| S.No | Question | Option A | Option B | Option C | Option D | Answer | Solution | Comments | Status | Action |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Identify the pressure indicated by C in the following figure. |
Vacuum pressure | Absolute pressure | Gauge pressure | Barometric pressure | c |  |
Comments | Active | |
| 2 | The Sl unit of couple is: | Kg-S | N-S | Pa-m | N-m | d | A couple in physics refers to a pair of equal and opposite forces whose lines of action do not coincide, creating a rotational effect (torque) but no resultant force. The magnitude of a couple (or torque) is calculated as: Torque=Force×Perpendicular distance between the forces Force is measured in newtons (N) Distance is measured in meters (m) So SI unit will N-m. |
Comments | Active | |
| 3 | Which of the following processes DOES NOT constitute in the Carnot cycle?" | Reversible Isothermal Heat Addition | Reversible Adiabatic Expansion | Reversible Isobaric Condensation | Reversible Isothermal Heat Rejection | c |  There is no process of Reversible Isobaric Condensation. |
Comments | Active | |
| 4 | Which of the following turbines is correctly paired with its type? | Mixed flow turbine → Francis turbine | Radial flow turbine→ Kaplan turbine | Reaction turbine→ Pelton wheel turbine | Inward flow turbine → Fourneyron turbine | a | Francis turbine is a mixed flow turbine, meaning water flows both radially and axially through the runner. The Kaplan turbine is an axial flow turbine, not radial. Water flows parallel to the axis of rotation. The Pelton wheel is an impulse turbine, not a reaction turbine. Reaction turbines involve pressure change across the runner, which is not the case for Pelton wheels. The Fourneyron turbine is an outward flow turbine, not inward. | Comments | Active | |
| 5 | Identify the correct option based on the given assertion and reason. Assertion (A): Steam turbines operate at fairly the same speed regardless of the load due to governing. Reason (R): Throttle governing is often done in small steam turbines. |
A is true but R is false | Both A and R are true | Both A and R are false | A is false but R is true | b | Assertion (A): Steam turbines are equipped with governing mechanisms that adjust the steam supply based on the load. This ensures that the turbine speed remains nearly constant, which is critical for applications like power generation where frequency stability is important. Reason (R): Throttle governing is a common method used in small steam turbines. It involves controlling the steam pressure and flow rate by throttling the steam before it enters the turbine. |
Comments | Active | |
| 6 | Calculate the depth of centre of pressure for the following body submerged in water.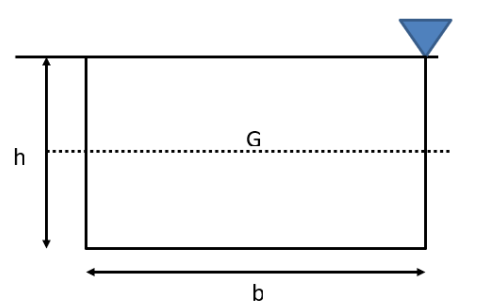 |
(2h) / 3 | (4h) / 3 | h/3 | (5h) / 3 | a | Surface C.G.( \(h)\) C.P.(P*) Rectangle 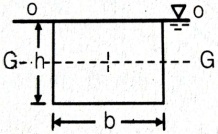 \(\frac{h}{3}\) \(\frac{2h}{3}\) Trapezium 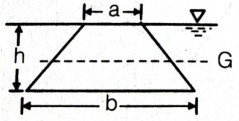 \(\frac{a+2b}{a+b}.\frac{h}{3}\) \(\frac{a+3b}{a+2b}.\frac{h}{2}\) Triangle 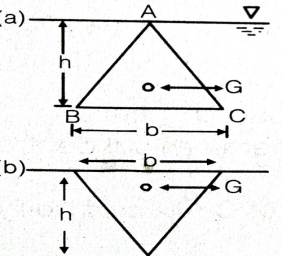 \(\frac{2h}{3}\) \(\frac{h}{3}\) \(\frac{3h}{4}\) \(\frac{h}{2}\) Circle 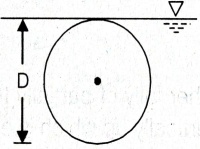 \(\frac{D}{2}\) \(\frac{5D}{8}\) Semi-circle 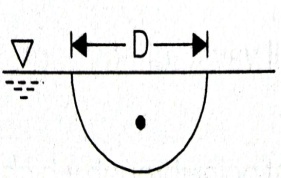 \(\frac{2D}{3Ï€}\) \(\frac{3Ï€D}{32}\) Parabola 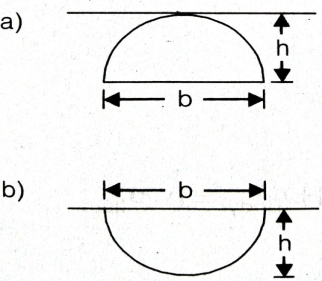 \(\frac{3h}{5}\) \(\frac{2h}{5}\) \(\frac{5h}{7}\) \(\frac{4h}{7}\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 7 | In ______, water flows parallel to the axis of the rotation of shaft. | Old Francis turbine | Francis turbine | Kaplan turbine | Pelton wheel | c | In a Kaplan turbine, water flows axially, meaning parallel to the axis of rotation of the shaft. It is an axial flow reaction turbine, commonly used for low-head, high Specific speed. |
Comments | Active | |
| 8 | The efficiency of Carnot cycle is expressed as | ratio of work done to amount of heat given | ratio of volume compressed to amount of heat given | ratio of work supplied to amount of work done | ratio of work done to pressure released | a | The efficiency of a Carnot cycle is defined as: η= \(\frac{Net work done by the engine}{Heat absorbed from the hot reservoir}\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 9 | Which of the following is NOT a type of boiler on the basis of its position? | Prone position boiler | Horizontal boiler | Inclined boiler | Vertical boiler | a | "Prone position boiler" is not a recognized classification in boiler terminology. | Comments | Active | |
| 10 | Identify which of the given statements are correct. Statements: A) A refrigerant should have high boiling point. B) A refrigerant should have high latent heat value. C) A refrigerant should have low freezing point. |
All A, B and C | Only A and C | Only B and C | Both A and B | c Solution  |
Comments | Active | ||
| 11 | Identify the thermodynamic device shown here. |
Refrigerator | Condenser | Compressor | Boiler | a | As we know that the work of refrigeration to absorb heat and transfer it to refrigerant as shown in figure.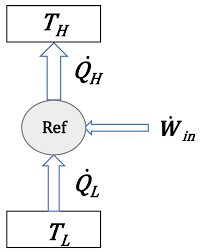 |
Comments | Active | |
| 12 | An air preheater is essentially a/an _____. | Heat exchanger | Cooler | Expander | Chiller | a | An air preheater is a device used to transfer heat from the flue gases to the incoming air before it enters the combustion chamber of a boiler or furnace. This increases thermal efficiency by preheating the combustion air, making it a type of heat exchanger. | Comments | Active | |
| 13 | Identify the correct pair on basis of types of components. | Venturimeter → Volume fan | Casing → Volute casing | Motor →Friction blades | Piston →Forward flow | b | A volute casing is a specific type of casing used in centrifugal pumps and compressors to collect and direct fluid flow efficiently. | Comments | Active | |
