| S.No | Question | Option A | Option B | Option C | Option D | Answer | Solution | Comments | Status | Action |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | In inventory control, the economic order quantity is the | Optimum lot size | Highest level of inventory | Capability of plant to produce | None of these | a | The economic order quantity (EOQ) is a company's optimal order quantity for minimizing its total costs related to ordering, receiving, and holding inventory. | Comments | Active | |
| 2 | Routing is essential in the following type of industry: | Assembly industry | Process industry | Job order industry | Mass production industry | a | Routing determines what work is to be done and where and how it will be done. Taking from raw material to the finished product, routing decides the path and sequence of operations to be performed on the job from one machine to another. Routing is essential in the Assembly industry. |
Comments | Active | |
| 3 | What does symbol imply in work study?  |
Operation | Inspection | Transport | Permanent Storage | b | Inspection: It is an act of Checking for correctness of the quantity or quality of the items. |
Comments | Active | |
| 4 | Bin cards are used for | Machine loading | Stores | Accounts | None of these | b | Bin cards, which are sometimes referred to as inventory cards or stock cards, are record-keeping documents used in retail and other businesses that require a stock room. They keep a running balance of a business's inventory. | Comments | Active | |
| 5 | Interchangeability can be achieved by | Standardization | Better process planning | Simplification | Better product planning | a | The concept of interchangeability is try to use parts that are standard. So interchangeability can be achieved by the standardization of the product. Interchangeability or interchangeable manufacturer means that any standardized component will assemble correctly with a mating component, both being chosen at random. |
Comments | Active | |
| 6 | Which of the following measuring instrument can’t be used to know the value of a dimension? |
Screw gauge | GO-NO GO gauge | Slip gauge | None of these | b | Go No-Go gauges are inspection tools used to determine if manufactured parts are within specified tolerance limits. | Comments | Active | |
| 7 | The word “Kanban†is used in | EOQ | JIT | MRP | SCM | b | Kanban is an inventory control system used in just-in-time (JIT) manufacturing. It was developed by TaiichiOhno, an industrial engineer at Toyota, and takes its name from the colored cards that track production and order new shipments of parts or materials as they run out. | Comments | Active | |
| 8 | Quality management standards are controlled by | ISO 7000 | ISO 8000 | ISO 9000 | ISO 14000 | c | Standards related to quality management systems include the rest of the ISO 9000 series (including ISO 9000 and ISO 9004), the ISO 14000 series (environmental management systems), ISO 13485 (quality management systems for medical devices), ISO 19011 (auditing management systems). | Comments | Active | |
| 9 | Basic tool in work study is | Graph paper | Process chart | Planning chart | Stop-watch | d | Stop watch is used for the time study or work measurement. | Comments | Active | |
| 10 | Which of the following production system is characterised by the low production volume? | Project Production System | Job Shop Production System | Batch Production System | Mass Production System | b | Job shop production system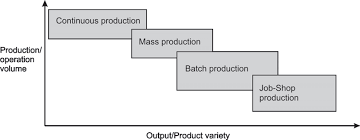 |
Comments | Active | |
| 11 | Which of the following has quick return mechanism? | Shaper | Drilling machine | Printing press | Milling machine | a | Shaper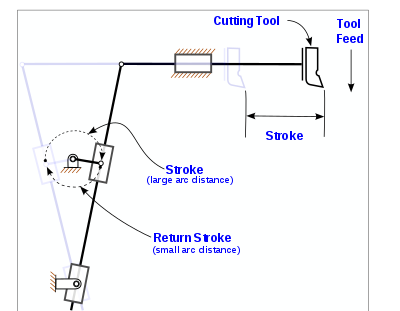 |
Comments | Active | |
| 12 | Process layout is employed for | Batch production | Continuous type of production | Effective utilisation of machines | None of these | a | Process layout is recommended for batch production. All machines performing a similar type of operations are grouped at one location in the process layout e.g., all lathes, milling machines, etc. are grouped in the shop will be clustered in like groups. | Comments | Active | |
| 13 | The chart used in Quality Control is/are | C-chart | R-chart | P-chart | All of these | d | 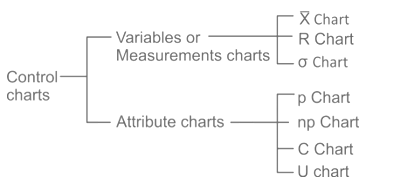 |
Comments | Active | |
| 14 | The symbol used for transport in work study is | 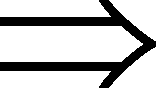 |
 |
 |
 |
a |  |
Comments | Active | |
| 15 | Which layout is suitable for multi-product company carring out batch production? | Product layout | Process layout | Point layout | All of these | b | Process layoutsuitable for multi-product company carring out batch production. | Comments | Active | |
| 16 | Which of the following is not significant in determination of economic order quantity in inventory control? | Ordering cost | Lead time | Inventory carrying cost | All of these | b | Lead time is not significant in determining the EOQ. \(EOQ=\frac{2DC_{o}}{C_{h}}\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 17 | Which of the following safety measures is used to promote the safety? | Excessive fine | Writing slogans | Stopping the work | All of these | b | Writing slogans promote the safety. | Comments | Active | |
| 18 | Plant layout used for automobile assembly unit is | Product layout | Process layout | Point layout | Static layout | a | In this layout equipment or work-processes are arranged according to the requirement of a specific product. The path for each part is, in effect, a straight line. Automobile manufacturing is an example of the product layout industry. | Comments | Active | |
| 19 | Work study is mainly aimed at | Determining the most efficient method of performing a job. | Estimating the minimum time of completion of job. | Developing the standard method and standard time for a job. | Economizing the motions involved on the part of the work while performing a job. | c | Work study involves Method study and time study. | Comments | Active | |
| 20 | Which of the following layout is useful when the product being processed is very big, heavy or difficult to move? | Fixed position layout | Process layout | Product layout | Cellular layout | a | In a fixed-position layout, the project remains in one place, and workers and equipment come to that one work area. Examples of this type of project are a ship, a highway, a bridge, a house, and an operating table in a hospital operating room. | Comments | Active | |
| 21 | Indian Boiler Act, 1923 is applicable to | All boilers | Boilers more than 100 litres capacity | Boilers more than 1000 litres capacity | None of the above | b | The Indian Boilers Act-1923 was enacted with the objective to provide mainly for the safety of life and Property of persons from the danger of explosions of steam boilers and for achieving uniformity in registration and inspection during operation and maintenance of boilers in India. | Comments | Active | |
| 22 | Which of the followings, leads to industrial hazards and causes accidents? | Noise and vibrations | Poor lighting and Poor ventilation | Heat and Humidity | All of these | d | common causes which leads to industrial hazards and accidents are: Poor lighting: Low visibility is a common cause of slips, trips, and falls. Ambient temperature: If a workplace is too hot, overheating can occur. If the workplace is too cold, frostbite or hypothermia can occur. Air pollution: Breathing issues can develop if a workplace has poor ventilation or air pollution. Sound pollution: The sound in a workplace can cause injury to a worker's hearing. |
Comments | Active | |
| 23 | Which of the followings helps in accident control? | Automatic safety guard | Interlock safety guard | Trip safety guard | All of these | d | Following points are helps in control accidents:i. Fixed guards.ii. Fixed limited access guards.iii. Fixed adjustable access guard.iv. Interlock guards.v. Automatic guards. vi. Trip safety guardvii. Safety by Machine Controls.viii. Safety by Precautions and Maintenance.ix. Criteria for Machine Guard Selection. |
Comments | Active | |
| 24 | Standard time is defined as | Normal time + allowance | Normal time + idle time | Normal time + idle time + allowance | None of these | a | Standard time = normal time + allowance | Comments | Active | |
| 25 | According to the definition of “week†under the Factory Act, 1948, it is a period of 7 days beginning at midnight on | Sunday | Monday | Saturday | Friday | c | An Act to consolidate and amend the law regulating labor in factories. It shall come into force on the 1April 1949. "Week" means a period of seven days beginning at midnight on Saturday night | Comments | Active | |
| 26 | In ABC analysis, A-type inventory represents | High value, High volume | High value, Low volume | Low value, Low volume | Low value, High volume | b | High value, Low volume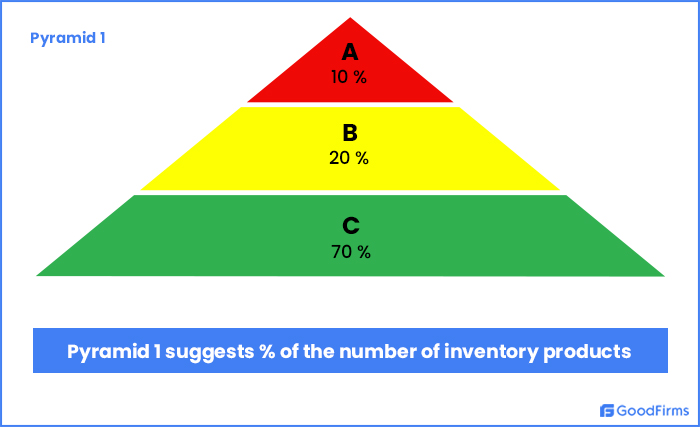  |
Comments | Active | |
| 27 | Which of the following material handling devices are used for the movement of materials in a fixed route and fixed area of operation? | Cranes | Pallets | Industrial Trucks | Elevators | a | Cranes are used to transport material from one fixed point to another fixed point. | Comments | Active | |
| 28 | Which of the followings control chart is variable control chart? | P-chart | C-chart | U-chart | R-chart | d | 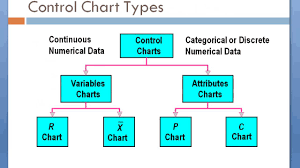 |
Comments | Active | |
| 29 | Per cent idle time for men and machine is found by | Work sampling | Time study | Method study | Work study | a | Percent idle time for men or machines is found by Work sampling. | Comments | Active | |
| 30 | Break Even point represents | Profit | Loss | No Profit and No Loss | None of these | c | The break-even point represents the time when unit can run without any loss and profit. | Comments | Active | |
| 31 | For transmitting power without slip, drive used is | Rope drive (b) Belt drive | Cone drive (d) Chain drive | d | A chain drive is also called a positive drive because there is no slip. | Comments | Active | |||
| 32 | Which one is not a part of cotter joint? | Socket | Spigot | Fork end | Collar | d | There is no point of mentioning collar alone in a cotter joint. It has to be a spigot collar or socket collar. Three main parts of the cotter joint: Cotter, Spigot, and Socket. |
Comments | Active | |
| 33 | What is the number of jaws in a self-centred chuck of a lathe? | Eight | Five | Four | Three | d | Three jaw, chuck is also known as universal or self centering chuck. The majority of the chucks have two sets of jaws for holding internal and external diameters. | Comments | Active | |
| 34 | Taylor’s tool life equation used to calculate the tool life is given by the equation | \(TV^{n} = constant\) | \(VT^{n} = constant\) | \(VT^{1/n} = constant\) | None of these | b | Taylor's tool life equation is given by, where V is in m/min and T (time) is in min. \(VT^{n}=constant\) | Comments | Active | |
| 35 | Which theory is best to estimate failure load for a ductile material? | Distortion energy theorem | Maximum strain energy theorem | Maximum shear stress theorem | None of these | c | For ductile material, maximum shear stress theorem is most suitable. | Comments | Active | |
| 36 | Rivets are made of following type of material: | Brittle | Low density | Ductile | Low melting point | c | Rivets are used in most applications are made of mild steel, which is a ductile material. There are two varieties of steel rivet bars 1. Hot rolled steel rivet 2. High tensile steel rivet |
Comments | Active | |
| 37 | For proper design of a shaft, it should be designed on the basis of | Maximum principal stress theory | Maximum shear stress theory | Both (a) and (b) | Maximum strain theory | b | For proper design of a shaft, it should be designed on the basis of Maximum shear stress theory. | Comments | Active | |
| 38 | Elastic modulus of steel is | 70 GPa | 210 GPa | 250 GPa | 300 GPa | b | Elastic modulus of steel is 210GPa | Comments | Active | |
| 39 | No. of inversions in a slider crank mechanism is | 1 | 2 | 4 | 6 | c | A slider-crank is a kinematic chain having four links so four inversions. It has one sliding pair and three turning pairs. | Comments | Active | |
| 40 | A steel bar of 5 m length is heated from 15 °C to 90 °C and is free to expand. The bar will induce | Tensile stress | Shear stress | No stress | None of these | c | Stress is nothing but the resisting force since due to temperature rise body will expand and if this expansion due to temperature change is restricted then only resisting stress (thermal stress) will come into play since expansion is not restricted that's why no stress is occurring. | Comments | Active | |
| 41 | A rivet is specified by | Shank diameter | type of load | Length of rivet | None of these | a | The rivet is specified by the diameter of its shank.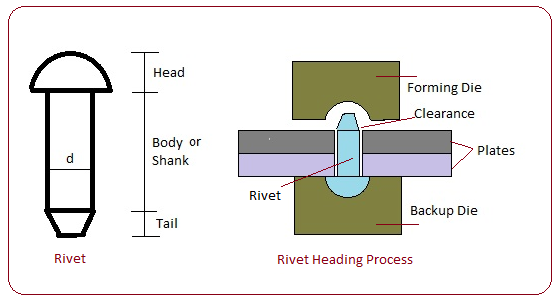 |
Comments | Active | |
| 42 | In a gib and cotter joint, the gib and cotter are subjected to | Single shear only | Double shear | Single shear and crushing | Double shear and crushing | d | Cotter and Gib are in double shear and crushing. |
Comments | Active | |
| 43 | Piston rod and cross head in a steam engine are usually connected by means of | Cotter joint | Knuckle joint | Ball joint | Universal joint | a | Cotter's joint is widely used to connect the piston rod and crosshead of a steam engine, as a joint between the piston rod crosshead, and the tailor pump rod, foundation bolt, etc.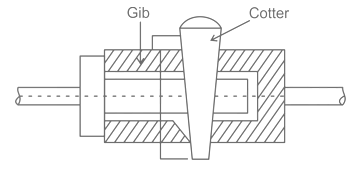 |
Comments | Active | |
| 44 | A key connecting a flange coupling to a shaft is likely to fail in | Shear | Tension | Torsion | Bending | a | A key connecting a flange coupling to a shaft is likely to fail in shear. | Comments | Active | |
| 45 | Anti-friction bearings are | Hydro-dynamic bearings | Sleeve bearings | Thin lubricated bearings | Ball and roller bearings | d | The antifriction bearing consists of rolling elements, races, and cage. Rolling elements are available in different shapes such as balls, parallel rollers, taper rollers, barrels, and needles. They are made of chromium or chrome-nickel steel with ground or polished surface. The load of the rotating member is carried by the rolling elements. Example: Ball bearing, Roller bearings, Needle bearing |
Comments | Active | |
| 46 | What is the function of a washer? | Provides cushioning effect | Provides bearing area | Absorbs shocks and vibrations | Provides smooth surface in place of rough surface | b | A washer is a thin plate (typically disk-shaped) with a hole (typically in the middle) that is normally used to distribute the load of a threaded fastener, such as a screw or nut. Washers are used to distribute the clamping pressure over a larger area and prevent surface damage. |
Comments | Active | |
| 47 | The usual proportion for the width of key is (where d is the diameter of the shaft) | \(\frac{d}{8}\) | \(\frac{d}{6}\) | \(\frac{d}{4}\) | \(\frac{d}{2}\) | c | The usual proportion for the width of the key used for transmitting power is d/4. Where d is the diameter of the shaft. | Comments | Active | |
| 48 | The sleeve of Muff coupling is designed as a | Thin cylinder | Thick cylinder | Solid shaft | Hollow shaft | d | The power is transmitted from one shaft to the other shaft by means of a key and a sleeve or muff. The sleeve or muff coupling is designed as a hollow shaft. | Comments | Active | |
