along the product flow line i.e. machines are arranged in the sequence in which the raw material will be operated upon. | Comments | Active | |
| 140 | In quality control , R charts are used to control : \(X \) | Central tendency and variability | Mean defectives and range | Average number of defects and variance | Process average and percent defectives | a | The x-bar and R-chart are quality control charts used to monitor the mean and variation of a process based on samples taken in a given time. | Comments | Active | |
| 141 | Ventilation and temperature is the included in the salient provisions of which Act? | Employee Provident Fund Act | Workmen’s Compensation Act | Factory Act | Minimum Wage Act | c | Factory Act 1948: Section 13: Ventilation and Temperature This section states: Effective and suitable provisions should be made in every factory for securing and maintaining in every workroom proper ventilation by circulation of fresh air. It also involves providing an adequate temperature at the workplace. |
Comments | Active | |
| 142 | The lead time is the time: | Time between receipt and using material | Time of receiving material | To place order for material | Time between placing the order and receiving the material | d | Lead time in inventory management is the amount of time between when a purchase order is placed to replenish products and when the order is received in the warehouse. | Comments | Active | |
| 143 | Standard time as compared to normal time is | Greater | Smaller | Equal | There is no correlation | a | Standard time = Normal time + Allowances | Comments | Active | |
| 144 | Product layout is employed for: | Continuous production | Batch production | Effective utilization of machine | All of the above | a | Product layout is used when machines and auxiliary services are located according to the processing sequence of the product. The product layout is selected when the volume of production of a product is high such that a separate production line to manufacture it, can be justified. | Comments | Active | |
| 145 | The purpose of case hardening of a part is: | Hardening only the surface of the part | Hardening when the part is very thick | Reducing the hardness of a part | Hardening very small parts | a | Case hardening is a heat treatment process that produces a surface which is resistant to wear, while maintaining toughness and strength of the core. This treatment is applied to low carbon steel parts after machining, as well as high alloy steel bearings, gears, and other components. | Comments | Active | |
| 146 | Melting point of pure iron | 1535 \(℃\) | \(1601℃\) | \(1489℃\) | \(1712℃\) | a | Iron exists in many allotropic forms, and every such allotropic form has a different melting, boiling and solidifying point. But, for pure iron, the melting point is 1535°(C) | Comments | Active | |
| 147 | Visco-elastic behavior is common in | Rubber | Plastics | Non-crystalline organic polymers | Non-crystalline materials | c | Viscoelastic behavior is a combination of elastic and viscous behavior where the applied stress results in an instantaneous elastic strain followed by a viscous, time-dependent strain. | Comments | Active | |
| 148 | The metallic structure of mild steel is: | BCC | FCC | HCP | None of the above | b | Examples of metals with the bcc structure are alpha iron, tungsten, chromium, and beta titanium. | Comments | Active | |
| 149 | In grey cast iron, carbon is present in the form of: | Cementite | Free carbon | Flakes | Spheroids | c | In grey cast iron the carbon is present in the form is the graphite flake structure that is created during the cooling process from the carbon that is in the component. | Comments | Active | |
| 150 | Corrundum contains more than 95% | Ag | \(Al_{2}O_{3}\) | \(SiO_{2}\) | MgO | b | Corundum, naturally occurring aluminum oxide mineral (Al2O3) that is, after diamond, the hardest known natural substance. | Comments | Active | |
| 151 | Hardness of steel is increased by addition of following metal: | Nickel | Chromium | Tungsten | Vanadium | b | Mainly hardness of steel is increased by adding C to it but it also increases brittleness. So Cr is added to steel to increase its corrosion resistance and it also improve hardenability of steel without sacrificing ductility. Nickel increases tensile strength and ductility of steel. Tungsten increases heat resistance of steel. Vanadium improves fine grain distribution in steel. |
Comments | Active | |