| 14 | Which of the following is NOT a classification of orifices? | Free discharging orifices | Drowned orifices | Submerged orifices | Blocked orifices | d | Blocked orifices is not a standard classification — a blocked orifice simply means it’s obstructed and not functional, not a recognized type of orifice in fluid mechanics. | Comments | Active | |
| 15 | ________ is done for keeping the steam turbine speed fairly same in-spite of load. | Positioning | Steering | Parting | Governing | d | Governing is the process used in steam turbines to maintain a nearly constant speed despite variations in the load. It involves controlling the steam flow to the turbine using a governor mechanism, which adjusts valves based on speed changes. | Comments | Active | |
| 16 | Identify the correct statement with respect to air standard cycle assumptions. | Water is a working fluid. | All processes in power cycles are internally irreversible. | Air is considered an ideal gas. | Steam is supplied at lower temperatures. | c | Air standard cycle assumptions: In the air standard cycle, we assume that the working fluid has a fixed mass. By assuming a closed system or fixed mass system, an ideal gas equation can be applied which makes the analysis easy. By assuming the fixed mass system we can use W = ∫Pdv because in closed system analysis swept volume is equal to displaced volume. The real open cycle is changed into a closed cycle by assuming that the gases being exhausted are fed back into the intake system. The working fluid is air which behaves as an ideal gas.  All the processes are internally reversible.  The specific heat of air remains constant during the cycle.  The combustion process is replaced by the heat addition process.  A cycle is assumed to be a closed cycle.  The exhaust process is modeled by a heat rejection process |
Comments | Active | |
| 17 | Negative gauge pressure is also known as | Barometric pressure | Atmospheric pressure | Vacuum pressure | Mercury pressure | c |  |
Comments | Active | |
| 18 | Identify the correct option based on the following statements pertaining to steam A: Condenser is a component of the refrigeration cycle. B: Throttling device is not a component of the refrigeration cycle. C: A compressor is a device of the refrigeration cycle. |
Only B and C are true | Only A and C are true | Both A and B are true | All A, B and C are true | b | An expansion valve (Throttling device) to regulate the flow of the refrigerant. So it is part of refrigeration cycle. | Comments | Active | |
| 19 | For which of the instrument out of given below, the coefficient of discharge is minimum? | Venturimeter | Orifice meter | Pirani gauge | Nozzle meter | b | Venturimeter: ~0.98 (highest, very efficient) Nozzle meter: ~0.95 Orifice meter: ~0.60 – 0.65 (lowest among flow meters listed) Pirani gauge: Not a flow-measuring device; it's used to measure low pressures (vacuum) using thermal conductivity – not applicable here |
Comments | Active | |
| 20 | Which of the following is true for stage efficiency for the steam turbines? | It is the product of blade efficiency and nozzle efficiency. | It is the addition of blade efficiency and nozzle efficiency. | It is the ratio of blade efficiency to nozzle efficiency. | It is the square of blade efficiency. | a | Stage Efficiency=Nozzle Efficiency×Blade Efficiency | Comments | Active | |
| 21 | Which of the following options is NOT true about viscosity? | It is caused by friction within a fluid. | Its unit is N-s/m². | It is the same as specific gravity. | It is an defined as the fluid's resistance to deformation at a given flow. | c | Specific Gravity is the density of any fluid w.r.t standard fluid i.e water, so it is simply ratio of densities and differ from viscosity. | Comments | Active | |
| 22 | Which of the following is NOT a type of clutch? | Cone clutch | Dry clutch | Cycloid clutch | Plate clutch | c | Cycloid clutch : Not a recognized type of clutch in mechanical systems. "Cycloid" typically refers to a type of gear profile (e.g., in cycloidal drives), not clutches. | Comments | Active | |
| 23 | Which of the following is NOT a component used in steam generation? | Evaporator | Governor | Boiler | Superheater | b | A governor is a mechanical or electronic device used to regulate the speed of a prime mover (such as a steam engine, diesel engine, or turbine) by controlling the fuel or steam input. | Comments | Active | |
| 24 | Which of the following is NOT an assumption made for Euler's equation of motion? | Frictional losses are zero. | Velocity of flow varies across the cross section. | Fluid is non-viscous. | Fluid is incompressible. | b | Velocity of flow varies across the cross section:- This is NOT an assumption of Euler's equation — it actually contradicts the assumptions, which treat the velocity as uniform across a cross-section along a streamline. | Comments | Active | |
| 25 | Identify the flow shown in the following figure. |
Turbulent flow | Laminar flow | Recoil flow | Transient flow | a | Turbulent flow is a type of fluid motion characterized by chaotic, irregular, and random fluctuations in velocity and pressure. | Comments | Active | |
| 26 | Which of the following is NOT a type of cam when classified according to follower movement? | Dwell-Rise-Dwell-Return-Dwell | Rise-Rise-Rise | Rise-Return-Rise | Dwell-Rise-Return-Dwell | b | Follower Movement (Reference – Theory of machine by SS Rattan – page No.-212) So, Rise-Rise-Rise is not any follower movement. |
Comments | Active | |
| 27 | ______ is a part of gas turbine fuel injector. | Plug | Screw gauge | Gun | Vaporiser | d | Vaporiser is a part of gas turbine fuel injector. | Comments | Active | |
| 28 | Identify the correct pair in terms of type of welding and the electrode used from the following options. | Tungsten electrode → TIG welding | Aluminium electrode → Laser welding | Monel electrode → Friction stir welding | Titanium electrode → Friction welding | a | Friction stir welding (FSW) is a solid-state process that does not use any electrodes or filler materials. Friction welding is another solid-state process that generates heat through mechanical friction. It does not use electrodes of any kind. Laser welding uses a high-energy laser beam to fuse materials. It does not use electrodes like traditional arc welding methods. | Comments | Active | |