| 49 | What strength is to be considered for ductile material under cyclic load? | Ultimate strength (b) Yield strength | Endurance strength (d) Fracture strength | c | Endurance strength: For cyclic loading conditions endurance strength is considered. | Comments | Active | |||
| 50 | Initial cost of making a product is ` 1,00,000 and variable cost per unit is ` 40. If it’s selling price is ` 80 per unit, what would be the break even quantity? | 2500 units | 3500 units | 5000 units | 7000 units | a | \( Break even quantity=\frac{Fixed cost}{Price per unit-Variable cost}\) \(=\frac{100000}{80-40}=2500 units \) |
Comments | Active | |
| 51 | Parallel fillet welded joints are designed for | Tensile strength | Compressive strength | Bending strength | Shear strength | d | When load acts parallel to the length of the weld, the weld is called parallel fillet weld. Parallel fillet welds are designed for shear strength. | Comments | Active | |
| 52 | A cotter joint is used to connect two rods which are in | Tension only | Compression only | Tension and Compression | Shear only | c | Cotter's joint is used to join two shafts which are in Rotation. Cotter's joint is used when the members are subjected to Axial Tensile or Compressive Loading. |
Comments | Active | |
| 53 | A knuckle pin may fail in | Shear | Bending | Crushing | All of these | d | The modes of failure are: Shear failure of pin (single shear).Crushing of pin against rod and tensile failure of flat end bar. Application:Tie rod joint of roof truss.Tension link in bridge structure.Link of roller chain.Tie rod joint of jib crane.The knuckle joint is also used in tractor.Connecting rods between locomotive wheels. |
Comments | Active | |
| 54 | In design of flange coupling, the weakest element should be | Key | Bolt | Flange | Shaft | a | Key is the weakest element of flange coupling which can be easily replaceable and economically it cost less in comparison other parts which much high. | Comments | Active | |
| 55 | The rated life of a bearing varies | Directly with load | Inversely as square of load | Inversely as cube of load | None of these | c | Let P=load on bearing \(Life of bearing, L=(\frac{C}{P})^{n}\) For ball bearing: n=3 so For roller bearing: n=10/3n is the exponent of life equation \(Lâˆ\frac{1}{P^{3}}\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 56 | In leaf springs, the longest leaf is known as | Lower leaf | Master leaf | Upper leaf | None of these | b | The longest leaf of the leaf spring is known as the "Master Leaf". The ends of the master leaf are rolled which are known as the "eye". | Comments | Active | |
| 57 | In case of straight turning operation, length of work piece is 120 mm and feed rate is 0.25 mm/se(c) How long will it take to complete the turning operation? | 8 minute | 10 minute | 12 minute | None of these | a | length of workpiece \( \) \(l=120 mm\) \(feed rate V_{f}=f×n=0.25 mm/sec\) \(Machining Time T_{m}=\frac{l}{f×n}=\frac{l}{V_{f}}=\frac{120}{0.25}=480sec=8 minute \) |
Comments | Active | |
| 58 | Nichrome is used in | Gas turbine | Air craft engine | Heater element | Brake lining | c | A nichrome wire is used as a heating element because of its high melting point and high resistivity (low conductivity) also. Having a high melting does not allow the nichrome wire to melt easily when a large amount of heat is produced. | Comments | Active | |
| 59 | When a nut is tightened by placing a washer below it, the bolt will be subjected to | Tensile stress | Compressive stress | Shear stress | None of these | a | Bolts are always subjected to tensile stress when nut is tightened. The washer will be in compression. | Comments | Active | |
| 60 | Which of the following materials is not desirable for rivets making? | Mild steel | Cast iron | Aluminium | Copper | b | Rivets are made up of ductile materials while cast iron is a brittle material. Therefore it is not recommended for rivets making. | Comments | Active | |
| 61 | In involute gears, pressure angle is | Dependent on size of teeth | Dependent on size of gear | Zero | Always constant | d | For involute gear profile, the pressure angle is constant throughout the engagement of teeth. | Comments | Active | |
| 62 | For oil-pumps in small IC engines which gears can be used? | Spur gears | Crossed helical gears | Gear train | None of these | b | Crossed helical gears are used for oil pumps in I.C. engines. | Comments | Active | |
| 63 | In a compound gear train there is | Only one gear on each shaft. | More than one gear on a shaft. | No gear on driving shaft. | None of these | b | When a series of gears are connected in such a way that two or more gears rotate about an axis with the same angular velocity, it is known as compound gear train. | Comments | Active | |
| 64 | Which of the followings is a higher pair? | Belt and pulley | Turning pair | Screw pair | Sliding pair | a | When a pair has point or line contact between the links, it is known as higher pair e.g. Belt and pulley, wheel rolling on a surface, cam and follower pair |
Comments | Active | |
| 65 | Piston, piston rod and cross-head of a steam engine constitute | One link | Two link | Three link | Do not constitute any link. | a | In a reciprocating steam engine, piston, piston rod and crosshead constitute one link; connecting rod with big and small end bearings constitute a second link; crank, crank shaft and flywheel a third link and the cylinder, engine frame and main bearings a fourth link. | Comments | Active | |
| 66 | The Brinell hardness is calculated by: (Where F is load in N, D is steel ball diameter and d is indentation diameter in millimetres.) | \(\frac{F}{Ï€D(D-D^{2}-d^{2}}\) | \(\frac{F}{Ï€DD^{2}-d^{2}}\) | \(\frac{2F}{Ï€D(D-D^{2}-d^{2}}\) | \(\frac{2F}{Ï€D^{2}}\) | c |  |
Comments | Active | |
| 67 | For a watt governor, what will be the angular speed corresponding to the height of 10 cm, if g = 10 ? \(m/sec^{2}\) | 1 rad/sec | 7.29 rad/sec | 10.0 rad/sec | 3.15 rad/sec | a | \( ω=10 rad/sec, h=?\) \(h=\frac{g}{ω^{2}}\) \(h=\frac{10}{100}=10 rad/sec\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 68 | Angle moved by the cam during which follower remains at its highest position is called | Angle of dwell | Angle of descent | Angle of ascent | Angle of action | a | It is the angle through which the cam turns while the follower remains stationary at the highest or the lowest position. |
Comments | Active | |
| 69 | In spur gears | Both shafts are parallel. | Teeth are straight. | Teeth are parallel to axis. | All of these. | d | The spur gear is cylindrical and has straight teeth cut parallel to its rotational axis. It can be manufactured to close tolerances and is used to connect parallel shafts that rotate in opposite directions. Because contact is simultaneous across the entire width of the meshing teeth, it tends to be noisy at high speeds. |
Comments | Active | |
| 70 | Backlash in gears is | Addendum + Dedendum | Circular pitch + Tooth thickness | Space width between two teeth – Tooth thickness | None of the above | c | Backlash in gears is defined as difference in width of tooth space and engaging tooth thickness. Backlash=Width of tooth space-Tooth thickness 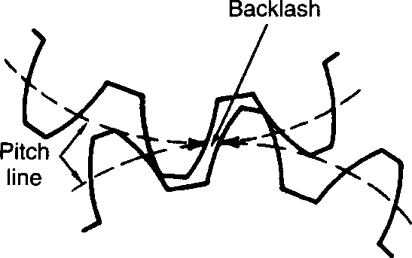 |
Comments | Active | |
| 71 | The creep in a belt drive is due to | Material of the pulleys | Material of the belt | Unequal size of pulleys | Unequal tensions and slackness of the belt | d | Creep is due to the elastic property of the belt material whereas, the conventional slip is due to insufficient frictional grip between the belt and pulley. However, the effect of the creep, as well as slip, is to reduce the speed ratio, and hence power transmission. | Comments | Active | |
| 72 | Cam converts the rotary motion into | Rotary motion | Translatory motion | Both rotary and translatory motions | None of these | c | A cam is a mechanical member used to impart desired motion to a follower by direct contact. The cam may be rotating or reciprocating or oscillating. It is used in automatic machines, IC engines, machine tools, printing control mechanisms. |
Comments | Active | |
| 73 | Sensitiveness of governor is defined as | \(\frac{Range of speed}{Mean speed}\) | \(\frac{Mean speed}{Range of speed}\) | Mean speed × Range of speed | None of these | a | The sensitiveness is defined as the ratio of the difference between the maximum and minimum equilibrium speeds to the mean equilibrium speed. \(Sensitiveness=\frac{Range of speed}{Mean speed}=\frac{N_{max}-N_{min}}{N_{mean}}\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 74 | The factor that decides the size of the cam is | Prime circle | Pitch circle | Base circle | Pitch curve | c | Base circle: it is a smallest circle, drawn tangential to the cam profile. The base circle decides the overall size of the cam and thus is a fundamental feature.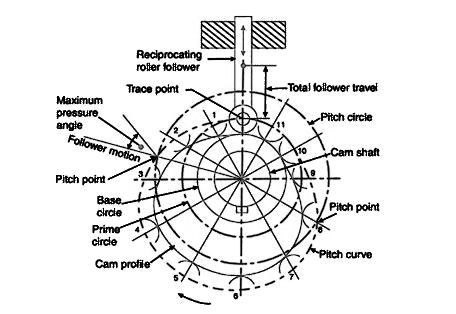 |
Comments | Active | |
| 75 | For maximum power to be transmitted by the belt, the maximum permissible tension in the belt is | Equal to centrifugal tension | Twice the centrifugal tension | Thrice the centrifugal tension | Four-times the centrifugal tension | c | Condition for Maximum power transmitted by the belt is:Â i.e. power transmitted will be maximum when tension is equal to three-time centrifugal tension or it shows that when the power transmitted is maximum, 1/3rd of the maximum tension is absorbed as centrifugal tension. \(T=3T_{C}\) | Comments | Active | |
| 76 | For a governor running at constant speed, the force acting on the sleeve is | Constant | Minimum | Maximum | Zero | d | When a governor is running at a constant speed, it is in equilibrium and the net force acting on the sleeve is zero. If the load on the engine changes, the speed also changes and hence, the sleeve of the governor changes its position. | Comments | Active | |
| 77 | Crowning on pulleys helps | In increasing velocity ratio. | For automatic adjustment of belt so that belt runs centrally. | Increase the belt life. | Decrease initial tension. | b | A crowned pulley is a pulley that has a slight hump in the middle, tapering off ever so slightly towards either edge. |
Comments | Active | |
| 78 | The height of Watt’s governor is proportional to (Where N: rpm of balls) |
N | \(N^{2}\) | \(\frac{1}{N}\) | \(\frac{1}{N^{2}}\) | d | where h is the height of governor. N is revolution per minute. \( h=\frac{895}{N^{2}}, hâˆ\frac{1}{N^{2}}\) | Comments | Active | |
| 79 | The working surface above the pitch surface of the gear tooth is termed as | Addendum | Dedendum | Face | Flank | c | Face of a tooth: This is the working surface of the tooth above the pitch circle. |
Comments | Active | |
| 80 | Factor of safety is the ratio of | Breaking stress to working stress | Endurance limit to yield stress | Elastic limit to ultimate stress | Ultimate stress to working stress | d | Factor of safety for ductile material \(FOS=\frac{Yield stress}{Working stress}\) Factor of safety for brittle material \(FOS=\frac{Ultimate stress}{Working stress}\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 81 | Which of the following concurrent forces cannot have a resultant of 4N? | 2N and 4N | 2N and 6N | 2N and 8N | All of these | c | We know that \(Resultant force, R=F_{1}^{2}+F_{1}^{2}+2F_{1}F_{2}cosθ\) For max R, \(cosθ=1\) \(R_{max}=F_{1}+F_{2}\) For min R, \(cosθ=-1\) \(R_{min}=F_{1}-F_{2}\) In option C, & \(F_{1}=2 \) \(F_{2}=8\) So, \(R_{max}=2+8=10 N\) \(R_{min}=2-8=-6 N\) So option C will be correct answer. |
Comments | Active | |
| 82 | Young’s modulus of elasticity for a perfectly rigid body is | Zero | Unity | Infinity | Cannot be known | c | The ratio of stress and strain is called young's modulus. For a perfectly rigid body, whatever may be the stress, strain will be always zero. So young's modulus will be infinite for a rigid body. | Comments | Active | |
| 83 | Jet engine works on the principle of | Conservation of energy | Conservation of linear momentum | Earth’s gravity | None of these | b | A jet engine works on the principle of conservation of linear momentum. In jet engines, a large volume of gases produced by the combustion of fuel is allowed to escape through a jet in the backward direction. Due to the very high speed or velocity, the backward rushing gases have a large momentum. They impart and equal and opposite momentum to the jet engine due to which the jet engine moves forward with a great speed. |
Comments | Active | |
| 84 | Two forces of equal magnitude ‘P’ act at an angle 120° to each other. What will be their resultant? | 2P | P | P \(2\) | \(\frac{P}{2}\) | b | \(F_{1}=F_{2}=P,θ=120^{0}\) \(Resultant (R)=F12+F22+2F_{1}F_{2}cosθ\) \(R=P^{2}+P^{2}+2P×P×cos120^{0}\) \(R=2P^{2}-2P^{2}×\frac{1}{2}\) \(R=P\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 85 | Four forces P, 2P, 3P and 4P act along the sides, taken in order of a square ABCD. The resultant force is | Zero | \(22 P\) | 2P | P \(5\) | b | \(Net force along x axis F_{x}=P-3P =-2P\)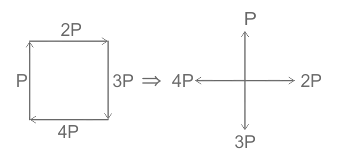 \(Net force along y axis F_{y}=4P-2P=-2P\) \(F_{net}=Fx2+Fy2=(-2P)^{2}+(2P)^{2}\) \(F_{net}=4P^{2}+4P^{2}\) \(F_{net}=22P\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 86 | A weight of 1000 N is supported by two chains as shown in Figure. What will be the tension in Chain-1 and Chain-2 respectively? 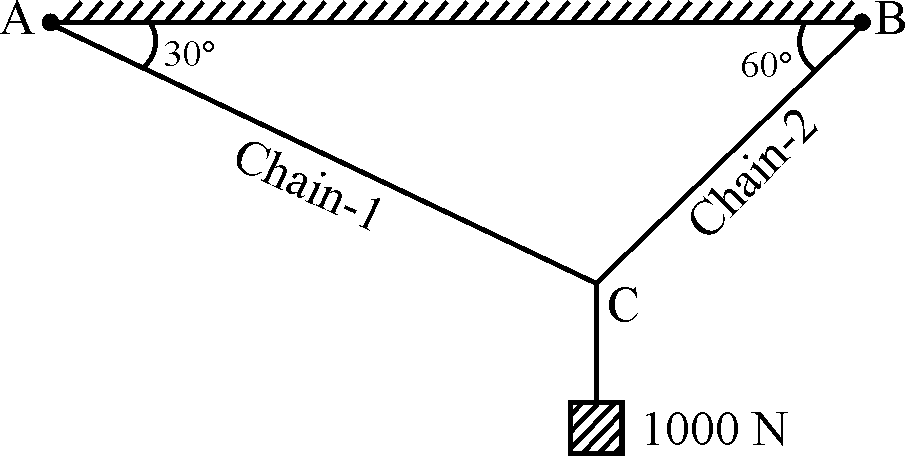 |
500 N; 866 N | 500 N; 433 N | 1000 N; 866 N | 1000 N; 433 N | a | Applying the lami’s theorem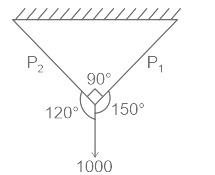 \(\frac{P_{2}}{sin150}=\frac{P_{1}}{sin120}=\frac{1000}{sin90}\) So \(P_{2}=1000sin150=500 N\) \(P_{1}=1000sin120=866.02 N\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 87 | Three parallel forces , and are acting on a log as shown in Figure and the body is in equilibrium. If force = 250 N and = 1000 N; and the distance between and is 1.0 m, then what is the distance of from ? \(F_{1}\) \(F_{2}\) \(F_{3}\) \(F_{1}\) \(F_{3}\) \(F_{1}\) \(F_{2}\) \(F_{2}\) \(F_{3}\)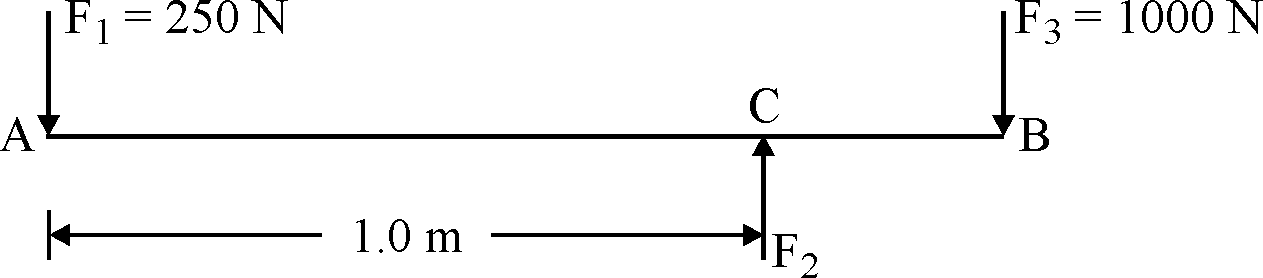 |
0.50 m | 0.25 m | 0.75 m | 0.15 m | b | From Fig \(F_{2}=250+1000=1250 N\) Taking moment about A \(1250×1=1000×(CB+1)\) \(CB=0.25 m\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 88 | A body of weight 100 N is placed on a rough horizontal plane. What will be the co-efficient of friction between surfaces if a horizontal force of 60 N just causes the body to slide over the horizontal plane? | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.6 | d | Weight of the body (W) = 100 N Force applied horizontally to move the body (F) = 60 N \(Cofficient of friction(μ)=\frac{F}{N}\) \(F=Limiting force, N=Normal reaction\) Normal reaction will be equal to the weight of the body \(μ=\frac{60}{100}=0.6\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 89 | For a perfect frame, the number of joints (j) and the number of members (n) are given by | n = 2j – 3 | j = 2n – 3 | n = j – 3 | j = n – 3 | a | \( n=2j-3\) n = Number of members, and j = Number of joints. |
Comments | Active | |