| 152 | Which of the following is a heat treatment process? | Tempering | Nitriding | Quenching | all of the above | d | Tempering is a process of improving the characteristics of a metal, especially steel, by heating it to a high temperature, though below the melting point, then cooling it, usually in air.Nitriding is a heat treating process that diffuses nitrogen into the surface of a metal to create a case-hardened surface. Quenching or rapid cooling, as by immersion in oil or water, of a metal object from the high temperature at which it has been shaped |
Comments | Active | |
| 153 | In steel, the pearlite phase is made up of alternate layers of: | Ferrite and martensite | Ferrite and cementite | Cementite and martensite | Cementite and bainite | b | Pearlite is a two-phased, lamellar (or layered) structure composed of alternating layers of ferrite (87.5 wt%) and cementite (12.5 wt%) that occurs in some steels and cast irons. | Comments | Active | |
| 154 | Which of the following is not a heat treatment process? | Glazing | Tempering | Spheroidizing | Case hardening | a | When the cutting edge of a grinding wheel takes a glass-like appearance due to wear of abrasive grains then it is called glazing of the grinding wheel. | Comments | Active | |
| 155 | Gun metal which is used in journal bearing, contains: | 88% Cu, 10% Sn, 2% Zn | 80%Cu, 10%Zn, 10% Al | 85%Cu, 5% Mg, 10% Al | 85% Cu, 5% Sn, 10% Pb | a | Gunmetal is typically composed of 88% copper, 10% tin, and 2% zinc | Comments | Active | |
| 156 | The phase boundary between alpha and (alpha and beta) region is called: | Liquidus | Solidus | Solvus | None of these | c | The boundary line between alpha and alpha + beta regions must be part of Solvus. | Comments | Active | |
| 157 | Line imperfection in a crystal is called: | Schottky defect | Frenkel defect | Edge dislocation | Miller defect | c | An edge dislocation therefore moves in the direction of the Burgers vector, whereas a screw dislocation moves in a direction perpendicular to the Burgers vector. | Comments | Active | |
| 158 | The carbon percentage in cast iron is approximately in the range: | 0.1 – 0.5 | 0.5 – 1.5 | 2.0 – 4.5 | 4.6 – 6.5 | c | Most cast irons have a chemical composition of 2.5–4.0% carbon, 1–3% silicon, and the remainder iron. | Comments | Active | |
| 159 | Brass is an alloy of | Copper and tin | Lead and tin | Copper and lead | Copper and zinc | d | Brass is an alloy of copper and zinc | Comments | Active | |
| 160 | Failure of a material under cyclic stresses is called: | Creep failure | Impact failure | Fatigue failure | None of the above | c | Fatigue failure is the formation and propagation of cracks due to a repetitive or cyclic load most fatigue failures are caused by cyclic loads significantly below the loads that would result in yielding of the material. | Comments | Active | |
| 161 | Teflon is a type of: | Thermoplastic | Thermosetting plastic | Biodegradable plastic | Metal | a | Thermoplastics become soft on heating. As saucepans are used for cooking, their handles should be able to sustain large amount of heat without melting. Therefore, thermoplastics are not used for making saucepan handles .Teflon is an example of thermoplastic. | Comments | Active | |
| 162 | Cementite phase has carbon content | More than 2% | More than 6.67% | Less than 2% | Less than 0.83% | b | The carbon content of cementite is only 6.69%, a small change in the carbon content of an iron causes a large change in the concentration of the cementite present in the iron. | Comments | Active | |
| 163 | Percentage of carbon in low carbon steel is: | 0.3% | 0.05% | 0.15% | 0.7% | c | Low C steel contains 0.15 to 0.3% (C) But commonly 0.15% C Mild steel or Low C steel is used commonly. |
Comments | Active | |
| 164 | Paramagnetic alpha iron changes to gamma iron at: | 910 \(℃\) | \(770℃\) | 1539 \(℃\) | \(1440℃\) | a | 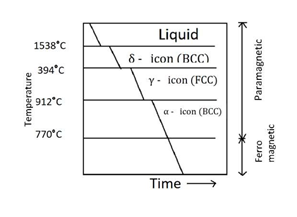 |
Comments | Active | |
| 165 | A weight of 1000 N can be lifted by an effort of 80 N. If the velocity ratio is 20, the machine is: | Reversible | Non-reversible | Ideal | None of the above | a | Given W = 1000 NP = 80 NV.R = 20M.A = W/P M.A = 1000/80 \(η=\frac{1000/80}{20}\) \(η=62.5%\) Efficiency is greater than 50%, hence the machine is reversible. |
Comments | Active | |
| 166 | If the radius of wire stretched by a load is halved, then its Young’s modulus will be: | Doubled | Halved | Zero | Unaffected | d | The Young's Modulus of a material is a fundamental property of every material that cannot be changed. | Comments | Active | |