| 29 | In a glass tube with water flowing, a liquid dye with the same specific weight is introduced. The resulting dye filament pattern is observed as shown in the figure. Identify the type of flow from the following options. |
Laminar flow | Recoil flow | Transient flow | Turbulent flow | d | Turbulent flow is a type of fluid motion characterized by chaotic, irregular, and random fluctuations in velocity and pressure. | Comments | Active | |
| 30 | Coefficient of friction depends on_____ | Density of the fluid | Surface roughness | Colour of the fluid | Weight of the fluid | b | Coefficient of fricition is simply the indication that how rough surface is . if this coefficient value is high then surface is rough and for smooth surface coefficient value will less and extremely smooth surface coefficient of friction value will very high. | Comments | Active | |
| 31 | Identify the correct option based on the given statements. A: Clearance ratio for a single stage reciprocating compressor is the ratio of clearance volume to swept volume. B: Clearance ratio for single stage reciprocating compressor is generally in the range of 2 to 10%. |
Both A and B are false | A is true, but B is false | Both A and B are true | A is false, but B is true | c | clearance Ratio = \(\frac{clearence Volume}{Swept Volume}\) The clearance ratio is typically in the range of 2% to 10% for single-stage compressors, depending on design and application. |
Comments | Active | |
| 32 | Identify the correct statement with respect to hydroelectric power plant. | Net head is the water level before tail race. | Net head or effective head is the head available at the inlet of the turbine. | Gross head is the effective head after the water is delivered. | Gross head is the water level before head race. | B | Net head or effective head is the head available at the inlet of the turbine. | Comments | Active | |
| 33 | Match column A with column B Column A (Property) Column B (Definition) A. Flash point 1. Temperature at which vapours are given off from oil B. Pour point 2. Temperature at which lubricant is able to flow C. Fire point 3. Temperature at which oil catches fire |
A-1; B-2: C-3 | A-2: B-3: C-1 | A-2: B-1: C-3 | A-3: B-1: C-2 | a | Flash point: Temperature at which vapours are given off from oil Pour point: Temperature at which lubricant is able to flow Fire point: Temperature at which oil catches fire |
Comments | Active | |
| 34 | Bernoulli’s equation is applied on _______. | Tachometer | Manometer | Side bar | Orifice meter | d | Orifice meter – A flow measurement device that uses Bernoulli’s principle to calculate flow rate from pressure differences across an orifice. | Comments | Active | |
| 35 | Identity the correct option based on the following statements. A. Refrigerant should be affected by moisture. B. Refrigerants should be non-toxic. C. Refrigerants should be non-corrosive. |
Only B, and C are true | Only A, and C are true | Only A,B and C are true | Both A and C are true | a | Refrigerant should not affected by moisture. |
Comments | Active | |
| 36 | Which of the following fuels is LEAST/NEVER used in a boiler? | Gas | Mercury | Oil | Coal | b | Mercury is never used as a fuel in boilers. It is a toxic metal, not combustible, and does not release energy through combustion like other fuels do. | Comments | Active | |
| 37 | Cochran boiler is a ______, ________ and _______ type of boiler. | Fire tube; vertical; low pressure | Fire tube; horizontal; low pressure | Water tube; horizontal ; high pressure | Water tube; vertical; high pressure | a | Cochran boiler: fire tube; vertical; low pressure boiler. |
Comments | Active | |
| 38 | Refer to the given figure which shows Power (P) versus Discharge (Q) for a centrifugal pump and match the columns accordingly. Column A (Curve) Column B (Type of vane) A. Curve B 1. Forward vane B. Curve A 2. Backward vane C. Curve C 3. Radial vane |
A-2, B-3, C-1 | A-1, B-2, C-3 | A-1, B-3, C-2 | A-3, B-1, C-2 | d | 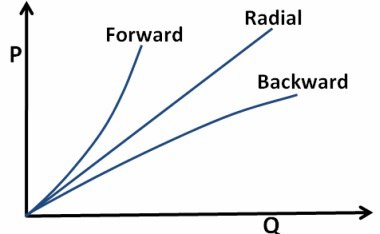 |
Comments | Active | |
| 39 | In ______ compressors, the compressor and the motor work on the same shaft and are housed in the same casing. | Hermetically sealed | Common cased | Ergonomically tabulated | Hydrophobically crafted | a | Comments | Active | ||
| 40 | Given in the options are terminologies related to the value timing diagram of an IC engine and their full forms. Identify the full form that is correctly paired with it short form. | FVO First Value operation \(→\) | TDC Top dead centre \(→\) | BDC Burden dead core \(→\) | IVC Intake valve corrosion \(→\) | b | FVO is not a standard term in IC engine valve timing diagrams, BDC stands for bottom dead center, IVC stands for Intake Valve Closing, part of the valve timing in an IC engine. | Comments | Active | |
| 41 | Which of the following is a 100% reaction turbine? | Hero's turbine | Rateau turbine | Curtis turbine | De-Laval turbine | a | 50 % reaction turbine : parson turbine , 100% reaction turbine : Hero's turbine | Comments | Active | |
| 42 | Which of the following is NOT a type of lathe machine? | Turret lathe | Tool room lathe | Boiler room lathe | Bench lathe | c | On the basis of their purpose, design, number of tools accommodated, degree of mechanisation and other factors, lathe-type machine tools may be classified as : 1. Limited or low-production Machines. The lathes included in this category are : engine lathe (centre lathe), bench lathe, tool room lathe and speed lathe. 2. Medium-production Machines. Turret lathes and duplicating (or tracer controlled) lathes. 3. High-production Machines. Semi automatic and automatic lathes. (Reference – A textbook of production technology by P.C. Sharma – page no.-449) |
Comments | Active | |