| 90 | An effort of 100 N is applied to a machine to lift a load of 900 N. The distance moved by the effort is 100 cm. The load is raised through a distance of 10 cm. What is the efficiency of the machine? | 80% | 90% | 70% | 60% | b | Effort applied P = 100 NLoad lifted W = 900 NDistance moved by effort, y = 100 cmDistance moved by load, x = 10 cm \(Mechanical advantage (M.(A))=\frac{W}{P}=\frac{900}{100}=9\) \(Velocity ratio (V.R.)=\frac{y}{x}=\frac{100}{10}=10\) \(Efficiency(η)=\frac{M.A}{V.R}=\frac{9}{10}=0.9=90%\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 91 | A simply supported beam AB of length 9 m, carries a uniformly distributed load of 10 kN/m for a distance of 6 m from end (A) What are the reaction forces at A and at B? | 40 N and 20 N | 60 N and 20 N | 20 N and 60 N | 30 N and 15 N | a | 6 m6 m 6 m 6 m 60 kN60 kN 60 kN 60 kN 3 m3 m3 m3 mR1R1R2R2 3 m 3 m 3 m 3 m R1 R1 R2 R2 \(R_{1}+R_{2}=60 kN\) Taking moment about point 1 \(R_{2}×9=60×3\) \(R_{2}=20 kN\) \(R_{1}=40 kN\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 92 | A body in Simple Harmonic Motion will have maximum velocity when its amplitude is | Maximum | Negative maximum | Zero | Average | c | where v is the velocity at any time t or displacement x, A is amplitude, t is time, and is the angular frequency. \( v=ωA^{2}-x^{2 }\) \( \) \( ω\) The maximum value of v in this equation can be obtained when x = 0 and x = 0 means mean position or equilibrium position. So at the mean position, the speed of a particle executing SHM is maximum and its value is Αω. Therefore, A body in Simple Harmonic Motion will have maximum velocity when its amplitude is zero. |
Comments | Active | |
| 93 | Moment of inertia of a body does not depend upon | Mass of the body | Distribution of mass in the body | Axis of rotation of the body | Angular velocity of the body | d | Moment of inertia of a body depends on the mass of the body, its shape and size, distribution of mass about the axis of rotation, and the position and orientation of the axis of rotation. | Comments | Active | |
| 94 | In case of concurrent and coplanar forces, the condition of equilibrium is | ∑H = 0; ∑V = 0; ∑M = 0 | ∑H = 0; ∑V = 0 | ∑H = 0; ∑V ≠0 | ∑H = 0; ∑M = 0 | b | For concurrent and coplanar forces, ∑H = 0; ∑V = 0. No moment equation will be taken as forces are concurrent. |
Comments | Active | |
| 95 | Which one of the following is not a unit of energy? | Newton-metre | kCal | Watt | Watt-hours | c | Watt is unit of power. | Comments | Active | |
| 96 | The ratio of limiting force and normal reaction is known as | Co-efficient of friction | Angle of friction | Angle of repose | Frictional resistance | a | The ratio of limiting friction and normal reaction is known as the coefficient of friction. | Comments | Active | |
| 97 | The unit of moment is | N/m | N-m | N/m2 | N-m/sec | b | Moment of force is defined as the product of force and perpendicular distance from the axis; so its SI unit is Newton-meter (Nm). | Comments | Active | |
| 98 | In comparison to rolling friction, the value of sliding friction is | More | Less | Equal | Double | a | When an object slides, sliding friction is involved, while rolling friction is involved when an object rolls over the surface of another object. As the area of contact is more in the case of sliding than in the case of rolling. Therefore, sliding friction is more than the rolling friction. | Comments | Active | |
| 99 | In thin cylindrical shell, the value of circumferential stress as compared to the longitudinal stress is | Equal | Double | Triple | None of these | b | \( Circumferential stress,σ_{h}=\frac{pd}{2t}\) \(Longitudinal stress, σ_{l} =\frac{pd}{4t}\) \(σ_{h}=2σ_{l}\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 100 | Bow’s notation is used to indicate | Forces | Moment | Pressure | Velocity | a | Bow's Notation is a labelling convention whereby the spaces in between any group of forces is labelled with a capital letter such that each force is then straddled by two letters.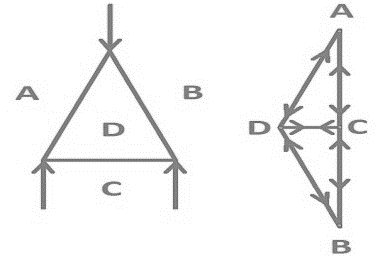 |
Comments | Active | |
| 101 | In first system of pulley, the mechanical advantage is equal to (Where n : no. of pulleys) |
\(2^{n-1}\) | \(2^{n}\) | n | \(2^{n} – 1 \) | b | In general, in the first order pulley system, velocity ratio (VR) is given by 2n, where, n is the number of movable pulleys present in the system. | Comments | Active | |
| 102 | The velocity ratio of Weston’s differential pulley is: (Where R: Radius of bigger pulley r: Radius of smaller pulley) |
\(\frac{2R}{R-r}\) | ) \(\frac{2r}{R-r}\) | \(\frac{R}{R-r}\) | \(\frac{R}{2R-r}\) | a | \( Velocity ratio=\frac{Distance moved by effort}{Distance moved by load}=\frac{Ï€D}{Ï€\frac{(D-d)}{2}}=\frac{2R}{R-r}\) | Comments | Active | |
| 103 | The value of Poisson’s ratio is always | More than 1 | 1 | Less than 1 | None of these | c | \( μ=0 to 0.5 (under uni-axial loading)\) \(μ=0 for cork\) \(μ=0.5 for perfectly plastic body (Rubber)\) | Comments | Active | |
| 104 | If the bulk modulus is K, modulus of Elasticity is E and Poisson’s ratio is then which of the following is true?0 \(\frac{1}{m},\) | \(E=3K(1+\frac{2}{m})\) | \(E=3K(1-\frac{1}{m})\) | \(E=3K(1-\frac{2}{m})\) | \(E=3K(1+\frac{1}{m})\) | c | Relation between E, G, K, \(μ(μ=\frac{1}{m})\) \(E=3K(1-\frac{2}{m})\) \(E=2G(1+\frac{1}{m})\) \(E=\frac{9KG}{3K+G}\) \(μ=\frac{3K-2G}{6K+2G}\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 105 | Limiting force of friction is defined as the frictional force which exists when a body | Is moving with maximum velocity | Is stationary | Just begins to slide over the surface | None of these | c | Limiting Friction: - The maximum friction that can be generated between two static surfaces in contact with each other. Once a force applied to the two surfaces exceeds the limiting friction, motion will occur. For two dry surfaces, the limiting friction is a product of the normal reaction force and the coefficient of limiting friction. Laws of limiting friction: (i) The force of limiting friction depends upon the nature of surfaces in contact and-acts tangentially to the interface between the two surfaces. (ii) The force of limiting friction between two surfaces in contact is independent of the area of contact. |
Comments | Active | |
| 106 | The ratio of linear stress to the linear strain is called | Modulus of rigidity | Modulus of elasticity | Bulk modulus | Poisson’s ratio | b | \( Modulus of rigidity (G)=\frac{Shear stress}{shear strain}\) \(Bulk modulus(K)=\frac{Direct stress}{Volumeteric strain}\) \(Poission Ratio (μ)=\frac{Lateral strain}{Longitudinal strain}\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 107 | A machine is one that | Transfer motion | Does useful work | Have relative motion between links | Have a number of members | b | A machine is a physical system using power to apply forces and control movement to perform an action. | Comments | Active | |
| 108 | Angle of friction is the | Angle between normal reaction and the resultant of normal reaction and the limiting frictional force | Ratio of limiting friction and normal reaction | Ratio of static and dynamic friction | None of the above | a | The angle of friction is defined as the angle between the normal force (RN) and the resultant force (R) of normal force and maximum friction force.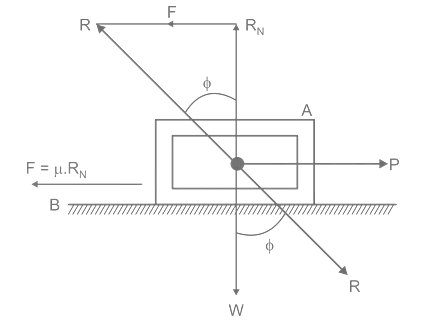 |
Comments | Active | |
| 109 | The co-efficient of friction depends on | Area of contact | Shape of surfaces | Strength of surfaces | Nature of surfaces | d | The coefficient of friction only depends on the nature of the surfaces. It does not depend on any other factors, including the relative speed of the surfaces and the surface area of contact. | Comments | Active | |
| 110 | The product of mass and velocity is known as | Impulse | Momentum | Power | Work | b | Momentum can be defined as "mass in motion." All objects have mass; so if an object is moving, then it has momentum - it has its mass in motion. Momentum depends upon the variables mass and velocity. Momentum=M.V |
Comments | Active | |
| 111 | Pure iron at room temperature has following micro structure: | γ-iron | δ-iron | Cementite | α-iron | ( undergoes a change in crystal structure when heated above forming or ‘austenite’. \(α-iron or 'ferrite')\) \(910^{0}C,\) \(γ-iron,\) | Comments | Active | ||
| 112 | If T is the recrystallization temperature, the cold working of steel is done at | Greater than T °C | Equal to T °C | Less than T °C | None of these | c | Hot working is the process of plastically deforming a metal above the metal's recrystallization temperature. Cold working or work hardening is the process of strengthening a metal by plastic deformation at temperatures below the recrystallization temperature. | Comments | Active | |
| 113 | The machinability of steel can be improved by alloying the steel with | Copper | Chromium | Nickel | Sulphur | d | Sulphur improves machinability but lowers transverse ductility and toughness. | Comments | Active | |
| 114 | Addition of Nickel to Steel helps in improving | Fatigue resistance | Creep resistance | Corrosion resistance | Cost reduction | a | Addition of nickel in steel increase the fatigue strength without the loss of ductility. | Comments | Active | |
| 115 | The chisel used for cutting steel sheets is usually | Annealed | Normalised | Hardened | Hardened and Tempered | d | The cutting edge of a chisel should be Hardened and tempered.A chisel is a tool with a characteristically shaped cutting edge of blade on its end, for cutting a hard material such as wood, stone, or metal. By hand, struck with a mallet, or mechanical power. | Comments | Active | |
| 116 | Which of the following is a case hardening process? | Carburizing | Nitriding | Cynading | All of these | d | There are different Surface Hardening or Case Hardening processes. They areCarburizingNitridingCyanidingInduction HardeningFlame Hardening | Comments | Active | |
| 117 | Which of the following is the amorphous material? | Lead | Brass | Glass | Silver | c | Amorphous or non-crystalline solid is a solid that lacks the long-range order that is characteristic of a crystal | Comments | Active | |
| 118 | Which among the followings is the most effective strengthening mechanism of non-ferrous materials? | Solid solution hardening | Strain hardening | Grain size refinement | Precipitation hardening | a | Precipitation hardening is also termed as age hardening. This is one of the important strengthening mechanism of nonferrous alloys. | Comments | Active | |
| 119 | Toughness is related to | Moment of inertia | Hardness | Energy absorbed before fracture | Fatigue loading | c | Energy absorbed before fracture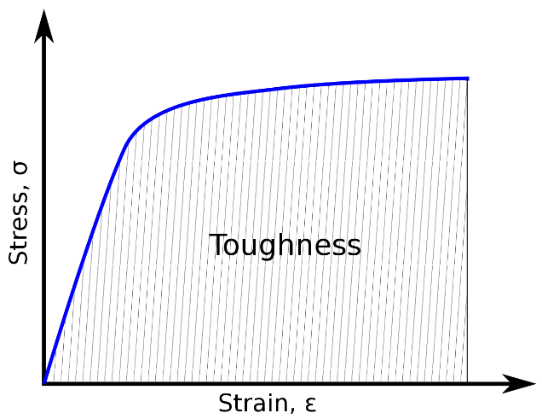 |
Comments | Active | |
| 120 | The slowest cooling rate is achieved when steel is quenched in | Fused salt | Air | Brine | Mixture of water and oil | b | Order of rate of cooling of most widely used quenching medium Brine>water>oil>air |
Comments | Active | |
| 121 | The ability of material to resist softening at higher temperature is known as | Creep | Hot tempering | Hot hardness | Fatigue | c | Hot hardness or red hardness corresponds to hardness of a material at high temperatures.As the temperature of material increases, hardness decreases and at some point a drastic change in hardness occurs | Comments | Active | |
| 122 | The material having same elastic property in all the directions are called | Ideal materials | Uniform materials | Isotropic materials | Practical materials | c | Isotropic materials are materials whose properties remain the same when tested in different directions. Isotropic materials differ from anisotropic materials, which display varying properties when tested in different directions. Common isotropic materials include glass, plastics, and metals. | Comments | Active | |
| 123 | Eutectoid steel contains following percentage of carbon | 0.02 | 0.30 | 0.63 | 0.87 | d | Eutectoid/Pearlite steel: AÂ 0.84%Â carbon steel or eutectoid steel is known as Pearlite steel. | Comments | Active | |
| 124 | Paramagnetic alpha iron changes to gamma iron at following temperature: | 768 °C | 1440 °C | 908 °C | 1539 °C | a | Below 912 °C (1,674 °F) iron again adopts the BCC structure characteristic of α-iron, also called ferrite. The substance assumes a paramagnetic property and it changes in to gamma iron. | Comments | Active | |
| 125 | Which of the following has maximum ductility? | Copper | Mild Steel | Cast Iron | 18-4-1 Steel | a | Copper is the softest material and usually more ductile among all the given materials in the options. However, Gold has the highest ductility. | Comments | Active | |
| 126 | Brass is an alloy of | Copper and Zinc | Copper and Tin | Arsenic and Tin | Gold and Tin | a | Brass is an alloy of copper and zinc. The colour is yellow or light yellow, or nearly white. Brass is also corrosion resistant Brass is widely used for making motor car radiator and water taps etc. | Comments | Active | |
| 127 | The process of formation of new grains on heating metals is called | Recrystallization | Oxidation | Microstructure | Hardening | a | Recrystallization is a process accomplished by heating where by deformed grains are replaced by a new set of grains that nucleate and grow until the original grains have been entirely consumed. | Comments | Active | |
| 128 | Which element makes stainless steel corrosion resistant? | Vanadium | Chromium | Carbon | Sulphur | b | Stainless steel is a corrosion-resistant alloy of iron, chromium and, in some cases, nickel and other metals. | Comments | Active | |
| 129 | Which of the following metals does not have hexagonal close packed structure? | Magnesium | Zinc | Cadmium | Copper | d | The HCP structure is very common for elemental metals and some examples include beryllium, cadmium, magnesium, titanium, zinc and zirconium. | Comments | Active | |
| 130 | Purpose of normalizing is to | Improve strength | Increase hardness | Remove internal stresses | None of these | c | Normalizing is used because it causes microstructures to reform into more ductile structures. This is important because it makes the metal more formable, more machinable, and reduces residual stresses in the material that could lead to unexpected failure. | Comments | Active | |
| 131 | Which tool is used for rapid machining of hard metals? | Cemented Carbide | High Speed Steel | Stellites | None of these | c | Stellite tools are ideal for rapid machining of hard metals. These are used for making form tools. Stellite is available in the form of bars of round or square section for manufacturing cutting tools; and as inserts to attach to tough steel milling cutter bodies. | Comments | Active | |
| 132 | Which of the following fundamental components of atom is uncharged? | Proton | Neutron | Electron | Positron | c | Common metal mirror coatings consist of thin films of aluminium, silver or gold Because of their high reflectivity. | Comments | Active | |
| 133 | Which metal coating is used in the mirror? | Lead | Tin | Gold | Brass | Comments | Active | |||
| 134 | Pure iron is a substance of | Ferrite | Pearlite | Austenite | Ferrite and Cementite | a | Pure iron is the structure of Ferrite. Austenite is not stable below 725°(C) So upon cooling the sample slowly carbon diffuses from one interstitial position to another and forms alternate plate like structure of ferrite and cementite. | Comments | Active | |
| 135 | Correct sequence of elements of 18 – 4 – 1 HSS tool is | W, Cr, V | Mo, Cr, V | Cr, Ni, C | Cu, Zn, Sn | a | 18-4-1 High-speed steel- contains 18 per cent tungsten (W), 4 per cent chromium (Cr), 1 per cent vanadium (V), 0.7% carbon and rest iron. | Comments | Active | |
| 136 | The unique property of cast iron is its high | Malleability | Ductility | Hardness | Damping characteristics | d | In gray cast iron, the graphite exists in the form of flakes. Due to the presence of these graphite flakes gray Cast Iron possesses high damping capacity and hence these materials are used for lathe machine beds and engine blocks. | Comments | Active | |