| 167 | A long thin walled cylinder closed at both ends, is subjected to an internal pressure. The ratio of hoop stress to longitudinal stress developed is: | 4.0 | 2.0 | 1.0 | 0.5 | b | Hoop stress ( = \(σ_{C})=\) \(\frac{Pd}{2t}\) Longitudinal stress ( = \(σ_{L})\) \(\frac{Pd}{4t}\) \(\frac{σ_{C}}{σ_{L}}=2\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 168 | Relation between modulus of elasticity (E), modulus of rigidity (G) and bulk modulus (K) is: | \(E=3KG/(G+9K)\) | \(E=9KG/(G+3K)\) | \(E=(G+9K)/3KG\) | \(E=(G+3K)/9KG\) | b | E = \(\frac{9KG}{3K+G}\) | Comments | Active | |
| 169 | A material has same values for its modulus of rigidity and bulk modulus. What is its Poisson’s ratio? | 0.25 | 0.20 | 0.15 | 0.125 | d | We know \(3K(1-2μ)=2C(1+μ)\) Given: K = C \(3(1-2μ)=2(1+μ)\) \(3-6μ=2+2μ\) \(μ=0.125\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 170 | The ratio of static and dynamic co-efficient of friction is: | Less than one | Equal to one | Greater than one | Uncertain | c | The coefficient of friction of kinetic friction is lesser than the coefficient of static friction. | Comments | Active | |
| 171 | Lami’s theorem is suitable only for | Concurrent forces | Coplanar forces | Coplanar and concurrent forces | Any type of forces | c | Lami's Theorem states, “When three forces acting at a point are in equilibrium, then each force is proportional to the sine of the angle between the other two forcesâ€. It is suitable for coplanar and concurrent forces. | Comments | Active | |
| 172 | Consider a plane as shown in figure below. Find the moment of inertia about its by method of integration: \(x-axis\) |
\(I_{XX}=x^{2}dA\) | \(I_{XX}=y^{2}dA\) | \(I_{XX}= x^{2}y^{2}dA\) | \(I_{XX}=(x^{2}+y^{2})dA\) | b | Comments | Active | ||
| 173 | The condition for a machine, to be reversible, if its efficiency should be: | 100% | More than 100% | More than 50% | 50% | c | If a machine is capable of doing some work in the reversed direction, after the effort is removed, then the machine is known as reversible machine. The condition for a machine to be reversible is that its efficiency should be more than 50 %. | Comments | Active | |
| 174 | In third system of pulleys having ‘n’ number of pulleys, then its velocity ratio is equal to: | \(2^{n}-1\) | \(2^{n}-2\) | \(2^{n-1}\) | \(2^{n-2}\) | a | For First system of pulleys the M.A = V.R = 2n For second system of pulleys the M.A = V.R = n (no. of movable pulleys) For third system of pulleys the M.A = V.R = \(2^{n}-1\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 175 | A frame is having joints equal to j, then a frame is called redundant frame, if the number of member in frame are: | Equal to (2j – 3) | Less than (2j – 3) | More than (2j – 3) | None of the above | c | For perfect frame: m = 2j – 3 For deficient frame: m < 2j – 3 For Redundant frame: m > 2j – 3 |
Comments | Active | |
| 176 | Consider a truss ABC loaded at A with a force F as shown below. Find the tension in member BC is: |
0.5 F | 0.75 F | 0.625 F | 0.871 F | c | From the given diagram \(tan30=\frac{x}{b}\) \(b=\frac{x}{tan30 }=1.732x\) \(Taking moment about Q\) \(=FxX=V_{R}×2.732x\) \(∴V_{R}=0.366F\) \(V_{Q}=F-0.366F=0.634F\) \(Let force in the member PQ is F_{1}\) \(∴F_{1}sin45=V_{Q}\) \(=F_{1}sin45=0.634 F\) \(Force in member QR\) \(=F_{1}cos45\) \(=0.634F \) |
Comments | Active | |
| 177 | The yield point of brittle material can be ascertained by drawing a line parallel to the stress-strain curve at: | 0.2 percent of maximum strain | 2 percent of maximum strain | 5 percent of maximum strain | 10 percent of maximum strain | a |  |
Comments | Active | |
| 178 | The net force on a body is equal to the product of the body’s mass and acceleration of the body. This is called: | Newton’s first law | Newton’s second law | Newton’s third law | None of the above | b | Newton’s second law states that the time rate of change of the momentum of a body is equal in both magnitude and direction to the force imposed on it. | Comments | Active | |
| 179 | The ability of the material to permanently deform without breaking is called: | Elasticity | Plasticity | Hardness | Toughness | b | Plasticity is the ability of a solid material to undergo plastic deformation without fracture. | Comments | Active | |
| 180 | The forces acting in a couple are: | Intersecting at the centre of the couple | Parallel with infinite distance between them | Parallel with finite distance between them | In a circular loop | c | Couple is the combination of two forces which are acting in the same sense of rotation. The forces acting in a couple are parallel with finite distance between them. | Comments | Active |