| 43 | Identify whether the given statements are true or false. Statements: A) Work done by a system on its surroundings is treated as a negative quantity. B) Energy transfer as heat to a system from its surroundings is treated as a positive quantity. |
Both A and B are true | A is true but B is false | A is false but B is true | Both A and B are false | c | Work done by the system is considered as positive work so option a is incorrect here. Remind sign work heat and work by this:  |
Comments | Active | |
| 44 | Calculate the depth of centre of pressure for the following body (circular plate) submerged in water (where D is diameter and G is centre of gravity). |
D/2 | D/3 | 5D/8 | 5D/4 | c | Surface C.G.( \(h)\) C.P.(P*) Rectangle  \(\frac{h}{3}\) \(\frac{2h}{3}\) Trapezium  \(\frac{a+2b}{a+b}.\frac{h}{3}\) \(\frac{a+3b}{a+2b}.\frac{h}{2}\) Triangle  \(\frac{2h}{3}\) \(\frac{h}{3}\) \(\frac{3h}{4}\) \(\frac{h}{2}\) Circle  \(\frac{D}{2}\) \(\frac{5D}{8}\) Semi-circle  \(\frac{2D}{3Ï€}\) \(\frac{3Ï€D}{32}\) Parabola  \(\frac{3h}{5}\) \(\frac{2h}{5}\) \(\frac{5h}{7}\) \(\frac{4h}{7}\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 45 | A______ is provided to remove the water from a steam-water mixture in a boiler. | Lever valve | Pin check | Fusible plug | Steam trap | d | steam trap: To "trap" steam in the system while removing condensate (water formed as steam cools down) and gases that can reduce efficiency or damage equipment. | Comments | Active | |
| 46 | Match column A with column B. Column A (Law of Thermodynamics) Column B (Concept) A. Zeroth law 1. Conservation of energy B. First law 2. Entropy C. Second law 3. Thermal equilibrium |
A-2; B-1; C-3 | A-1; B-3; C-2 | A-3; B-1: C-2 | A-2; B-3; C-1 | c | Zeroth Law of thermodynamics (Temperature Measurement) when a body A is in thermal equilibrium with a body B & also separately with a body C then body B & C will be in thermal equilibrium with each other. First Law of Thermodynamics (Law of Conversion of Energy)- Joule’s Experiment “It states that, a definite amount of mechanical work is needed to produce a definite amount of heat and vice versa i.e. “Heat and mechanical work are inter-convertibleâ€. Second Law of Thermodynamics : define entropy |
Comments | Active | |
| 47 | Based on the following P-V and T-s diagrams, identify the IC engine cycle.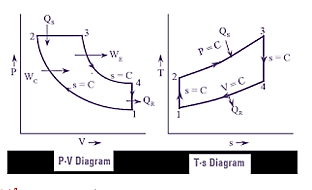 |
Brayton cycle | Diesel cycle | Otto cycle | Stirling cycle | b | 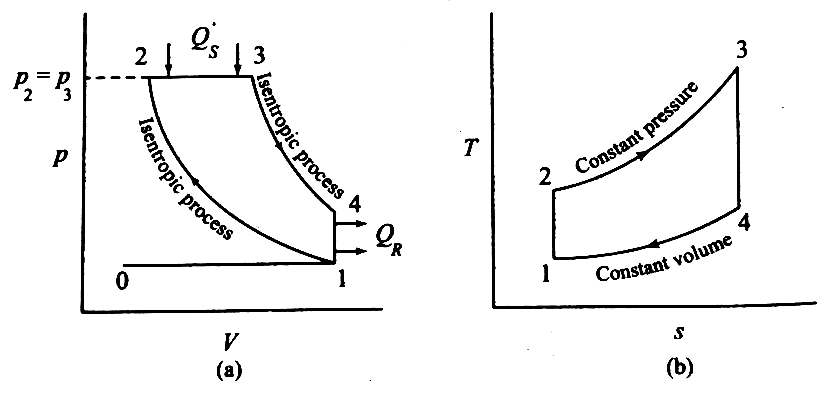 Diesel cycle: Isentropic Process 1-2 (compression) Isobaric Process 2-3 (heat addition) Isentropic Process 3-4 (expansion) Isochoric Process 4-1 (heat rejection) |
Comments | Active | |
| 48 | In order to grind material with high tensile strength abrasive is predominantly used on abrasive wheels. | Aluminium oxide | Sodium chloride | Manganese | Copper | a | Aluminium oxide it is extensively used for grinding materials of high tensile strength, such as, most steels, H.S.S., ferrous alloys, non-ferrous cast alloys and annealed malleable and ductile iron. (Reference – A textbook of production technology by P.C Sharma – page no.-532) |
Comments | Active | |
| 49 | The value of static friction is between___ and limiting friction. | 10 | 0 | 15 | 5 | b | As we can see in bleow diagram that between zero to limiting friction is reprenented by Static friction. |
Comments | Active | |
| 50 | Archimedes principle discusses____ | viscosity | illuminance | potency | buoyancy | d | Archimedes Principle- Whenever a body is either partially or completely submerged in a fluid, it experiences a force in upward direction which is equal to the weight of the fluid displaced. So it discuss about buoyancy, option d will be correct answer. |
Comments | Active | |
| 51 | Identify point A in the following figure. |
Critical point | Triple point | Saturation point | Superheated point | a | Point a represent the critical point .At this point solid directly convert into vapour. | Comments | Active | |
| 52 | In case of liquids, can be seen as cohesive forces between molecules of liquid | Adaptability | Transferability | Permeability | Viscosity | d | cohesive forces between molecules of liquid can be seen by viscosity. Dynamic viscosity: 10 poise \(\frac{N-s}{m^{2}}=Pa-s=\frac{kg}{m-s}=\) Kinematic viscosity: = m2/s \(ν=\frac{μ}{Ï}\) 1stoke = cm2/sec m2 / s = 104 stokes T \(↑\) \(μ\) ν Liquid \(↓\) \(↓\) Gases \(↑\) \(↑\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 53 | In a rotameter, the float position indicates____ | Weight | Viscosity | Density | Flow rate | d | Rotameter Operation principle: When fluid is entered into the tube, some of the fluid strikes the float & some pass by. This makes the float move upwards until the buoyant force is equal to the weight of the float. At this point, the float will stop to move upwards and the float position will indicate the flow rate. Annular space increasing upward, thus giving more area, more flow, more upward movement of the float & hence more flow rate.  |
Comments | Active | |
| 54 | An oil of specific gravity 0.9 flows through a 0.1 m diameter pipe under a pressure of 100 kPa. The centre line of the pipe is 5 m above the datum line and the total energy with respect to the datum is 0.04 kJ/N. Then the discharge of the oil through the pipe in litre per second is | 170 | 340 | 85 | 677 | a | Bernoulli equation \(\frac{p}{5g}+\frac{v^{2}}{2g}+z=H \) \(11.33+\frac{v^{2}}{2g}+5=40 \) \(v=464.28 ≈21.54 m/sec\) \(Q=A.v=0.007×21.54\) \(=169.2 Lites/sec\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 55 | Which of the following statements based on the given figure is/are correct? Statements: A) Point Y represents rupture strength. B) Point E represents elastic limit. C) Point P represents proportional limit. |
Only Statements B and C | Only Statement A | Only Statement C | Only Statement B | a A = Proportional limitB = Elastic limitC = Upper yield pointD = Lower yield pointF = Ultimate pointG = Breaking point A = Proportional limitB = Elastic limitC = Upper yield pointD = Lower yield pointF = Ultimate pointG = Breaking point Solution: |
Comments | Active | ||