| 137 | 18/8 stainless steel contains | 18% Nickel, 8% Chromium | 18% Chromium, 8% Nickel | 18% Tungsten, 8% Nickel | 18% Tungsten, 8% Chromium | b | The numbers 18/8 represent the composition of this steel as 18% chromium and 8% nickel, making it very resistant to corrosion and oxidation. | Comments | Active | |
| 138 | The co-ordination number of face centred cubic structure is | 4 | 8 | 12 | 16 | c | The face-centered cubic (FCC) has a coordination number of 12 and contains 4 atoms per unit cell. The body-centered cubic (bcc) has a coordination number of 8 and contains 2 atoms per unit cell | Comments | Active | |
| 139 | The percentage of carbon in low carbon steel : | 1.0% | 0.15% | 0.87% | 0.50% | b | Dead carbon steel - 0.05% to 0.15% carbon Low carbon or mild steel - 0.15% to 0.45% carbon Medium carbon steel - 0.45% to 0.8% carbon High carbon steel - 0.8% to 2% carbon |
Comments | Active | |
| 140 | Which of the following is close to the purest form of Iron ? | Cast Iron | Wrought Iron | Grey Iron | Mild Steel | b | Wrought iron is the purest form of iron. It contains 0.12 to 0.25% carbon and is thus the purest form of iron. | Comments | Active | |
| 141 | Slenderness ratio is the ratio of | Maximum size of column to minimum size of column. | Width of column to depth of column. | Effective length of column to least radius of gyration of the column. | Effective length of column to width of column. | c | Slenderness ratio of a compression member is defined as the ratio of its effective length to least radius of gyration. Se = Le = Effective length K = Least radius of gyration K = \(\frac{L_{e}}{K}\) \(\frac{I_{Min}}{A}\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 142 | A long column fails by | Crushing | Tension | Shearing | Buckling | d | Failure’s in Column: Short column Medium Column Long column Mode of failure crushing or compression compression and buckling both Buckling (lateral displacement of body) |
Comments | Active | |
| 143 | Euler’s Buckling theory is applicable for | Short columns | Long columns | Medium long columns | All of these | b | Euler’s theory is applicable only for long column. While Rankine theory is applicable to any column (short and long). | Comments | Active | |
| 144 | The most economical section of a beam to bear maximum bending moment is | Square | Circular | Rectangular | I - section | d | In I section, the web resists shear forces, while the flanges resist more than 80% of the bending moment. Beam theory shows that the I-shaped section is a very efficient form for carrying both bending and shear loads in the plane of the web. | Comments | Active | |
| 145 | When a wire is stretched to double its length, the longitudinal strain produced in it is | 0.5 | 1.0 | 1.5 | 2.0 | b | Let original length \(l_{1}=l\) \(l_{2}=2l\) \(Strain=\frac{change in length}{original length}=\frac{l_{2}-l_{1}}{l_{1}}=\frac{2l-l}{l}=1\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 146 | The bending moment on a section is maximum where shear force is | Maximum | Minimum | Changing sign | Zero | d |  |
Comments | Active | |
| 147 | The bending moment diagram for a cantilever beam carrying concentrated load at end of beam will be a | Rectangle | Cubic parabola | Triangle | Parabola | c | 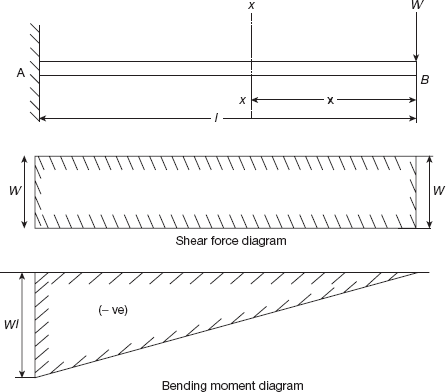 |
Comments | Active | |
| 148 | The property of a material which enables it to resist fracture due to impact loads is known as | Elasticity | endurance | Resilience | toughness | d | Toughness is property of a material to resist fracture due to high impact loads like hammer blows | Comments | Active | |
| 149 | In case of both the ends fixed of a column, the effective length is | Its own length | Twice its length | Half of its length | None of these | c | Euler’s load for different column with different end condition Boundary Condition Le Pe Both ends fixed 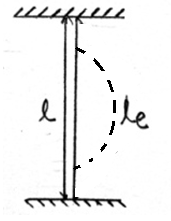 \(\frac{l}{2}\) \(\frac{4π^{2}EI}{l^{2}}\) Both ends are hinged  L \(\frac{π^{2}EI}{l^{2}}\) One end fixed and other end hinged  \(\frac{l}{2}\) \(\frac{2π^{2}EI}{l^{2}}\) One end fixed and other free  2l \(\frac{π^{2}EI}{4l^{2}}\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 150 | The ratio of moment of inertia of a rectangle and that of a triangle, having same base and height with respect to their bases would be | 2 : 1 | 3 : 1 | G. dd d d bb b b MOI with respect to base \(I_{base}=\frac{bd^{3}}{36}+\frac{1}{2}b×d×(\frac{d}{3})^{2}\) \(Traingle,I_{base}=\frac{bd^{3}}{12}\) Therefore the ratio is \(=\frac{\frac{bd^{3}}{3}}{\frac{bd^{3}}{12}}=\frac{4}{1}\) Or ratio is 4:1 |
5 : 1 | c | Comments | Active | ||
| 151 | Which of the following is more elastic? | Rubber | Plastic | Brass | Steel | d | Steel is the most elastic material. If the object is elastic, the body regains its original shape when the pressure is removed. Steel having the steepest linear stress-strain curve among all. | Comments | Active | |
| 152 | Necking phenomenon in stress-strain is observed for | Brittle materials | Ductile materials | Both brittle as well as ductile materials | None of the above | b | Necking is a type of plastic deformation observed in ductile materials subjected to tensile stress. | Comments | Active | |
| 153 | Strain is defined as the ratio of | Change in volume to original volume. | Change in length to original length. | Change in lateral dimension to original lateral dimension. | All of the above | d | Change in volume to original volume is called volumetric strain. Change in length to original length is called the linear strain. Change in lateral dimension to original lateral dimension lateral strain. |
Comments | Active | |
| 154 | The longitudinal joint of a boiler shell is always a | Lap joint | Butt joint | Lozenge joint | Diamond joint | b | The boiler has a longitudinal butt joint as well as circumferential lap joint. The longitudinal joint is used to join the ends of the plate to get the required diameter of a boiler. For this purpose, a butt joint with two cover plates is used. | Comments | Active | |
| 155 | 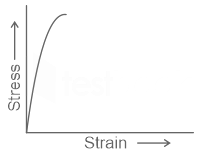 The above stress-strain diagram is for |
Ductile material | Brittle material | Soft material | None of these | b | 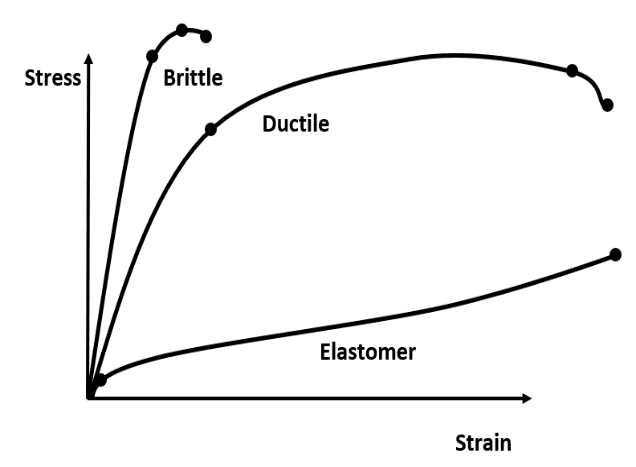 |
Comments | Active | |
| 156 | Moment of inertia of a solid sphere is (Where M = mass of the solid sphere r = radius of the sphere) |
\(Mr^{2}\) | \(\frac{2}{3}Mr^{2}\) | \(\frac{2}{5}Mr^{2}\) | \(\frac{1}{2}Mr^{2}\) | c | \( Solid cylinder=\frac{1}{2}Mr^{2}\) \(Thin cylinder=Mr^{2}\) Solid Sphere = \(Thin Spherical Shell=\frac{2}{3}Mr^{2}\) \(\frac{2}{5}Mr^{2}\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 157 | Flow stress corresponds to | Fluid in motion | Breaking point | Plastic deformation of solids | Rupture stress | c | Flow stress is the stress that must be applied to cause a material to deform at a constant strain rate in its plastic range | Comments | Active | |
| 158 | The fatigue life of a part can be improved by | Electroplating | Polishing | Coating | Shot peening | d | Shot peening is a process specifically designed to enhance the fatigue strength of components which are subject to high alternating stress. | Comments | Active | |
| 159 | Slow plastic deformation of metals under a constant stress at high temperature is known as | Fatigue | Plastic deformation | Creep | Endurance | c | Creep is time dependent inelastic deformation. Creep is the slow plastic deformation of metal under constant stress or under prolonged loading. | Comments | Active | |
| 160 | stress in thin walled cylinder is | Longitudinal tensile stress | Radial stress | Circumferential tensile stress | Compressive stress | c | Hoop stress in thin circumferential tensile stress | Comments | Active | |
| 161 | For perfectly elastic body, the value of co-efficient of restitution is | Zero | 0.5 | 1 | between 0 and 1 | c | If e = 0, then it is a perfectly inelastic collision If 0 < e < 1, then it is a real-world inelastic collision, in which some kinetic energy is dissipated. If e = 1, then it is a perfectly elastic collision in which no kinetic energy is dissipated, and the objects rebound from one another with the same relative speed with which they approached. |
Comments | Active | |
| 162 | Spiral springs are used in | Cycles | Scooters | Watches | Railway Wagons | c | Flat spiral springs are also known as spiral torsion, clock springs or brush springs. Their special character is that the coil contact is minimized during operation. It is used in watches and it has also application in automotive, medical, industrial and office equipment markets | Comments | Active | |
| 163 | In a beam, the point of contraflexure is a point where | Shear force is maximum. | Shear force is zero. | Bending moment changes its sign. | Bending moment is maximum. | c | A point of contra flexure is a location where the bending moment is zero or changes its sign. | Comments | Active | |
| 164 | When two springs (each having stiffness constant K) are connected in series, the equivalent stiffness will be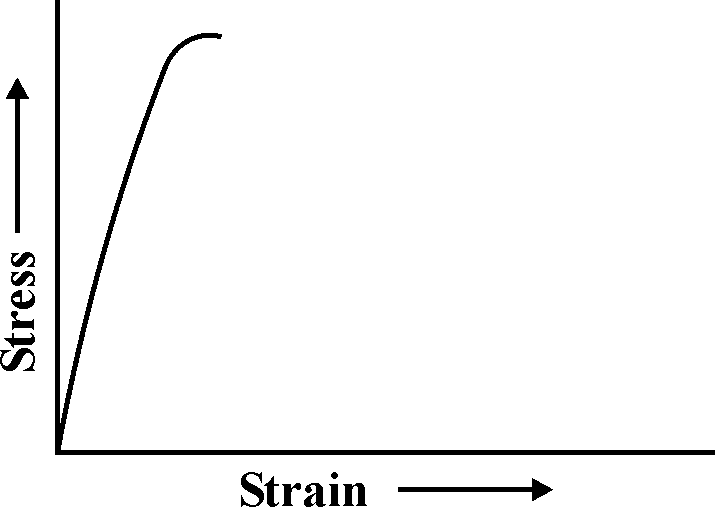 |
K | 2K | \(\frac{K}{2}\) | \(\frac{1}{K}\) | c | Equivalent stiffness of spring for series combination \(\frac{1}{K_{eq}}=\frac{1}{K_{1}}+\frac{1}{K_{2}}\) But here \(K_{1}=K_{2}=K\) \(\frac{1}{K_{eq}}=\frac{1}{K}+\frac{1}{K}=\frac{2}{K}\) \(K_{eq}=\frac{K}{2}\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 165 | Spring index is | Ratio of coil diameter to wire diameter. | Load required to produce unit deflection. | Its capability of storing energy. | None of the above | a | The spring index is the relationship between the mean diameter and wire diameter. Spring index C=D/d | Comments | Active | |
| 166 | Which of the following statements is correct? | Stress is proportional to strain. | Stress is force per unit area. | Within elastic limit, the ratio of stress to strain is called Young’s modulus. | All of the above | d | \( Stress σ=\frac{Force}{Area}=\frac{F}{A}, Strain=\frac{change in dim}{original dim}\) \(Young modulus E=σ/∈ \) All statements are correct. |
Comments | Active | |
| 167 | What is the unit of strain? | Centimetre | Millimetre | Micron | None of these | d | Strain is the deformation of a material from stress. It is simply a ratio of the change in length to the original length. \(ϵ=\frac{δ}{L}\) It is a dimensionless quantity. |
Comments | Active | |
| 168 | A dead load is one that | Remains constant | Varies with time | Cannot be determined | Whose value is zero | a | The dead load includes loads that are relatively constant over time, including the weight of the structure itself, and immovable fixtures such as walls, plasterboard or carpet. The roof is also a dead load. Dead loads are also known as permanent or static loads. | Comments | Active | |
| 169 | For a shaft transmitting power ‘P’ at rpm N, the diameter of shaft would be proportional to | \((\frac{P}{N})^{1/3}\) | \((\frac{P}{N})^{1/2}\) | \((\frac{P}{N})^{2/3}\) | \((\frac{P}{N})^{3}\) | a | We know that \(Ï„_{s}=\frac{16T}{Ï€d^{3}}\) \(Tâˆd^{3}\) Also, \(P=\frac{2Ï€NT}{60}\) \(\frac{P}{N}âˆd^{3}âˆT\) \((\frac{P}{N})^{\frac{1}{3}}âˆd\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 170 | Outside diameter of a hollow shaft is twice its inside diameter. Ratio of torque carrying capacity to that of a solid shaft of same outside diameter and same material is | 3/4 | 15/16 | 1/2 | 1/16 | b | The ratio of its torque carrying capacity to that a solid shaft of the same material and the same outside diameter is. 15/16. We know that, for hollow shaft \(τ_{h}=\frac{16T_{1}}{πD^{3}(1-K^{4})}\) For solid shaft \(τ_{s}=\frac{16T_{2}}{πD^{3}}\) As and (Given) \(τ_{h}=τ_{s}\) \(K=\frac{d}{D}=\frac{1}{2}\) \(T_{1}=T_{2}(1-K^{4})\) \(\frac{T_{1}}{T_{2}}=(1-K^{4})=(1-\frac{1}{16})=\frac{15}{16}\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 171 | Which of the following brakes is commonly used in motor cars? | Band Brake | Shoe Brake | Band and Block Brake | Internal Expanding Shoe Brake | d | The internal expanding type of brake is commonly used in motor cars and light trucks. | Comments | Active | |
| 172 | Axial thrust is minimum in case of | Spur gear | Bevel gear | Mitre gear | Double helical gear | d | In double-helical gear, the helix angle is 45°. Axial thrust occurs in the case of single helical gears eliminated in double helical gears. This is because the axial thrust of two rows of teeth cancels each other.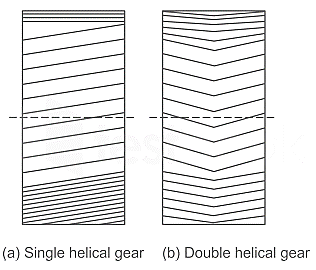 |
Comments | Active | |
| 173 | The product of circular pitch and diametral pitch is equal to | 1 | 1.57 | π | Infinite | c | Circular Pitch (C) \( =\frac{πD}{T}\) Diametric Pitch \(P_{d}=\frac{T}{D}\) D = Pitch circle-diameterT = Number of teeth |
Comments | Active | |
| 174 | The maximum fluctuation of energy in a flywheel is equal to Where: I = Mass moment of inertia of the flywheel E = Mean kinetic energy of the flywheel CS = Co-efficient of fluctuation of speed ω = Mean angular speed = \(\frac{ω_{1}+ω_{2}}{2}\) |
Iω ( – ) \(ω_{1}\) \(ω_{2}\) | \(Iω_{2}C_{S}\) | 2ECS | All of these | d | Maximum fluctuation of energy: \(∆E=\frac{1}{2}Iω^{2}_{2}-\frac{1}{2}Iω^{2}_{1}=\frac{1}{2}I(ω^{2}_{2}-ω^{2}_{1})\) \(∆E=\frac{1}{2}I(ω_{2}+ω_{1})(ω_{2}-ω_{1})\) \(∆E=\frac{1}{2}Iω(ω_{2}-ω_{1})\) \(∆E=Iω^{2}C_{s}=2EC_{s}\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 175 | Which one of the following is not a friction clutch? | Disc or plate clutch | Cone clutch | Centrifugal clutch | Jaw clutch | d | Types of Clutch Friction clutchFriction clutchPositive clutchPositive clutch Friction clutch Friction clutch Positive clutch Positive clutch 1.Square-Jaw clutch2.Spiral-Jaw clutch1.Square-Jaw clutch2.Spiral-Jaw clutch1.Cone clutch2.Centrifugal clutch3.Dry clutch4.Plate clutch1.Cone clutch2.Centrifugal clutch3.Dry clutch4.Plate clutch 1.Square-Jaw clutch 2.Spiral-Jaw clutch 1.Square-Jaw clutch 2.Spiral-Jaw clutch 1.Cone clutch 2.Centrifugal clutch 3.Dry clutch 4.Plate clutch 1.Cone clutch 2.Centrifugal clutch 3.Dry clutch 4.Plate clutch |
Comments | Active | |
| 176 | A Portor governor could be classified as | Inertia type governor | Pendulum type governor | Centrifugal governor | Dead weight type governor | d | Porter governor is dead weight loaded type of gravity controlled centrifugal governor.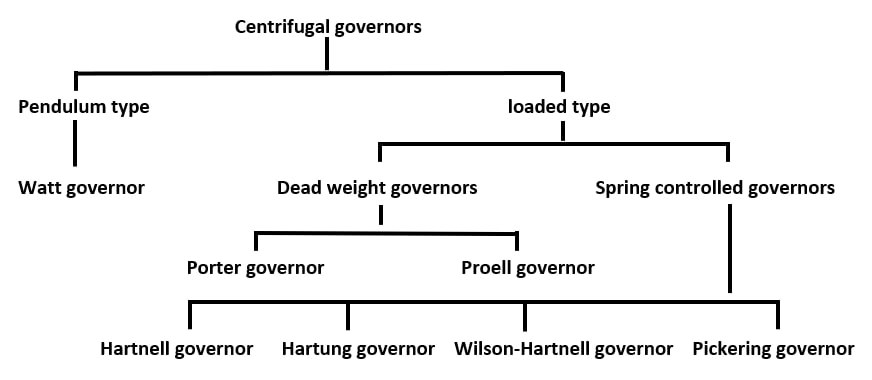 |
Comments | Active | |
| 177 | The height of Watt’s governor is | Directly proportional to speed | Directly proportional to (speed)2 | Inversely proportional to speed | Inversely proportional to (speed)2 | d | \(h=\frac{g}{ω^{2}}=\frac{895}{N^{2}}\) h = height of each ball = Angular velocity of the balls, arms and the sleeve \(ω\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 178 | A cam and follower mechanisms constitutes a/an | Open pair | Screw pair | Closed pair | Spherical pair | c | When two elements of the pair are held together mechanically in such a manner that only the required type of relative motion occurs they are called a closed pair. All lower pairs and some higher pairs (for example cam and follower) are closed pairs. | Comments | Active | |
| 179 | The size of gear is usually specified by | Pressure angle | Pitch circle diameter | Circular pitch | Diametric pitch | b | The size of the gear is usually specified by the pitch circle diameter. It is also known as pitch diameter. | Comments | Active | |