| 56 | The work of a compressor in a vapour compression refrigeration system is to____ | Increase the volume of the refrigerant at constant entropy | Increase the temperature of the refrigerant at constant entropy | Increase the pressure of the refrigerant at constant entropy | Increase the velocity of the refrigerant at constant entropy | b | 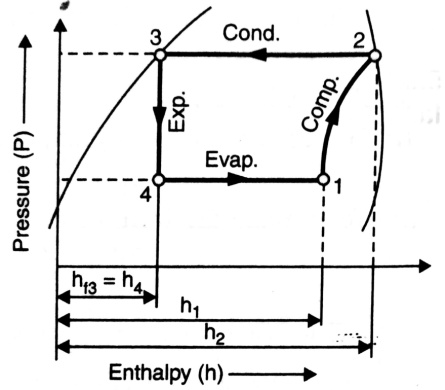 |
Comments | Active | |
| 57 | Identify the correct statement with reference to definition of coefficient of discharge for a steam nozzle | Ratio of actual discharge to theoretical discharge. | Ratio of total discharge to leaked discharge. | Ratio of theoretical discharge to total discharge. | Ratio of theoretical discharge to actual discharge | a | Co-efficient of Discharge () is defined as the ratio of the actual discharge from an orifice to the theoretical discharge from the orifice. \(C_{d}\) \(C_{d}=\frac{Q}{Q_{th}}=\frac{Actual velocity× Actual area}{Theoretical velocity×Theoretical area} \) \(C_{d}=\frac{Actual velocity}{Theoretical velocity}×\frac{Actual area}{Theoretical area}= C_{v}× C_{c}\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 58 | Loss of head occurring due to bend in pipe during fluid flow is considered as___ | Minor loss | Resultant loss | Recording loss | Major loss | a | Loss of head occurring due to bend in pipe during fluid flow is considered as minor loss while fricition losses are considered as major loss. | Comments | Active | |
| 59 | The graphical representation of transformation of 1 kg of ice into 1 kg of superheated steam at constant pressure is known as ____ | u-v diagram | h-s diagram | p-v diagram | t-h diagram | d | The T-h diagram (Temperature vs. Enthalpy) clearly shows: Temperature plateaus during phase changes (melting and boiling) Sloped regions during sensible heating (solid, liquid, and superheated phases) It's ideal for representing processes involving heat addition and phase changes. |
Comments | Active | |
| 60 | Which of the following is NOT a minor energy (head) loss? | Loss due to enlargement | Loss due to obstruction in pipe | Loss due to friction | Loss due to contraction | c | Friction loss is considered as major loss in pipe flow. | Comments | Active | |
| 61 | Identify whether the given statements are true or false. Statements: A) In a double acting compressor, suction and expansion take place in two different strokes. B) In single acting compressors, both suction and expansion stroke take place in two different strokes. |
Both statements are false | Statement B is true but Statement A is false | Statement A is true but Statement B is false | Both statements are true | b | In a double-acting compressor, suction and compression occur simultaneously on opposite sides of the piston during each stroke. That means: On one side of the piston: suction takes place. On the other side of the piston: compression happens. There is no separate "expansion" stroke like in internal combustion engines. Instead, both sides of the piston are active during every stroke, which increases efficiency and output. |
Comments | Active | |
| 62 | Velocity potential function is a/an_____ | Infinite quantity | Vector quantity | Elemental quantity | Scalar quantity | b | (Reference -Fluid mechanics and machine by RK Bansal – page no .-181) Velocity Potential Function. It is defined as a scalar function of space and time such that its negative derivative with respect to any direction gives the fluid velocity in that direction. It is defined by ϕ (Phi). Mathematically, the velocity, potential is defined as ) for steady flow such that \(ϕ = f(x, y, z\) \(μ=-\frac{∂ϕ}{∂x} \) \(v =-\frac{∂ϕ}{∂y} \) \(w =-\frac{∂ϕ}{∂z}\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 63 | Identify the INCORRECT statement from the following options. | Stainless steels are a type of alloy steels. | Stainless steel contains chromium. | Stainless steels are a type of non-ferrous steels. | Stainless steels are resistant to corrosion. | c | Steel by definition is a ferrous alloy, meaning it is primarily composed of iron. Non-ferrous metals do not contain significant amounts of iron (e.g., aluminum, copper, titanium). |
Comments | Active | |
| 64 | Identify the correct option based on the given assertion and reason. Assertion (A): Hot tea kept in a thermos flask remains hot for a longer duration. Reason (R): A thermos flask is an example of a closed system. |
Both A and R are true | A is false but R is true | Both A and R are false | A is true but R is false | d | A thermos flask is designed to minimize heat loss through conduction, convection, and radiation. A closed system allows energy (heat or work) to cross the boundary, but not mass. A thermos flask ideally tries to minimize energy exchange (especially heat), so it is closer to an isolated system, although in practice, it's not perfectly isolated. So, A is true but R is false. |
Comments | Active | |
| 65 | Which of the following efficiencies is NOT related to turbines? | Mechanical efficiency | Hydraulic efficiency | Machine efficiency | Volumetric efficiency | c | Machine efficiency is NOT related to turbine.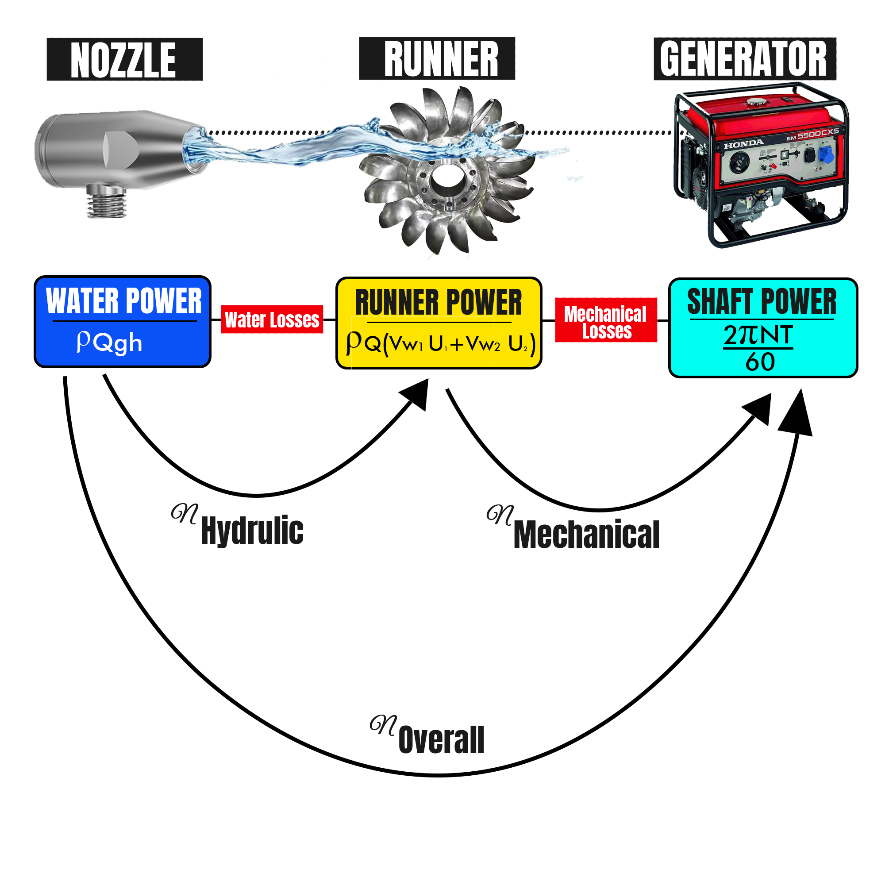 |
Comments | Active | |
| 66 | Two types of radiators used for IC engine systems are____and______ | Tubular core type, cellular core type | Tubular core type, reciprocating core type | Reciprocating core type, rotating core type | Rotating core type, cellular core type | a | 1. Tubular Core Type: Consists of tubes through which the coolant flows. Heat is transferred from the coolant to the fins attached to the tubes and then to the air. Common in older or simpler vehicles. 2. Cellular Core Type (also called honeycomb type): Made of numerous small air passages (cells) with coolant circulating around them. Offers a larger surface area for heat transfer. Common in modern vehicles due to better cooling efficiency. |
Comments | Active | |