| 180 | The velocity of belt for maximum power is (Where m = mass of the belt in kg per metre length. T = Tension) | \(\frac{T}{3m}\) | \(\frac{T}{4m}\) | \(\frac{T}{5m}\) | \(\frac{T}{6m}\) | a | Centrifugal tension for maximum power; Velocity of the belt for maximum power; \(T_{c}=\frac{T}{3}\) \(v=\frac{T}{3m}\) Here, T = Maximum tension = Centrifugal tension v = Velocity of belt in m/s m = mass of belt per unit length in kg \(T_{c}\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 181 | In inventory control, the economic order quantity is the | Optimum lot size | Highest level of inventory | Capability of plant to produce | None of these | a | The economic order quantity (EOQ) is a company's optimal order quantity for minimizing its total costs related to ordering, receiving, and holding inventory. | Comments | Active | |
| 182 | Routing is essential in the following type of industry: | Assembly industry | Process industry | Job order industry | Mass production industry | a | Routing determines what work is to be done and where and how it will be done. Taking from raw material to the finished product, routing decides the path and sequence of operations to be performed on the job from one machine to another. Routing is essential in the Assembly industry. |
Comments | Active | |
| 183 | What does symbol imply in work study?  |
Operation | Inspection | Transport | Permanent Storage | b | Inspection: It is an act of Checking for correctness of the quantity or quality of the items. |
Comments | Active | |
| 184 | Bin cards are used for | Machine loading | Stores | Accounts | None of these | b | Bin cards, which are sometimes referred to as inventory cards or stock cards, are record-keeping documents used in retail and other businesses that require a stock room. They keep a running balance of a business's inventory. | Comments | Active | |
| 185 | Interchangeability can be achieved by | Standardization | Better process planning | Simplification | Better product planning | a | The concept of interchangeability is try to use parts that are standard. So interchangeability can be achieved by the standardization of the product. Interchangeability or interchangeable manufacturer means that any standardized component will assemble correctly with a mating component, both being chosen at random. |
Comments | Active | |
| 186 | Which of the following measuring instrument can’t be used to know the value of a dimension? |
Screw gauge | GO-NO GO gauge | Slip gauge | None of these | b | Go No-Go gauges are inspection tools used to determine if manufactured parts are within specified tolerance limits. | Comments | Active | |
| 187 | The word “Kanban†is used in | EOQ | JIT | MRP | SCM | b | Kanban is an inventory control system used in just-in-time (JIT) manufacturing. It was developed by TaiichiOhno, an industrial engineer at Toyota, and takes its name from the colored cards that track production and order new shipments of parts or materials as they run out. | Comments | Active | |
| 188 | Quality management standards are controlled by | ISO 7000 | ISO 8000 | ISO 9000 | ISO 14000 | c | Standards related to quality management systems include the rest of the ISO 9000 series (including ISO 9000 and ISO 9004), the ISO 14000 series (environmental management systems), ISO 13485 (quality management systems for medical devices), ISO 19011 (auditing management systems). | Comments | Active | |
| 189 | Basic tool in work study is | Graph paper | Process chart | Planning chart | Stop-watch | d | Stop watch is used for the time study or work measurement. | Comments | Active | |
| 190 | Which of the following production system is characterised by the low production volume? | Project Production System | Job Shop Production System | Batch Production System | Mass Production System | b | Job shop production system |
Comments | Active | |
| 191 | Which of the following has quick return mechanism? | Shaper | Drilling machine | Printing press | Milling machine | a | Shaper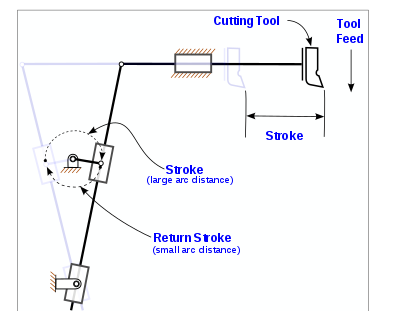 |
Comments | Active | |
| 192 | Process layout is employed for | Batch production | Continuous type of production | Effective utilisation of machines | None of these | a | Process layout is recommended for batch production. All machines performing a similar type of operations are grouped at one location in the process layout e.g., all lathes, milling machines, etc. are grouped in the shop will be clustered in like groups. | Comments | Active | |
| 193 | The chart used in Quality Control is/are | C-chart | R-chart | P-chart | All of these | d | 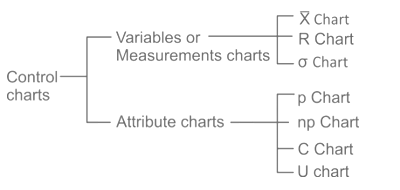 |
Comments | Active | |
| 194 | The symbol used for transport in work study is | 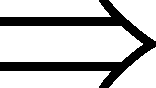 |
 |
 |
 |
a |  |
Comments | Active | |
| 195 | Which layout is suitable for multi-product company carring out batch production? | Product layout | Process layout | Point layout | All of these | b | Process layoutsuitable for multi-product company carring out batch production. | Comments | Active | |
| 196 | Which of the following is not significant in determination of economic order quantity in inventory control? | Ordering cost | Lead time | Inventory carrying cost | All of these | b | Lead time is not significant in determining the EOQ. \(EOQ=\frac{2DC_{o}}{C_{h}}\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 197 | Which of the following safety measures is used to promote the safety? | Excessive fine | Writing slogans | Stopping the work | All of these | b | Writing slogans promote the safety. | Comments | Active | |
| 198 | Plant layout used for automobile assembly unit is | Product layout | Process layout | Point layout | Static layout | a | In this layout equipment or work-processes are arranged according to the requirement of a specific product. The path for each part is, in effect, a straight line. Automobile manufacturing is an example of the product layout industry. | Comments | Active | |
| 199 | Work study is mainly aimed at | Determining the most efficient method of performing a job. | Estimating the minimum time of completion of job. | Developing the standard method and standard time for a job. | Economizing the motions involved on the part of the work while performing a job. | c | Work study involves Method study and time study. | Comments | Active | |
| 200 | Which of the following layout is useful when the product being processed is very big, heavy or difficult to move? | Fixed position layout | Process layout | Product layout | Cellular layout | a | In a fixed-position layout, the project remains in one place, and workers and equipment come to that one work area. Examples of this type of project are a ship, a highway, a bridge, a house, and an operating table in a hospital operating room. | Comments | Active | |
| 201 | Indian Boiler Act, 1923 is applicable to | All boilers | Boilers more than 100 litres capacity | Boilers more than 1000 litres capacity | None of the above | b | The Indian Boilers Act-1923 was enacted with the objective to provide mainly for the safety of life and Property of persons from the danger of explosions of steam boilers and for achieving uniformity in registration and inspection during operation and maintenance of boilers in India. | Comments | Active | |
| 202 | Which of the followings, leads to industrial hazards and causes accidents? | Noise and vibrations | Poor lighting and Poor ventilation | Heat and Humidity | All of these | d | common causes which leads to industrial hazards and accidents are: Poor lighting: Low visibility is a common cause of slips, trips, and falls. Ambient temperature: If a workplace is too hot, overheating can occur. If the workplace is too cold, frostbite or hypothermia can occur. Air pollution: Breathing issues can develop if a workplace has poor ventilation or air pollution. Sound pollution: The sound in a workplace can cause injury to a worker's hearing. |
Comments | Active | |
| 203 | Which of the followings helps in accident control? | Automatic safety guard | Interlock safety guard | Trip safety guard | All of these | d | Following points are helps in control accidents:i. Fixed guards.ii. Fixed limited access guards.iii. Fixed adjustable access guard.iv. Interlock guards.v. Automatic guards. vi. Trip safety guardvii. Safety by Machine Controls.viii. Safety by Precautions and Maintenance.ix. Criteria for Machine Guard Selection. |
Comments | Active | |
| 204 | Standard time is defined as | Normal time + allowance | Normal time + idle time | Normal time + idle time + allowance | None of these | a | Standard time = normal time + allowance | Comments | Active | |
| 205 | According to the definition of “week†under the Factory Act, 1948, it is a period of 7 days beginning at midnight on | Sunday | Monday | Saturday | Friday | c | An Act to consolidate and amend the law regulating labor in factories. It shall come into force on the 1April 1949. "Week" means a period of seven days beginning at midnight on Saturday night | Comments | Active | |
| 206 | In ABC analysis, A-type inventory represents | High value, High volume | High value, Low volume | Low value, Low volume | Low value, High volume | b | High value, Low volume  |
Comments | Active | |
| 207 | Which of the following material handling devices are used for the movement of materials in a fixed route and fixed area of operation? | Cranes | Pallets | Industrial Trucks | Elevators | a | Cranes are used to transport material from one fixed point to another fixed point. | Comments | Active | |
| 208 | Which of the followings control chart is variable control chart? | P-chart | C-chart | U-chart | R-chart | d |  |
Comments | Active | |
| 209 | Per cent idle time for men and machine is found by | Work sampling | Time study | Method study | Work study | a | Percent idle time for men or machines is found by Work sampling. | Comments | Active | |
| 210 | Break Even point represents | Profit | Loss | No Profit and No Loss | None of these | c | The break-even point represents the time when unit can run without any loss and profit. | Comments | Active | |
| 211 | For transmitting power without slip, drive used is | Rope drive (b) Belt drive | Cone drive (d) Chain drive | d | A chain drive is also called a positive drive because there is no slip. | Comments | Active | |||
| 212 | Which one is not a part of cotter joint? | Socket | Spigot | Fork end | Collar | d | There is no point of mentioning collar alone in a cotter joint. It has to be a spigot collar or socket collar. Three main parts of the cotter joint: Cotter, Spigot, and Socket. |
Comments | Active | |
| 213 | What is the number of jaws in a self-centred chuck of a lathe? | Eight | Five | Four | Three | d | Three jaw, chuck is also known as universal or self centering chuck. The majority of the chucks have two sets of jaws for holding internal and external diameters. | Comments | Active | |
| 214 | Taylor’s tool life equation used to calculate the tool life is given by the equation | \(TV^{n} = constant\) | \(VT^{n} = constant\) | \(VT^{1/n} = constant\) | None of these | b | Taylor's tool life equation is given by, where V is in m/min and T (time) is in min. \(VT^{n}=constant\) | Comments | Active | |
| 215 | Which theory is best to estimate failure load for a ductile material? | Distortion energy theorem | Maximum strain energy theorem | Maximum shear stress theorem | None of these | c | For ductile material, maximum shear stress theorem is most suitable. | Comments | Active | |
| 216 | Rivets are made of following type of material: | Brittle | Low density | Ductile | Low melting point | c | Rivets are used in most applications are made of mild steel, which is a ductile material. There are two varieties of steel rivet bars 1. Hot rolled steel rivet 2. High tensile steel rivet |
Comments | Active | |
| 217 | For proper design of a shaft, it should be designed on the basis of | Maximum principal stress theory | Maximum shear stress theory | Both (a) and (b) | Maximum strain theory | b | For proper design of a shaft, it should be designed on the basis of Maximum shear stress theory. | Comments | Active | |
| 218 | Elastic modulus of steel is | 70 GPa | 210 GPa | 250 GPa | 300 GPa | b | Elastic modulus of steel is 210GPa | Comments | Active | |
| 219 | No. of inversions in a slider crank mechanism is | 1 | 2 | 4 | 6 | c | A slider-crank is a kinematic chain having four links so four inversions. It has one sliding pair and three turning pairs. | Comments | Active | |
| 220 | A steel bar of 5 m length is heated from 15 °C to 90 °C and is free to expand. The bar will induce | Tensile stress | Shear stress | No stress | None of these | c | Stress is nothing but the resisting force since due to temperature rise body will expand and if this expansion due to temperature change is restricted then only resisting stress (thermal stress) will come into play since expansion is not restricted that's why no stress is occurring. | Comments | Active | |
| 221 | A rivet is specified by | Shank diameter | type of load | Length of rivet | None of these | a | The rivet is specified by the diameter of its shank.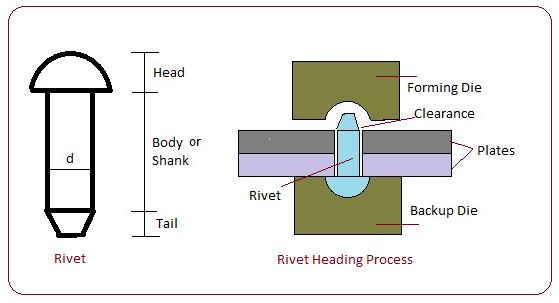 |
Comments | Active | |
| 222 | In a gib and cotter joint, the gib and cotter are subjected to | Single shear only | Double shear | Single shear and crushing | Double shear and crushing | d | Cotter and Gib are in double shear and crushing. |
Comments | Active | |
| 223 | Piston rod and cross head in a steam engine are usually connected by means of | Cotter joint | Knuckle joint | Ball joint | Universal joint | a | Cotter's joint is widely used to connect the piston rod and crosshead of a steam engine, as a joint between the piston rod crosshead, and the tailor pump rod, foundation bolt, etc.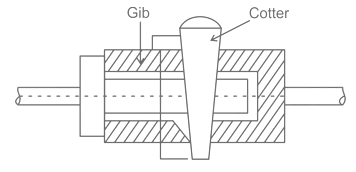 |
Comments | Active | |
| 224 | A key connecting a flange coupling to a shaft is likely to fail in | Shear | Tension | Torsion | Bending | a | A key connecting a flange coupling to a shaft is likely to fail in shear. | Comments | Active | |
| 225 | Anti-friction bearings are | Hydro-dynamic bearings | Sleeve bearings | Thin lubricated bearings | Ball and roller bearings | d | The antifriction bearing consists of rolling elements, races, and cage. Rolling elements are available in different shapes such as balls, parallel rollers, taper rollers, barrels, and needles. They are made of chromium or chrome-nickel steel with ground or polished surface. The load of the rotating member is carried by the rolling elements. Example: Ball bearing, Roller bearings, Needle bearing |
Comments | Active | |
| 226 | What is the function of a washer? | Provides cushioning effect | Provides bearing area | Absorbs shocks and vibrations | Provides smooth surface in place of rough surface | b | A washer is a thin plate (typically disk-shaped) with a hole (typically in the middle) that is normally used to distribute the load of a threaded fastener, such as a screw or nut. Washers are used to distribute the clamping pressure over a larger area and prevent surface damage. |
Comments | Active | |
| 227 | The usual proportion for the width of key is (where d is the diameter of the shaft) | \(\frac{d}{8}\) | \(\frac{d}{6}\) | \(\frac{d}{4}\) | \(\frac{d}{2}\) | c | The usual proportion for the width of the key used for transmitting power is d/4. Where d is the diameter of the shaft. | Comments | Active | |
| 228 | The sleeve of Muff coupling is designed as a | Thin cylinder | Thick cylinder | Solid shaft | Hollow shaft | d | The power is transmitted from one shaft to the other shaft by means of a key and a sleeve or muff. The sleeve or muff coupling is designed as a hollow shaft. | Comments | Active | |