| 67 | Identify which of the given statements related to IC engines is/are correct. Statements: A) Mechanical efficiency of a single-cylinder four-stroke engine is the ratio of brake power to indicated power. B) Volumetric efficiency of Sl engine is generally less than 30%. C) Volumetric efficiency of Cl engine is generally less than 30%. |
Only Statement C | Only Statement A | Only Statement B | Only Statements B and C | b | Volumetric efficiency of a Spark Ignition (SI) engine is typically in the range of 70% to 90% under normal operating conditions. Compression Ignition (CI) engines (diesel engines) often have volumetric efficiencies greater than 85%, sometimes even exceeding 100% due to turbocharging. | Comments | Active | |
| 68 | Barometric pressure is also known as____ | Fluid pressure | Volumetric pressure | Atmospheric pressure | Density | c | Barometer is the device used to measure the atmospheric pressure. | Comments | Active | |
| 69 | Match column A with column B. Column A (Boiler) Column B (Pressure) A. Cochran boiler 1. Medium pressure B. Babcock and Wilcox boiler 2. Low pressure C. Locomotive 3. High pressure boilers |
A-2: B-3: C-1 | A-1; B-2; C-3 | A-2: B-1: C-3 | A-1; B-3; C-2 | c | Cochran boiler: Low pressure (6.7 bar) Babcock and Wilcox boiler: Medium pressure (11.5 – 17.5 bar) Locomotive: High pressure boilers (20-25 bar) |
Comments | Active | |
| 70 | Identify whether the given statements related to IC engines are true or false. Statements: A) SI engine does not consist of a spark plug. B) CI engine does not consist of a spark plug. |
Both statements are true | Statement B is true but Statement A is false | Both statements are false | Statement A is true but Statement B is false | b | SI stands for spark ignition i.e petrol engine . we use spark plug to ignite fuel here so a is incorrect. | Comments | Active | |
| 71 | The temperature at which liquid droplets just appear when moist air is cooled continuously is called, | Flash point temperature | Fire temperature | Pour point temperature | Dew point temperature | d | Dry Bulb Temperature: Actual temperature of gas or mixture of gases. Wet-bulb temperature: Temperature obtained by an accurate thermometer having a wick moistened with distilled water. Dew point temperature: Temperature at which the liquid droplets just appear when the moist air is cooled continuously. |
Comments | Active | |
| 72 | Identify the correct statement with respect to centrifugal pumps. | Forward curved vanes can handle high flow rates. | Forward curved vanes have concave side of curvature facing direction of fluid flow. | In radial vanes, the fluid does not flow radially outward/inward from centre of rotation. | Backward curved vanes can handle high flow rates. | a | Forward curved vanes can handle high flow rates. | Comments | Active | |
| 73 | According to the Darcy-Weisbach equation for flow through pipe, head loss due to friction is inversely proportional to which of the following pipe parameters? | Diameter of the pipe | Material type of the pipe | Colour of the pipe | Weight of the pipe | a | According to the Darcy-Weisbach equation for flow through pipe, head loss due to friction is inversely proportional to Diameter of the pipe. According to the Darcy-Weisbach equation: \(h_{f}=\frac{f. L.V^{2}}{2g.D}\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 74 | Identify the part of the flywheel indicated as 'A' in the following figure. |
Hub | Frame | Spoke | Rim | a | A indicate hub of the flywheel. | Comments | Active | |
| 75 | Match the columns. Column A (Compressor) Column B (Feature) A. Screw compressor 1. Compressor and motor operate on same shaft B. Hermetically sealed compressor 2. Uses piston assembly C. Reciprocating compressor 3. Rotary type |
A-3; B-1; C-2 | A-2; B-3; C-1 | A-2; B-1; C-3 | A-1; B-3; C-2 | a | Screw compressor: Rotary type Hermetically sealed compressor: Compressor and motor operate on same shaft Reciprocating compressor: Uses piston assembly |
Comments | Active | |
| 76 | _____ is also known as the principle of transmission of fluid pressure. | Buoyancy law | Pascal's law | Newton's law | Archimedes' principle | b | Pascal law: In a static fluid pressure at point is equal in all directioon.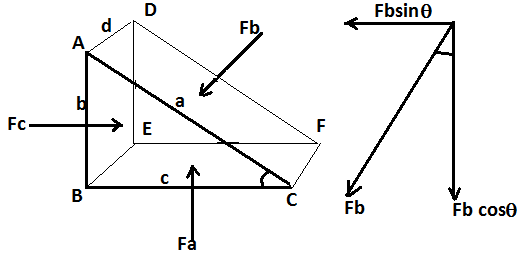 |
Comments | Active | |
| 77 | ____ is a vertical boiler | Cochran boiler | Locomotive boiler | Babcock and Wilcox boiler | Lancashire boiler | a |  |
Comments | Active | |
| 78 | Identify the correct expression from the following options. | Brake power = Indicated power + Friction power | Brake power = Indicated power/Friction power | Brake power = Indicated power* Friction power | Brake power = Indicated power - Friction power | d | \(HA/sec=m_{f}(Cv)_{f}\) \(H.RI.P(At Piston) \) \(-F.P⟶due to mechanical arrangement B.P=τ×w(At engine shaft)\) | Comments | Active | |
| 79 | Which of the following statements is correct with respect to definition of sensible heat factor? | It is a ratio of sensible heat to total heat of the system. | It is a ratio of total heat to usable heat of the system. | It is a ratio of total heat to sensible heat of the system. | It is a ratio of total heat to available heat of the system | a | Sensible heat factor (S.H.F) The sensible heat factor is the ration of sensible heat to total heat. \(SHF=\frac{SH}{SH+LH}=\frac{S.H}{T.H}\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 80 | Match the given stages of the valve timing diagram for four-stroke petrol engines with their respective positions Column A (Stages) Column B (Position) A. Exhaust valve opens 1. 10°-20° before top dead centre B. Exhaust valve closes 2. 30°-50° before bottom dead centre C. Inlet valve opens 3. 10"-15" after top dead centre |
A-3; B-1; C-2 | A-2; B-3; C-1 | A-2; B-1; C-3 | A-1; B-3; C-2 | b | (Reference: Internal combustion engine by V ganeshan – page no.-140 ) |
Comments | Active | |
| 81 | Natural draught for exhaust gases is provided during the working of a steam generator by….. | Feed valves | Chimneys | Conductors | Compressors | b | In a steam generator (boiler) system, natural draught is the flow of air and exhaust gases due to natural convection, created by the difference in density between the hot gases inside the chimney and the cooler outside air. Chimneys create this pressure difference, allowing the exhaust gases to rise and escape naturally without the use of fans or compressors. |