| 229 | What strength is to be considered for ductile material under cyclic load? | Ultimate strength (b) Yield strength | Endurance strength (d) Fracture strength | c | Endurance strength: For cyclic loading conditions endurance strength is considered. | Comments | Active | |||
| 230 | Initial cost of making a product is ` 1,00,000 and variable cost per unit is ` 40. If it’s selling price is ` 80 per unit, what would be the break even quantity? | 2500 units | 3500 units | 5000 units | 7000 units | a | \( Break even quantity=\frac{Fixed cost}{Price per unit-Variable cost}\) \(=\frac{100000}{80-40}=2500 units \) |
Comments | Active | |
| 231 | Parallel fillet welded joints are designed for | Tensile strength | Compressive strength | Bending strength | Shear strength | d | When load acts parallel to the length of the weld, the weld is called parallel fillet weld. Parallel fillet welds are designed for shear strength. | Comments | Active | |
| 232 | A cotter joint is used to connect two rods which are in | Tension only | Compression only | Tension and Compression | Shear only | c | Cotter's joint is used to join two shafts which are in Rotation. Cotter's joint is used when the members are subjected to Axial Tensile or Compressive Loading. |
Comments | Active | |
| 233 | A knuckle pin may fail in | Shear | Bending | Crushing | All of these | d | The modes of failure are: Shear failure of pin (single shear).Crushing of pin against rod and tensile failure of flat end bar. Application:Tie rod joint of roof truss.Tension link in bridge structure.Link of roller chain.Tie rod joint of jib crane.The knuckle joint is also used in tractor.Connecting rods between locomotive wheels. |
Comments | Active | |
| 234 | In design of flange coupling, the weakest element should be | Key | Bolt | Flange | Shaft | a | Key is the weakest element of flange coupling which can be easily replaceable and economically it cost less in comparison other parts which much high. | Comments | Active | |
| 235 | The rated life of a bearing varies | Directly with load | Inversely as square of load | Inversely as cube of load | None of these | c | Let P=load on bearing \(Life of bearing, L=(\frac{C}{P})^{n}\) For ball bearing: n=3 so For roller bearing: n=10/3n is the exponent of life equation \(Lâˆ\frac{1}{P^{3}}\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 236 | In leaf springs, the longest leaf is known as | Lower leaf | Master leaf | Upper leaf | None of these | b | The longest leaf of the leaf spring is known as the "Master Leaf". The ends of the master leaf are rolled which are known as the "eye". | Comments | Active | |
| 237 | In case of straight turning operation, length of work piece is 120 mm and feed rate is 0.25 mm/se(c) How long will it take to complete the turning operation? | 8 minute | 10 minute | 12 minute | None of these | a | length of workpiece \( \) \(l=120 mm\) \(feed rate V_{f}=f×n=0.25 mm/sec\) \(Machining Time T_{m}=\frac{l}{f×n}=\frac{l}{V_{f}}=\frac{120}{0.25}=480sec=8 minute \) |
Comments | Active | |
| 238 | Nichrome is used in | Gas turbine | Air craft engine | Heater element | Brake lining | c | A nichrome wire is used as a heating element because of its high melting point and high resistivity (low conductivity) also. Having a high melting does not allow the nichrome wire to melt easily when a large amount of heat is produced. | Comments | Active | |
| 239 | When a nut is tightened by placing a washer below it, the bolt will be subjected to | Tensile stress | Compressive stress | Shear stress | None of these | a | Bolts are always subjected to tensile stress when nut is tightened. The washer will be in compression. | Comments | Active | |
| 240 | Which of the following materials is not desirable for rivets making? | Mild steel | Cast iron | Aluminium | Copper | b | Rivets are made up of ductile materials while cast iron is a brittle material. Therefore it is not recommended for rivets making. | Comments | Active | |
| 241 | In involute gears, pressure angle is | Dependent on size of teeth | Dependent on size of gear | Zero | Always constant | d | For involute gear profile, the pressure angle is constant throughout the engagement of teeth. | Comments | Active | |
| 242 | For oil-pumps in small IC engines which gears can be used? | Spur gears | Crossed helical gears | Gear train | None of these | b | Crossed helical gears are used for oil pumps in I.C. engines. | Comments | Active | |
| 243 | In a compound gear train there is | Only one gear on each shaft. | More than one gear on a shaft. | No gear on driving shaft. | None of these | b | When a series of gears are connected in such a way that two or more gears rotate about an axis with the same angular velocity, it is known as compound gear train. | Comments | Active | |
| 244 | Which of the followings is a higher pair? | Belt and pulley | Turning pair | Screw pair | Sliding pair | a | When a pair has point or line contact between the links, it is known as higher pair e.g. Belt and pulley, wheel rolling on a surface, cam and follower pair |
Comments | Active | |
| 245 | Piston, piston rod and cross-head of a steam engine constitute | One link | Two link | Three link | Do not constitute any link. | a | In a reciprocating steam engine, piston, piston rod and crosshead constitute one link; connecting rod with big and small end bearings constitute a second link; crank, crank shaft and flywheel a third link and the cylinder, engine frame and main bearings a fourth link. | Comments | Active | |
| 246 | The Brinell hardness is calculated by: (Where F is load in N, D is steel ball diameter and d is indentation diameter in millimetres.) | \(\frac{F}{Ï€D(D-D^{2}-d^{2}}\) | \(\frac{F}{Ï€DD^{2}-d^{2}}\) | \(\frac{2F}{Ï€D(D-D^{2}-d^{2}}\) | \(\frac{2F}{Ï€D^{2}}\) | c |  |
Comments | Active | |
| 247 | For a watt governor, what will be the angular speed corresponding to the height of 10 cm, if g = 10 ? \(m/sec^{2}\) | 1 rad/sec | 7.29 rad/sec | 10.0 rad/sec | 3.15 rad/sec | a | \( ω=10 rad/sec, h=?\) \(h=\frac{g}{ω^{2}}\) \(h=\frac{10}{100}=10 rad/sec\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 248 | Angle moved by the cam during which follower remains at its highest position is called | Angle of dwell | Angle of descent | Angle of ascent | Angle of action | a | It is the angle through which the cam turns while the follower remains stationary at the highest or the lowest position. |
Comments | Active | |
| 249 | In spur gears | Both shafts are parallel. | Teeth are straight. | Teeth are parallel to axis. | All of these. | d | The spur gear is cylindrical and has straight teeth cut parallel to its rotational axis. It can be manufactured to close tolerances and is used to connect parallel shafts that rotate in opposite directions. Because contact is simultaneous across the entire width of the meshing teeth, it tends to be noisy at high speeds. |
Comments | Active | |
| 250 | Backlash in gears is | Addendum + Dedendum | Circular pitch + Tooth thickness | Space width between two teeth – Tooth thickness | None of the above | c | Backlash in gears is defined as difference in width of tooth space and engaging tooth thickness. Backlash=Width of tooth space-Tooth thickness 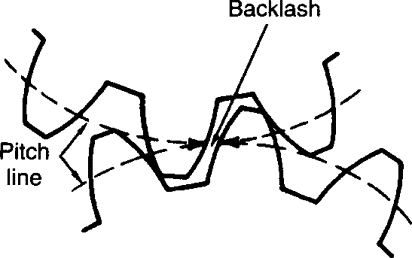 |
Comments | Active | |
| 251 | The creep in a belt drive is due to | Material of the pulleys | Material of the belt | Unequal size of pulleys | Unequal tensions and slackness of the belt | d | Creep is due to the elastic property of the belt material whereas, the conventional slip is due to insufficient frictional grip between the belt and pulley. However, the effect of the creep, as well as slip, is to reduce the speed ratio, and hence power transmission. | Comments | Active | |
| 252 | Cam converts the rotary motion into | Rotary motion | Translatory motion | Both rotary and translatory motions | None of these | c | A cam is a mechanical member used to impart desired motion to a follower by direct contact. The cam may be rotating or reciprocating or oscillating. It is used in automatic machines, IC engines, machine tools, printing control mechanisms. |
Comments | Active | |
| 253 | Sensitiveness of governor is defined as | \(\frac{Range of speed}{Mean speed}\) | \(\frac{Mean speed}{Range of speed}\) | Mean speed × Range of speed | None of these | a | The sensitiveness is defined as the ratio of the difference between the maximum and minimum equilibrium speeds to the mean equilibrium speed. \(Sensitiveness=\frac{Range of speed}{Mean speed}=\frac{N_{max}-N_{min}}{N_{mean}}\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 254 | The factor that decides the size of the cam is | Prime circle | Pitch circle | Base circle | Pitch curve | c | Base circle: it is a smallest circle, drawn tangential to the cam profile. The base circle decides the overall size of the cam and thus is a fundamental feature. |
Comments | Active | |
| 255 | For maximum power to be transmitted by the belt, the maximum permissible tension in the belt is | Equal to centrifugal tension | Twice the centrifugal tension | Thrice the centrifugal tension | Four-times the centrifugal tension | c | Condition for Maximum power transmitted by the belt is:Â i.e. power transmitted will be maximum when tension is equal to three-time centrifugal tension or it shows that when the power transmitted is maximum, 1/3rd of the maximum tension is absorbed as centrifugal tension. \(T=3T_{C}\) | Comments | Active | |
| 256 | For a governor running at constant speed, the force acting on the sleeve is | Constant | Minimum | Maximum | Zero | d | When a governor is running at a constant speed, it is in equilibrium and the net force acting on the sleeve is zero. If the load on the engine changes, the speed also changes and hence, the sleeve of the governor changes its position. | Comments | Active | |
| 257 | Crowning on pulleys helps | In increasing velocity ratio. | For automatic adjustment of belt so that belt runs centrally. | Increase the belt life. | Decrease initial tension. | b | A crowned pulley is a pulley that has a slight hump in the middle, tapering off ever so slightly towards either edge. |
Comments | Active | |
| 258 | The height of Watt’s governor is proportional to (Where N: rpm of balls) |
N | \(N^{2}\) | \(\frac{1}{N}\) | \(\frac{1}{N^{2}}\) | d | where h is the height of governor. N is revolution per minute. \( h=\frac{895}{N^{2}}, hâˆ\frac{1}{N^{2}}\) | Comments | Active | |
| 259 | The working surface above the pitch surface of the gear tooth is termed as | Addendum | Dedendum | Face | Flank | c | Face of a tooth: This is the working surface of the tooth above the pitch circle. |
Comments | Active | |
| 260 | Factor of safety is the ratio of | Breaking stress to working stress | Endurance limit to yield stress | Elastic limit to ultimate stress | Ultimate stress to working stress | d | Factor of safety for ductile material \(FOS=\frac{Yield stress}{Working stress}\) Factor of safety for brittle material \(FOS=\frac{Ultimate stress}{Working stress}\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 261 | Which of the following concurrent forces cannot have a resultant of 4N? | 2N and 4N | 2N and 6N | 2N and 8N | All of these | c | We know that \(Resultant force, R=F_{1}^{2}+F_{1}^{2}+2F_{1}F_{2}cosθ\) For max R, \(cosθ=1\) \(R_{max}=F_{1}+F_{2}\) For min R, \(cosθ=-1\) \(R_{min}=F_{1}-F_{2}\) In option C, & \(F_{1}=2 \) \(F_{2}=8\) So, \(R_{max}=2+8=10 N\) \(R_{min}=2-8=-6 N\) So option C will be correct answer. |
Comments | Active | |
| 262 | Young’s modulus of elasticity for a perfectly rigid body is | Zero | Unity | Infinity | Cannot be known | c | The ratio of stress and strain is called young's modulus. For a perfectly rigid body, whatever may be the stress, strain will be always zero. So young's modulus will be infinite for a rigid body. | Comments | Active | |
| 263 | Jet engine works on the principle of | Conservation of energy | Conservation of linear momentum | Earth’s gravity | None of these | b | A jet engine works on the principle of conservation of linear momentum. In jet engines, a large volume of gases produced by the combustion of fuel is allowed to escape through a jet in the backward direction. Due to the very high speed or velocity, the backward rushing gases have a large momentum. They impart and equal and opposite momentum to the jet engine due to which the jet engine moves forward with a great speed. |
Comments | Active | |
| 264 | Two forces of equal magnitude ‘P’ act at an angle 120° to each other. What will be their resultant? | 2P | P | P \(2\) | \(\frac{P}{2}\) | b | \(F_{1}=F_{2}=P,θ=120^{0}\) \(Resultant (R)=F12+F22+2F_{1}F_{2}cosθ\) \(R=P^{2}+P^{2}+2P×P×cos120^{0}\) \(R=2P^{2}-2P^{2}×\frac{1}{2}\) \(R=P\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 265 | Four forces P, 2P, 3P and 4P act along the sides, taken in order of a square ABCD. The resultant force is | Zero | \(22 P\) | 2P | P \(5\) | b | \(Net force along x axis F_{x}=P-3P =-2P\)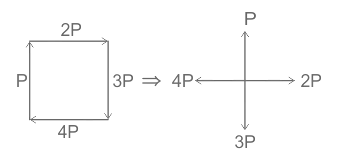 \(Net force along y axis F_{y}=4P-2P=-2P\) \(F_{net}=Fx2+Fy2=(-2P)^{2}+(2P)^{2}\) \(F_{net}=4P^{2}+4P^{2}\) \(F_{net}=22P\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 266 | A weight of 1000 N is supported by two chains as shown in Figure. What will be the tension in Chain-1 and Chain-2 respectively? 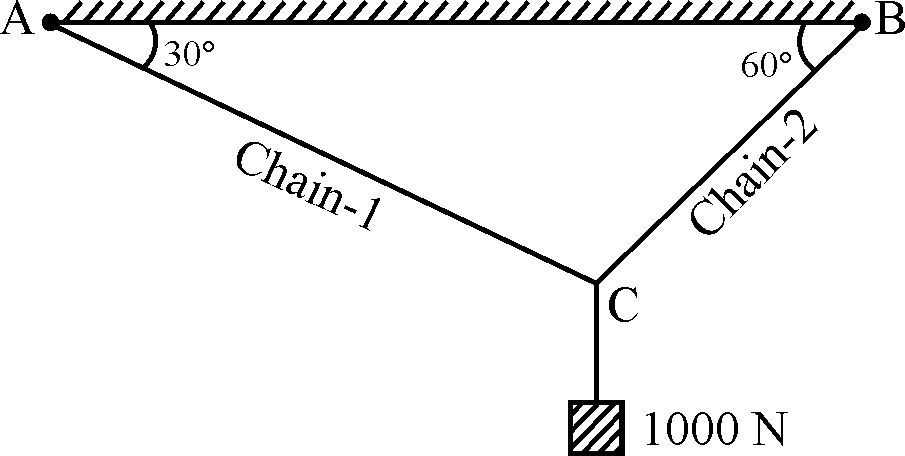 |
500 N; 866 N | 500 N; 433 N | 1000 N; 866 N | 1000 N; 433 N | a | Applying the lami’s theorem \(\frac{P_{2}}{sin150}=\frac{P_{1}}{sin120}=\frac{1000}{sin90}\) So \(P_{2}=1000sin150=500 N\) \(P_{1}=1000sin120=866.02 N\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 267 | Three parallel forces , and are acting on a log as shown in Figure and the body is in equilibrium. If force = 250 N and = 1000 N; and the distance between and is 1.0 m, then what is the distance of from ? \(F_{1}\) \(F_{2}\) \(F_{3}\) \(F_{1}\) \(F_{3}\) \(F_{1}\) \(F_{2}\) \(F_{2}\) \(F_{3}\)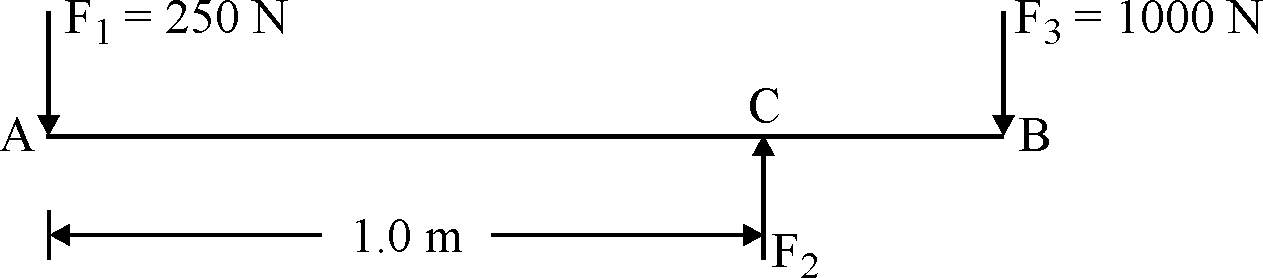 |
0.50 m | 0.25 m | 0.75 m | 0.15 m | b | From Fig \(F_{2}=250+1000=1250 N\) Taking moment about A \(1250×1=1000×(CB+1)\) \(CB=0.25 m\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 268 | A body of weight 100 N is placed on a rough horizontal plane. What will be the co-efficient of friction between surfaces if a horizontal force of 60 N just causes the body to slide over the horizontal plane? | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.6 | d | Weight of the body (W) = 100 N Force applied horizontally to move the body (F) = 60 N \(Cofficient of friction(μ)=\frac{F}{N}\) \(F=Limiting force, N=Normal reaction\) Normal reaction will be equal to the weight of the body \(μ=\frac{60}{100}=0.6\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 269 | For a perfect frame, the number of joints (j) and the number of members (n) are given by | n = 2j – 3 | j = 2n – 3 | n = j – 3 | j = n – 3 | a | \( n=2j-3\) n = Number of members, and j = Number of joints. |
Comments | Active | |
| 270 | An effort of 100 N is applied to a machine to lift a load of 900 N. The distance moved by the effort is 100 cm. The load is raised through a distance of 10 cm. What is the efficiency of the machine? | 80% | 90% | 70% | 60% | b | Effort applied P = 100 NLoad lifted W = 900 NDistance moved by effort, y = 100 cmDistance moved by load, x = 10 cm \(Mechanical advantage (M.(A))=\frac{W}{P}=\frac{900}{100}=9\) \(Velocity ratio (V.R.)=\frac{y}{x}=\frac{100}{10}=10\) \(Efficiency(η)=\frac{M.A}{V.R}=\frac{9}{10}=0.9=90%\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 271 | A simply supported beam AB of length 9 m, carries a uniformly distributed load of 10 kN/m for a distance of 6 m from end (A) What are the reaction forces at A and at B? | 40 N and 20 N | 60 N and 20 N | 20 N and 60 N | 30 N and 15 N | a | 6 m6 m 6 m 6 m 60 kN60 kN 60 kN 60 kN 3 m3 m3 m3 mR1R1R2R2 3 m 3 m 3 m 3 m R1 R1 R2 R2 \(R_{1}+R_{2}=60 kN\) Taking moment about point 1 \(R_{2}×9=60×3\) \(R_{2}=20 kN\) \(R_{1}=40 kN\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 272 | A body in Simple Harmonic Motion will have maximum velocity when its amplitude is | Maximum | Negative maximum | Zero | Average | c | where v is the velocity at any time t or displacement x, A is amplitude, t is time, and is the angular frequency. \( v=ωA^{2}-x^{2 }\) \( \) \( ω\) The maximum value of v in this equation can be obtained when x = 0 and x = 0 means mean position or equilibrium position. So at the mean position, the speed of a particle executing SHM is maximum and its value is Αω. Therefore, A body in Simple Harmonic Motion will have maximum velocity when its amplitude is zero. |
Comments | Active | |
| 273 | Moment of inertia of a body does not depend upon | Mass of the body | Distribution of mass in the body | Axis of rotation of the body | Angular velocity of the body | d | Moment of inertia of a body depends on the mass of the body, its shape and size, distribution of mass about the axis of rotation, and the position and orientation of the axis of rotation. | Comments | Active | |
| 274 | In case of concurrent and coplanar forces, the condition of equilibrium is | ∑H = 0; ∑V = 0; ∑M = 0 | ∑H = 0; ∑V = 0 | ∑H = 0; ∑V ≠0 | ∑H = 0; ∑M = 0 | b | For concurrent and coplanar forces, ∑H = 0; ∑V = 0. No moment equation will be taken as forces are concurrent. |
Comments | Active | |
| 275 | Which one of the following is not a unit of energy? | Newton-metre | kCal | Watt | Watt-hours | c | Watt is unit of power. | Comments | Active | |
| 276 | The ratio of limiting force and normal reaction is known as | Co-efficient of friction | Angle of friction | Angle of repose | Frictional resistance | a | The ratio of limiting friction and normal reaction is known as the coefficient of friction. | Comments | Active | |
| 277 | The unit of moment is | N/m | N-m | N/m2 | N-m/sec | b | Moment of force is defined as the product of force and perpendicular distance from the axis; so its SI unit is Newton-meter (Nm). | Comments | Active | |
| 278 | In comparison to rolling friction, the value of sliding friction is | More | Less | Equal | Double | a | When an object slides, sliding friction is involved, while rolling friction is involved when an object rolls over the surface of another object. As the area of contact is more in the case of sliding than in the case of rolling. Therefore, sliding friction is more than the rolling friction. | Comments | Active | |
| 279 | In thin cylindrical shell, the value of circumferential stress as compared to the longitudinal stress is | Equal | Double | Triple | None of these | b | \( Circumferential stress,σ_{h}=\frac{pd}{2t}\) \(Longitudinal stress, σ_{l} =\frac{pd}{4t}\) \(σ_{h}=2σ_{l}\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 280 | Bow’s notation is used to indicate | Forces | Moment | Pressure | Velocity | a | Bow's Notation is a labelling convention whereby the spaces in between any group of forces is labelled with a capital letter such that each force is then straddled by two letters. |
Comments | Active | |
| 281 | In first system of pulley, the mechanical advantage is equal to (Where n : no. of pulleys) |
\(2^{n-1}\) | \(2^{n}\) | n | \(2^{n} – 1 \) | b | In general, in the first order pulley system, velocity ratio (VR) is given by 2n, where, n is the number of movable pulleys present in the system. | Comments | Active | |
| 282 | The velocity ratio of Weston’s differential pulley is: (Where R: Radius of bigger pulley r: Radius of smaller pulley) |
\(\frac{2R}{R-r}\) | ) \(\frac{2r}{R-r}\) | \(\frac{R}{R-r}\) | \(\frac{R}{2R-r}\) | a | \( Velocity ratio=\frac{Distance moved by effort}{Distance moved by load}=\frac{Ï€D}{Ï€\frac{(D-d)}{2}}=\frac{2R}{R-r}\) | Comments | Active | |
| 283 | The value of Poisson’s ratio is always | More than 1 | 1 | Less than 1 | None of these | c | \( μ=0 to 0.5 (under uni-axial loading)\) \(μ=0 for cork\) \(μ=0.5 for perfectly plastic body (Rubber)\) | Comments | Active | |
| 284 | If the bulk modulus is K, modulus of Elasticity is E and Poisson’s ratio is then which of the following is true?0 \(\frac{1}{m},\) | \(E=3K(1+\frac{2}{m})\) | \(E=3K(1-\frac{1}{m})\) | \(E=3K(1-\frac{2}{m})\) | \(E=3K(1+\frac{1}{m})\) | c | Relation between E, G, K, \(μ(μ=\frac{1}{m})\) \(E=3K(1-\frac{2}{m})\) \(E=2G(1+\frac{1}{m})\) \(E=\frac{9KG}{3K+G}\) \(μ=\frac{3K-2G}{6K+2G}\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 285 | Limiting force of friction is defined as the frictional force which exists when a body | Is moving with maximum velocity | Is stationary | Just begins to slide over the surface | None of these | c | Limiting Friction: - The maximum friction that can be generated between two static surfaces in contact with each other. Once a force applied to the two surfaces exceeds the limiting friction, motion will occur. For two dry surfaces, the limiting friction is a product of the normal reaction force and the coefficient of limiting friction. Laws of limiting friction: (i) The force of limiting friction depends upon the nature of surfaces in contact and-acts tangentially to the interface between the two surfaces. (ii) The force of limiting friction between two surfaces in contact is independent of the area of contact. |
Comments | Active | |
| 286 | The ratio of linear stress to the linear strain is called | Modulus of rigidity | Modulus of elasticity | Bulk modulus | Poisson’s ratio | b | \( Modulus of rigidity (G)=\frac{Shear stress}{shear strain}\) \(Bulk modulus(K)=\frac{Direct stress}{Volumeteric strain}\) \(Poission Ratio (μ)=\frac{Lateral strain}{Longitudinal strain}\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 287 | A machine is one that | Transfer motion | Does useful work | Have relative motion between links | Have a number of members | b | A machine is a physical system using power to apply forces and control movement to perform an action. | Comments | Active | |
| 288 | Angle of friction is the | Angle between normal reaction and the resultant of normal reaction and the limiting frictional force | Ratio of limiting friction and normal reaction | Ratio of static and dynamic friction | None of the above | a | The angle of friction is defined as the angle between the normal force (RN) and the resultant force (R) of normal force and maximum friction force.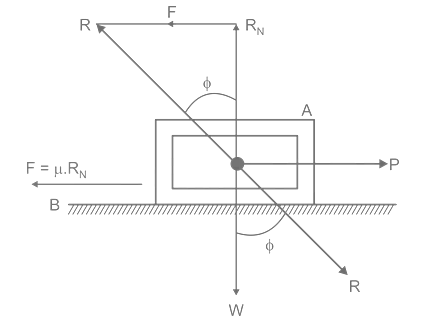 |
Comments | Active | |
| 289 | The co-efficient of friction depends on | Area of contact | Shape of surfaces | Strength of surfaces | Nature of surfaces | d | The coefficient of friction only depends on the nature of the surfaces. It does not depend on any other factors, including the relative speed of the surfaces and the surface area of contact. | Comments | Active | |
| 290 | The product of mass and velocity is known as | Impulse | Momentum | Power | Work | b | Momentum can be defined as "mass in motion." All objects have mass; so if an object is moving, then it has momentum - it has its mass in motion. Momentum depends upon the variables mass and velocity. Momentum=M.V |
Comments | Active | |
| 291 | Pure iron at room temperature has following micro structure: | γ-iron | δ-iron | Cementite | α-iron | ( undergoes a change in crystal structure when heated above forming or ‘austenite’. \(α-iron or 'ferrite')\) \(910^{0}C,\) \(γ-iron,\) | Comments | Active | ||
| 292 | If T is the recrystallization temperature, the cold working of steel is done at | Greater than T °C | Equal to T °C | Less than T °C | None of these | c | Hot working is the process of plastically deforming a metal above the metal's recrystallization temperature. Cold working or work hardening is the process of strengthening a metal by plastic deformation at temperatures below the recrystallization temperature. | Comments | Active | |
| 293 | The machinability of steel can be improved by alloying the steel with | Copper | Chromium | Nickel | Sulphur | d | Sulphur improves machinability but lowers transverse ductility and toughness. | Comments | Active | |
| 294 | Addition of Nickel to Steel helps in improving | Fatigue resistance | Creep resistance | Corrosion resistance | Cost reduction | a | Addition of nickel in steel increase the fatigue strength without the loss of ductility. | Comments | Active | |
| 295 | The chisel used for cutting steel sheets is usually | Annealed | Normalised | Hardened | Hardened and Tempered | d | The cutting edge of a chisel should be Hardened and tempered.A chisel is a tool with a characteristically shaped cutting edge of blade on its end, for cutting a hard material such as wood, stone, or metal. By hand, struck with a mallet, or mechanical power. | Comments | Active | |
| 296 | Which of the following is a case hardening process? | Carburizing | Nitriding | Cynading | All of these | d | There are different Surface Hardening or Case Hardening processes. They areCarburizingNitridingCyanidingInduction HardeningFlame Hardening | Comments | Active | |
| 297 | Which of the following is the amorphous material? | Lead | Brass | Glass | Silver | c | Amorphous or non-crystalline solid is a solid that lacks the long-range order that is characteristic of a crystal | Comments | Active | |
| 298 | Which among the followings is the most effective strengthening mechanism of non-ferrous materials? | Solid solution hardening | Strain hardening | Grain size refinement | Precipitation hardening | a | Precipitation hardening is also termed as age hardening. This is one of the important strengthening mechanism of nonferrous alloys. | Comments | Active | |
| 299 | Toughness is related to | Moment of inertia | Hardness | Energy absorbed before fracture | Fatigue loading | c | Energy absorbed before fracture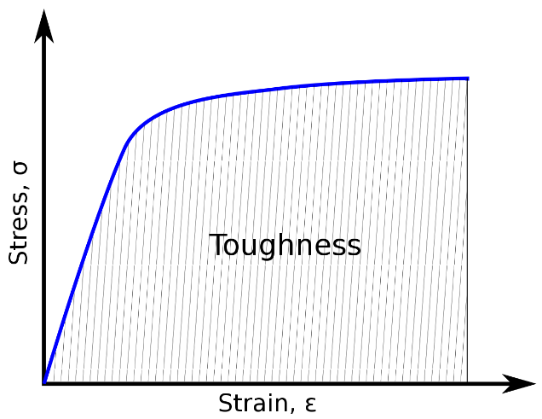 |
Comments | Active | |
| 300 | The slowest cooling rate is achieved when steel is quenched in | Fused salt | Air | Brine | Mixture of water and oil | b | Order of rate of cooling of most widely used quenching medium Brine>water>oil>air |
Comments | Active | |
| 301 | The ability of material to resist softening at higher temperature is known as | Creep | Hot tempering | Hot hardness | Fatigue | c | Hot hardness or red hardness corresponds to hardness of a material at high temperatures.As the temperature of material increases, hardness decreases and at some point a drastic change in hardness occurs | Comments | Active | |
| 302 | The material having same elastic property in all the directions are called | Ideal materials | Uniform materials | Isotropic materials | Practical materials | c | Isotropic materials are materials whose properties remain the same when tested in different directions. Isotropic materials differ from anisotropic materials, which display varying properties when tested in different directions. Common isotropic materials include glass, plastics, and metals. | Comments | Active | |
| 303 | Eutectoid steel contains following percentage of carbon | 0.02 | 0.30 | 0.63 | 0.87 | d | Eutectoid/Pearlite steel: AÂ 0.84%Â carbon steel or eutectoid steel is known as Pearlite steel. | Comments | Active | |
| 304 | Paramagnetic alpha iron changes to gamma iron at following temperature: | 768 °C | 1440 °C | 908 °C | 1539 °C | a | Below 912 °C (1,674 °F) iron again adopts the BCC structure characteristic of α-iron, also called ferrite. The substance assumes a paramagnetic property and it changes in to gamma iron. | Comments | Active | |
| 305 | Which of the following has maximum ductility? | Copper | Mild Steel | Cast Iron | 18-4-1 Steel | a | Copper is the softest material and usually more ductile among all the given materials in the options. However, Gold has the highest ductility. | Comments | Active | |
| 306 | Brass is an alloy of | Copper and Zinc | Copper and Tin | Arsenic and Tin | Gold and Tin | a | Brass is an alloy of copper and zinc. The colour is yellow or light yellow, or nearly white. Brass is also corrosion resistant Brass is widely used for making motor car radiator and water taps etc. | Comments | Active | |
| 307 | The process of formation of new grains on heating metals is called | Recrystallization | Oxidation | Microstructure | Hardening | a | Recrystallization is a process accomplished by heating where by deformed grains are replaced by a new set of grains that nucleate and grow until the original grains have been entirely consumed. | Comments | Active | |
| 308 | Which element makes stainless steel corrosion resistant? | Vanadium | Chromium | Carbon | Sulphur | b | Stainless steel is a corrosion-resistant alloy of iron, chromium and, in some cases, nickel and other metals. | Comments | Active | |
| 309 | Which of the following metals does not have hexagonal close packed structure? | Magnesium | Zinc | Cadmium | Copper | d | The HCP structure is very common for elemental metals and some examples include beryllium, cadmium, magnesium, titanium, zinc and zirconium. | Comments | Active | |
| 310 | Purpose of normalizing is to | Improve strength | Increase hardness | Remove internal stresses | None of these | c | Normalizing is used because it causes microstructures to reform into more ductile structures. This is important because it makes the metal more formable, more machinable, and reduces residual stresses in the material that could lead to unexpected failure. | Comments | Active | |
| 311 | Which tool is used for rapid machining of hard metals? | Cemented Carbide | High Speed Steel | Stellites | None of these | c | Stellite tools are ideal for rapid machining of hard metals. These are used for making form tools. Stellite is available in the form of bars of round or square section for manufacturing cutting tools; and as inserts to attach to tough steel milling cutter bodies. | Comments | Active | |
| 312 | Which of the following fundamental components of atom is uncharged? | Proton | Neutron | Electron | Positron | c | Common metal mirror coatings consist of thin films of aluminium, silver or gold Because of their high reflectivity. | Comments | Active | |
| 313 | Which metal coating is used in the mirror? | Lead | Tin | Gold | Brass | Comments | Active | |||
| 314 | Pure iron is a substance of | Ferrite | Pearlite | Austenite | Ferrite and Cementite | a | Pure iron is the structure of Ferrite. Austenite is not stable below 725°(C) So upon cooling the sample slowly carbon diffuses from one interstitial position to another and forms alternate plate like structure of ferrite and cementite. | Comments | Active | |
| 315 | Correct sequence of elements of 18 – 4 – 1 HSS tool is | W, Cr, V | Mo, Cr, V | Cr, Ni, C | Cu, Zn, Sn | a | 18-4-1 High-speed steel- contains 18 per cent tungsten (W), 4 per cent chromium (Cr), 1 per cent vanadium (V), 0.7% carbon and rest iron. | Comments | Active | |
| 316 | The unique property of cast iron is its high | Malleability | Ductility | Hardness | Damping characteristics | d | In gray cast iron, the graphite exists in the form of flakes. Due to the presence of these graphite flakes gray Cast Iron possesses high damping capacity and hence these materials are used for lathe machine beds and engine blocks. | Comments | Active | |