Comments | Active | |
| 82 | Steam tables are available either on…. Or….. basis | Temperature, velocity | Pressure, dryness | Pressure, temperature | Velocity, dryness | c | "Steam tables are available either on pressure or temperature basis." | Comments | Active | |
| 83 | Identify the correct option based on following statements pertaining to steam. A: At a given pressure, the capacity of superheated steam to do work will be comparatively higher. B: Dryness fraction is a term related to quality of steam. C: Wet steam does not exists. |
Both A and B are true | Only C is true | Only A is true | Both A and C are true | a | Superheated steam contains more energy (enthalpy) than saturated steam at the same pressure. This extra energy can be converted to work, especially in turbines, making it more efficient. Dryness fraction indicates the proportion of vapor in wet steam. It is used to measure the quality of steam. Wet steam does exist and is a common state in steam systems. It is a mixture of saturated liquid water and saturated steam. |
Comments | Active | |
| 84 | Calculate the depth of the centre of pressure for the following body submerged in water. |
h/4 | h/3 | h | h/2 | d | Surface C.G.( \(h)\) C.P.(P*) Rectangle  \(\frac{h}{3}\) \(\frac{2h}{3}\) Trapezium  \(\frac{a+2b}{a+b}.\frac{h}{3}\) \(\frac{a+3b}{a+2b}.\frac{h}{2}\) Triangle  \(\frac{2h}{3}\) \(\frac{h}{3}\) \(\frac{3h}{4}\) \(\frac{h}{2}\) Circle  \(\frac{D}{2}\) \(\frac{5D}{8}\) Semi-circle  \(\frac{2D}{3Ï€}\) \(\frac{3Ï€D}{32}\) Parabola  \(\frac{3h}{5}\) \(\frac{2h}{5}\) \(\frac{5h}{7}\) \(\frac{4h}{7}\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 85 | Identify the correct pair in terms of type of process and the temperatures they are carried out from the following options. | Brazing → Below 300°C | Soldering → Above 1500°C | Brazing → Above 1500°C | Soldering → Below 300°C | d | Brazing: the brazing process can be define as the process to join two metal pieces heated to suitable temperature by using a filler metal having a liquidus above 427 and below the solidus of the base metals. \(℃\) Soldering: in soldering, two parts are joined by the use of a molten filler metal whose melting point is below the solidus (melting point of the base metals) and in all cases below 427 . \(℃\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 86 | Coefficient of performance for vapour compression refrigeration is proportional to evaporator temperature and proportional to condenser temperature. | Inversely, inversely | Directly, directly | Directly, inversely | Inversely, directly | c | The coefficient of performance (COP) of a vapour compression refrigeration cycle is directly proportional to the evaporator temperature and inversely proportional to the condenser temperature. | Comments | Active | |
| 87 | Which of the following statements is correct with respect to the Cochran boiler? | It has high rate of steam generation. | It requires high floor area. | High room head is required for its installation due to the vertical design | It has high initial installation cost. | c |  Cochran boiler: high room head required for its installation due to the vertical design. |
Comments | Active | |
| 88 | Tensile forces on the arms of a flywheel are due to the | Kinetic forces | Lateral deviation | Longitudinal variation | Centrifugal forces | d | Flywheel The rotating rim of a flywheel is subjected to a uniformly distributed centrifugal force Pc , which acts in a radially outward direction. This includes a tensile force P in the cross-section of the rim acting in the tangential direction and a bending moment M.  From the above diagram we can observe that the tensile forces on the arms of a flywheel are due to centrifugal force Pc. |
Comments | Active | |
| 89 | Relative density is also termed as…… | Buoyancy | Floatability | Acceleration | Specific gravity | d | Relative density is the density of any fluid w.r.t another fluid if this other fluid is standard fluid i.e water then this relative density is called as specific gravity. | Comments | Active | |
| 90 | Identify the correct pair from the following. | Secondary refrigerant : R12 | Secondary refrigerant : R1150 | Secondary refrigerant : Brine | Secondary refrigerant :R11 | c | Primary Refrigerant - These are the refrigerants or working substance which are directly used for cooling purpose. These refrigerants undergo a cyclic process and produce lower temperature. There is a latent heat transformation for the refrigerants. For e.g. R-11, R-12, R-22, R-134a, R-1150, Ammonia etc. Secondary Refrigerant - These are the working fluids or working substance which are first cooled by primary refrigerant and then used for cooling at the desired place.eg, H2O , Brine, Ethylene glycol. Uses of different refrigerants R-11 – Large central air conditioning plant R-12- Domestic refrigerator, water cooler etc. R-22- Window AC NH3 - Cold storage or Icing plants CO2 - Transportation of dry ice Air- Air-craft refrigeration system Brine- Milk chilling plants |
Comments | Active | |
| 91 | Match the columns. |
A-2; B-3; C-1 | A-2; B-1; C-3 | A-1; B-3; C-2 | A-3; B-1; C-2 | a | Beam A: Cantiliver beam having UDL over the entire length , then SFD will be Triangle Beam B: simply supported beam having UDL over the entire length , then SFD will be diag.3, at middle point shear force will zero and B.M have maximum value at that point. Beam C: Simply supported beam having point load at mid point then SFD Will be diag.1, at middle point shear force will zero and B.M have maximum value at that point. |
Comments | Active | |