| 317 | 18/8 stainless steel contains | 18% Nickel, 8% Chromium | 18% Chromium, 8% Nickel | 18% Tungsten, 8% Nickel | 18% Tungsten, 8% Chromium | b | The numbers 18/8 represent the composition of this steel as 18% chromium and 8% nickel, making it very resistant to corrosion and oxidation. | Comments | Active | |
| 318 | The co-ordination number of face centred cubic structure is | 4 | 8 | 12 | 16 | c | The face-centered cubic (FCC) has a coordination number of 12 and contains 4 atoms per unit cell. The body-centered cubic (bcc) has a coordination number of 8 and contains 2 atoms per unit cell | Comments | Active | |
| 319 | The percentage of carbon in low carbon steel : | 1.0% | 0.15% | 0.87% | 0.50% | b | Dead carbon steel - 0.05% to 0.15% carbon Low carbon or mild steel - 0.15% to 0.45% carbon Medium carbon steel - 0.45% to 0.8% carbon High carbon steel - 0.8% to 2% carbon |
Comments | Active | |
| 320 | Which of the following is close to the purest form of Iron ? | Cast Iron | Wrought Iron | Grey Iron | Mild Steel | b | Wrought iron is the purest form of iron. It contains 0.12 to 0.25% carbon and is thus the purest form of iron. | Comments | Active | |
| 321 | Slenderness ratio is the ratio of | Maximum size of column to minimum size of column. | Width of column to depth of column. | Effective length of column to least radius of gyration of the column. | Effective length of column to width of column. | c | Slenderness ratio of a compression member is defined as the ratio of its effective length to least radius of gyration. Se = Le = Effective length K = Least radius of gyration K = \(\frac{L_{e}}{K}\) \(\frac{I_{Min}}{A}\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 322 | A long column fails by | Crushing | Tension | Shearing | Buckling | d | Failure’s in Column: Short column Medium Column Long column Mode of failure crushing or compression compression and buckling both Buckling (lateral displacement of body) |
Comments | Active | |
| 323 | Euler’s Buckling theory is applicable for | Short columns | Long columns | Medium long columns | All of these | b | Euler’s theory is applicable only for long column. While Rankine theory is applicable to any column (short and long). | Comments | Active | |
| 324 | The most economical section of a beam to bear maximum bending moment is | Square | Circular | Rectangular | I - section | d | In I section, the web resists shear forces, while the flanges resist more than 80% of the bending moment. Beam theory shows that the I-shaped section is a very efficient form for carrying both bending and shear loads in the plane of the web. | Comments | Active | |
| 325 | When a wire is stretched to double its length, the longitudinal strain produced in it is | 0.5 | 1.0 | 1.5 | 2.0 | b | Let original length \(l_{1}=l\) \(l_{2}=2l\) \(Strain=\frac{change in length}{original length}=\frac{l_{2}-l_{1}}{l_{1}}=\frac{2l-l}{l}=1\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 326 | The bending moment on a section is maximum where shear force is | Maximum | Minimum | Changing sign | Zero | d |  |
Comments | Active | |
| 327 | The bending moment diagram for a cantilever beam carrying concentrated load at end of beam will be a | Rectangle | Cubic parabola | Triangle | Parabola | c |  |
Comments | Active | |
| 328 | The property of a material which enables it to resist fracture due to impact loads is known as | Elasticity | endurance | Resilience | toughness | d | Toughness is property of a material to resist fracture due to high impact loads like hammer blows | Comments | Active | |
| 329 | In case of both the ends fixed of a column, the effective length is | Its own length | Twice its length | Half of its length | None of these | c | Euler’s load for different column with different end condition Boundary Condition Le Pe Both ends fixed 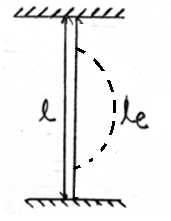 \(\frac{l}{2}\) \(\frac{4π^{2}EI}{l^{2}}\) Both ends are hinged  L \(\frac{π^{2}EI}{l^{2}}\) One end fixed and other end hinged  \(\frac{l}{2}\) \(\frac{2π^{2}EI}{l^{2}}\) One end fixed and other free  2l \(\frac{π^{2}EI}{4l^{2}}\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 330 | The ratio of moment of inertia of a rectangle and that of a triangle, having same base and height with respect to their bases would be | 2 : 1 | 3 : 1 | G. dd d d bb b b MOI with respect to base \(I_{base}=\frac{bd^{3}}{36}+\frac{1}{2}b×d×(\frac{d}{3})^{2}\) \(Traingle,I_{base}=\frac{bd^{3}}{12}\) Therefore the ratio is \(=\frac{\frac{bd^{3}}{3}}{\frac{bd^{3}}{12}}=\frac{4}{1}\) Or ratio is 4:1 |
5 : 1 | c | Comments | Active | ||
| 331 | Which of the following is more elastic? | Rubber | Plastic | Brass | Steel | d | Steel is the most elastic material. If the object is elastic, the body regains its original shape when the pressure is removed. Steel having the steepest linear stress-strain curve among all. | Comments | Active | |
| 332 | Necking phenomenon in stress-strain is observed for | Brittle materials | Ductile materials | Both brittle as well as ductile materials | None of the above | b | Necking is a type of plastic deformation observed in ductile materials subjected to tensile stress. | Comments | Active | |
| 333 | Strain is defined as the ratio of | Change in volume to original volume. | Change in length to original length. | Change in lateral dimension to original lateral dimension. | All of the above | d | Change in volume to original volume is called volumetric strain. Change in length to original length is called the linear strain. Change in lateral dimension to original lateral dimension lateral strain. |
Comments | Active | |
| 334 | The longitudinal joint of a boiler shell is always a | Lap joint | Butt joint | Lozenge joint | Diamond joint | b | The boiler has a longitudinal butt joint as well as circumferential lap joint. The longitudinal joint is used to join the ends of the plate to get the required diameter of a boiler. For this purpose, a butt joint with two cover plates is used. | Comments | Active | |
| 335 | 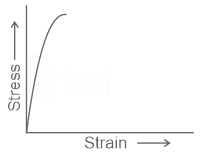 The above stress-strain diagram is for |
Ductile material | Brittle material | Soft material | None of these | b |  |
Comments | Active | |
| 336 | Moment of inertia of a solid sphere is (Where M = mass of the solid sphere r = radius of the sphere) |
\(Mr^{2}\) | \(\frac{2}{3}Mr^{2}\) | \(\frac{2}{5}Mr^{2}\) | \(\frac{1}{2}Mr^{2}\) | c | \( Solid cylinder=\frac{1}{2}Mr^{2}\) \(Thin cylinder=Mr^{2}\) Solid Sphere = \(Thin Spherical Shell=\frac{2}{3}Mr^{2}\) \(\frac{2}{5}Mr^{2}\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 337 | Flow stress corresponds to | Fluid in motion | Breaking point | Plastic deformation of solids | Rupture stress | c | Flow stress is the stress that must be applied to cause a material to deform at a constant strain rate in its plastic range | Comments | Active | |
| 338 | The fatigue life of a part can be improved by | Electroplating | Polishing | Coating | Shot peening | d | Shot peening is a process specifically designed to enhance the fatigue strength of components which are subject to high alternating stress. | Comments | Active | |
| 339 | Slow plastic deformation of metals under a constant stress at high temperature is known as | Fatigue | Plastic deformation | Creep | Endurance | c | Creep is time dependent inelastic deformation. Creep is the slow plastic deformation of metal under constant stress or under prolonged loading. | Comments | Active | |
| 340 | stress in thin walled cylinder is | Longitudinal tensile stress | Radial stress | Circumferential tensile stress | Compressive stress | c | Hoop stress in thin circumferential tensile stress | Comments | Active | |
| 341 | For perfectly elastic body, the value of co-efficient of restitution is | Zero | 0.5 | 1 | between 0 and 1 | c | If e = 0, then it is a perfectly inelastic collision If 0 < e < 1, then it is a real-world inelastic collision, in which some kinetic energy is dissipated. If e = 1, then it is a perfectly elastic collision in which no kinetic energy is dissipated, and the objects rebound from one another with the same relative speed with which they approached. |
Comments | Active | |
| 342 | Spiral springs are used in | Cycles | Scooters | Watches | Railway Wagons | c | Flat spiral springs are also known as spiral torsion, clock springs or brush springs. Their special character is that the coil contact is minimized during operation. It is used in watches and it has also application in automotive, medical, industrial and office equipment markets | Comments | Active | |
| 343 | In a beam, the point of contraflexure is a point where | Shear force is maximum. | Shear force is zero. | Bending moment changes its sign. | Bending moment is maximum. | c | A point of contra flexure is a location where the bending moment is zero or changes its sign. | Comments | Active | |
| 344 | When two springs (each having stiffness constant K) are connected in series, the equivalent stiffness will be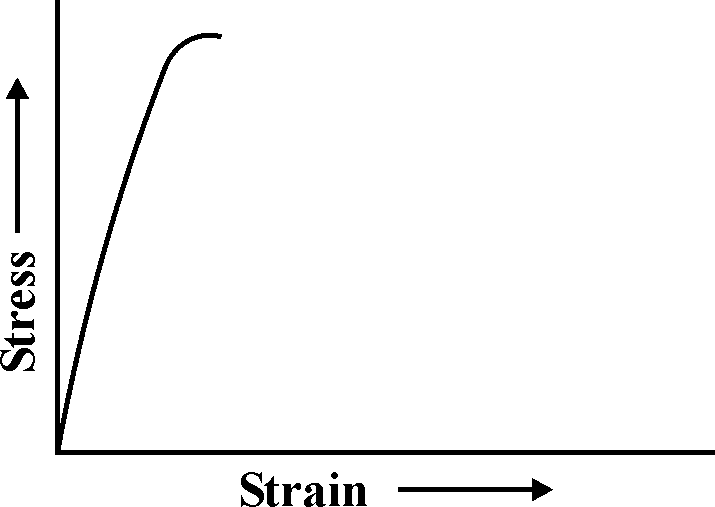 |
K | 2K | \(\frac{K}{2}\) | \(\frac{1}{K}\) | c | Equivalent stiffness of spring for series combination \(\frac{1}{K_{eq}}=\frac{1}{K_{1}}+\frac{1}{K_{2}}\) But here \(K_{1}=K_{2}=K\) \(\frac{1}{K_{eq}}=\frac{1}{K}+\frac{1}{K}=\frac{2}{K}\) \(K_{eq}=\frac{K}{2}\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 345 | Spring index is | Ratio of coil diameter to wire diameter. | Load required to produce unit deflection. | Its capability of storing energy. | None of the above | a | The spring index is the relationship between the mean diameter and wire diameter. Spring index C=D/d | Comments | Active | |
| 346 | Which of the following statements is correct? | Stress is proportional to strain. | Stress is force per unit area. | Within elastic limit, the ratio of stress to strain is called Young’s modulus. | All of the above | d | \( Stress σ=\frac{Force}{Area}=\frac{F}{A}, Strain=\frac{change in dim}{original dim}\) \(Young modulus E=σ/∈ \) All statements are correct. |
Comments | Active | |
| 347 | What is the unit of strain? | Centimetre | Millimetre | Micron | None of these | d | Strain is the deformation of a material from stress. It is simply a ratio of the change in length to the original length. \(ϵ=\frac{δ}{L}\) It is a dimensionless quantity. |
Comments | Active | |
| 348 | A dead load is one that | Remains constant | Varies with time | Cannot be determined | Whose value is zero | a | The dead load includes loads that are relatively constant over time, including the weight of the structure itself, and immovable fixtures such as walls, plasterboard or carpet. The roof is also a dead load. Dead loads are also known as permanent or static loads. | Comments | Active | |
| 349 | For a shaft transmitting power ‘P’ at rpm N, the diameter of shaft would be proportional to | \((\frac{P}{N})^{1/3}\) | \((\frac{P}{N})^{1/2}\) | \((\frac{P}{N})^{2/3}\) | \((\frac{P}{N})^{3}\) | a | We know that \(Ï„_{s}=\frac{16T}{Ï€d^{3}}\) \(Tâˆd^{3}\) Also, \(P=\frac{2Ï€NT}{60}\) \(\frac{P}{N}âˆd^{3}âˆT\) \((\frac{P}{N})^{\frac{1}{3}}âˆd\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 350 | Outside diameter of a hollow shaft is twice its inside diameter. Ratio of torque carrying capacity to that of a solid shaft of same outside diameter and same material is | 3/4 | 15/16 | 1/2 | 1/16 | b | The ratio of its torque carrying capacity to that a solid shaft of the same material and the same outside diameter is. 15/16. We know that, for hollow shaft \(τ_{h}=\frac{16T_{1}}{πD^{3}(1-K^{4})}\) For solid shaft \(τ_{s}=\frac{16T_{2}}{πD^{3}}\) As and (Given) \(τ_{h}=τ_{s}\) \(K=\frac{d}{D}=\frac{1}{2}\) \(T_{1}=T_{2}(1-K^{4})\) \(\frac{T_{1}}{T_{2}}=(1-K^{4})=(1-\frac{1}{16})=\frac{15}{16}\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 351 | Which of the following brakes is commonly used in motor cars? | Band Brake | Shoe Brake | Band and Block Brake | Internal Expanding Shoe Brake | d | The internal expanding type of brake is commonly used in motor cars and light trucks. | Comments | Active | |
| 352 | Axial thrust is minimum in case of | Spur gear | Bevel gear | Mitre gear | Double helical gear | d | In double-helical gear, the helix angle is 45°. Axial thrust occurs in the case of single helical gears eliminated in double helical gears. This is because the axial thrust of two rows of teeth cancels each other. |
Comments | Active | |
| 353 | The product of circular pitch and diametral pitch is equal to | 1 | 1.57 | π | Infinite | c | Circular Pitch (C) \( =\frac{πD}{T}\) Diametric Pitch \(P_{d}=\frac{T}{D}\) D = Pitch circle-diameterT = Number of teeth |
Comments | Active | |
| 354 | The maximum fluctuation of energy in a flywheel is equal to Where: I = Mass moment of inertia of the flywheel E = Mean kinetic energy of the flywheel CS = Co-efficient of fluctuation of speed ω = Mean angular speed = \(\frac{ω_{1}+ω_{2}}{2}\) |
Iω ( – ) \(ω_{1}\) \(ω_{2}\) | \(Iω_{2}C_{S}\) | 2ECS | All of these | d | Maximum fluctuation of energy: \(∆E=\frac{1}{2}Iω^{2}_{2}-\frac{1}{2}Iω^{2}_{1}=\frac{1}{2}I(ω^{2}_{2}-ω^{2}_{1})\) \(∆E=\frac{1}{2}I(ω_{2}+ω_{1})(ω_{2}-ω_{1})\) \(∆E=\frac{1}{2}Iω(ω_{2}-ω_{1})\) \(∆E=Iω^{2}C_{s}=2EC_{s}\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 355 | Which one of the following is not a friction clutch? | Disc or plate clutch | Cone clutch | Centrifugal clutch | Jaw clutch | d | Types of Clutch Friction clutchFriction clutchPositive clutchPositive clutch Friction clutch Friction clutch Positive clutch Positive clutch 1.Square-Jaw clutch2.Spiral-Jaw clutch1.Square-Jaw clutch2.Spiral-Jaw clutch1.Cone clutch2.Centrifugal clutch3.Dry clutch4.Plate clutch1.Cone clutch2.Centrifugal clutch3.Dry clutch4.Plate clutch 1.Square-Jaw clutch 2.Spiral-Jaw clutch 1.Square-Jaw clutch 2.Spiral-Jaw clutch 1.Cone clutch 2.Centrifugal clutch 3.Dry clutch 4.Plate clutch 1.Cone clutch 2.Centrifugal clutch 3.Dry clutch 4.Plate clutch |
Comments | Active | |
| 356 | A Portor governor could be classified as | Inertia type governor | Pendulum type governor | Centrifugal governor | Dead weight type governor | d | Porter governor is dead weight loaded type of gravity controlled centrifugal governor. |
Comments | Active | |
| 357 | The height of Watt’s governor is | Directly proportional to speed | Directly proportional to (speed)2 | Inversely proportional to speed | Inversely proportional to (speed)2 | d | \(h=\frac{g}{ω^{2}}=\frac{895}{N^{2}}\) h = height of each ball = Angular velocity of the balls, arms and the sleeve \(ω\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 358 | A cam and follower mechanisms constitutes a/an | Open pair | Screw pair | Closed pair | Spherical pair | c | When two elements of the pair are held together mechanically in such a manner that only the required type of relative motion occurs they are called a closed pair. All lower pairs and some higher pairs (for example cam and follower) are closed pairs. | Comments | Active | |
| 359 | The size of gear is usually specified by | Pressure angle | Pitch circle diameter | Circular pitch | Diametric pitch | b | The size of the gear is usually specified by the pitch circle diameter. It is also known as pitch diameter. | Comments | Active | |
| 360 | The velocity of belt for maximum power is (Where m = mass of the belt in kg per metre length. T = Tension) | \(\frac{T}{3m}\) | \(\frac{T}{4m}\) | \(\frac{T}{5m}\) | \(\frac{T}{6m}\) | a | Centrifugal tension for maximum power; Velocity of the belt for maximum power; \(T_{c}=\frac{T}{3}\) \(v=\frac{T}{3m}\) Here, T = Maximum tension = Centrifugal tension v = Velocity of belt in m/s m = mass of belt per unit length in kg \(T_{c}\) |
Comments | Active |