| 92 | Which of the following is NOT a safety valve used in a boiler? | Pin safety valve | Dead weight safety valve | Lever safety valve | Spring loaded safety valve | a | Safety valves The function is to release the excess steam when the pressure of steam inside the boiler exceeds the rated pressure. Types of safety valves: Deadweight safety valve Lever safety valve Spring-loaded safety valve High steam and low water safety valve. |
Comments | Active | |
| 93 | Which of the following statements related to the efficiency of a roots blower is correct? | It is a ratio of actual work done to ideal work done. | It is a ratio of actual volume to ideal volume required | It is a ratio of ideal volume to actual volume required. | It is a ratio of isentropic work done to actual work done. | d | Isentropic Efficiency = \(\frac{Isentropic Work}{Actual Work}\) | Comments | Active | |
| 94 | Identify the correct pair from the following. | Otto cycle: Petrol engines | Diesel engines: Electric vehicles | Carnot cycle: Compressors | Brayton cycle: Chillers | a | Ic engine cycle: otto cycle – petrol engine , diesel cycle – CI engine , lenior cycle – jet engine | Comments | Active | |
| 95 | Identify Point A in the given figure.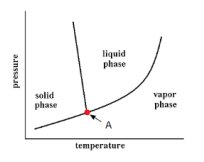 |
Triple point | Saturation point | Critical point | Superheated point | a | 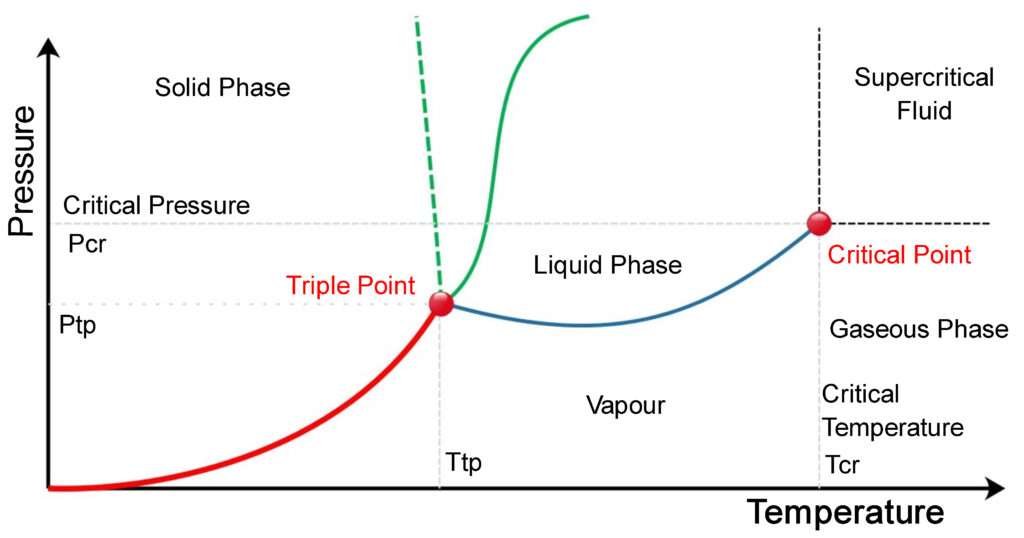 |
Comments | Active | |
| 96 | Thermo-siphon type of IC engine cooling system | Does not use a pump for water circulation | Uses a condenser for cooling | Uses grease as working fluid | Uses a compressor for water circulation | a | A thermo-siphon cooling system works based on the principle of natural convection. In this system: Hot water from the engine rises naturally due to decreased density. It flows to the radiator, where it cools down. The cooler, denser water then sinks and returns to the engine. This cycle happens without any pump, relying purely on the difference in density due to temperature changes. |
Comments | Active | |
| 97 | Identify the correct option based on the given assertion and reason. Assertion (A): While tensile testing of gold, necking phenomenon occurred. Reason (R): Gold is a brittle material. |
A is true but R is false | Both A and R are true | A is false but R is true | Both A and R are false | a | As we know that gold have good ductility and meleable so reason is false. | Comments | Active | |
| 98 | Identify the cycle on the basis of its P-h diagram.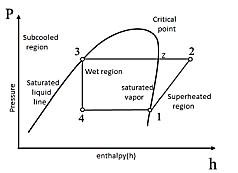 |
Stirling cycle | Vapour compression refrigerant cycle | Brayton cycle | mollier cycle | b | Given P-h diagram shows VCRS cycle.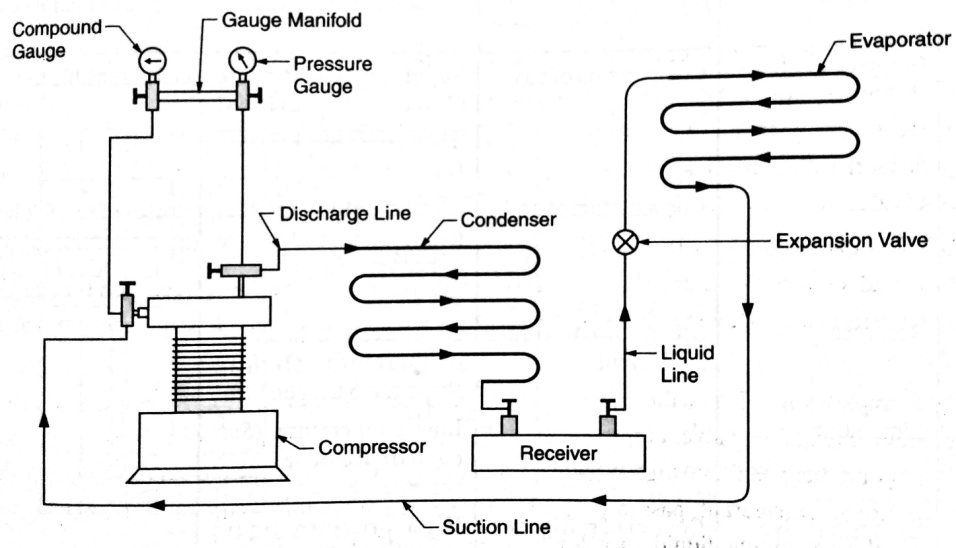 |
Comments | Active | |
| 99 | Identify the measuring set-up shown in the following figure.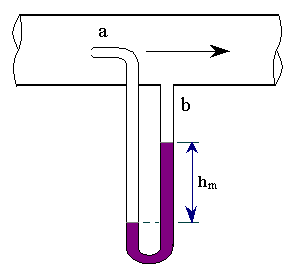 |
Pitot tube | Diaphragm gauge | Bernoulli's tube | Switch gauge | a | A pitot tube is a simple glass tube bent at an angle of 90° that is used to measure the velocity of flow.It is based on principle of conversion of kinetic head into pressure head. The point at which velocity reduces to zero is called stagnation point. Used to measure velocity of flow. The point at which velocity of flow tends to zero – stagnation point ( velocity in open channels) \(V_{th}=2gh= \frac{2g(p_{s}-p_{o})}{Ïg}\) Vact = Cv \(2gh\) Coefficeint of velocity (0.98) \(C_{v}=\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 100 | While deaerating the steam, when water is heated to 100 another steam is introduced known as \(℃ \) | Scorching steam | Pegging steam | Charging steam | Monochrome steam | b | In deaeration, the process aims to remove dissolved gases (especially oxygen and carbon dioxide) from feedwater in steam systems, which can cause corrosion. When the water is heated to 100°C, it reaches its boiling point at atmospheric pressure. To drive off the remaining dissolved gases, additional steam is introduced. This introduced steam is known as pegging steam. |
Comments | Active | |
| 101 | Identify the pressure indicated by C in the following figure. |
Vacuum pressure | Absolute pressure | Gauge pressure | Barometric pressure | c | 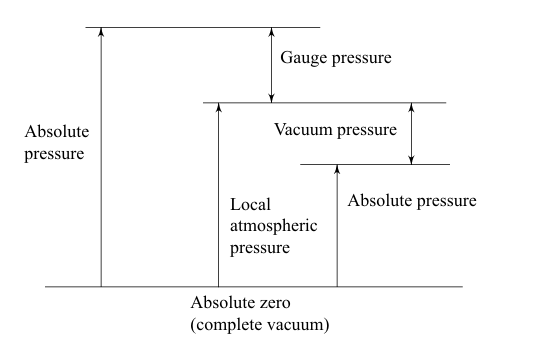 |
Comments | Active | |
| 102 | The Sl unit of couple is: | Kg-S | N-S | Pa-m | N-m | d | A couple in physics refers to a pair of equal and opposite forces whose lines of action do not coincide, creating a rotational effect (torque) but no resultant force. The magnitude of a couple (or torque) is calculated as: Torque=Force×Perpendicular distance between the forces Force is measured in newtons (N) Distance is measured in meters (m) So SI unit will N-m. |
Comments | Active | |
| 103 | Which of the following processes DOES NOT constitute in the Carnot cycle?" | Reversible Isothermal Heat Addition | Reversible Adiabatic Expansion | Reversible Isobaric Condensation | Reversible Isothermal Heat Rejection | c | 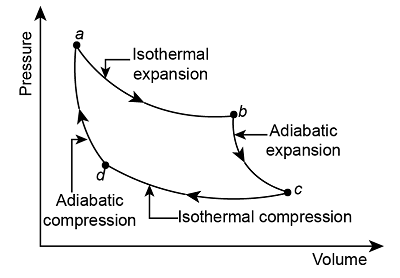 There is no process of Reversible Isobaric Condensation. |
Comments | Active | |
| 104 | Which of the following turbines is correctly paired with its type? | Mixed flow turbine → Francis turbine | Radial flow turbine→ Kaplan turbine | Reaction turbine→ Pelton wheel turbine | Inward flow turbine → Fourneyron turbine | a | Francis turbine is a mixed flow turbine, meaning water flows both radially and axially through the runner. The Kaplan turbine is an axial flow turbine, not radial. Water flows parallel to the axis of rotation. The Pelton wheel is an impulse turbine, not a reaction turbine. Reaction turbines involve pressure change across the runner, which is not the case for Pelton wheels. The Fourneyron turbine is an outward flow turbine, not inward. | Comments | Active | |
| 105 | Identify the correct option based on the given assertion and reason. Assertion (A): Steam turbines operate at fairly the same speed regardless of the load due to governing. Reason (R): Throttle governing is often done in small steam turbines. |
A is true but R is false | Both A and R are true | Both A and R are false | A is false but R is true | b | Assertion (A): Steam turbines are equipped with governing mechanisms that adjust the steam supply based on the load. This ensures that the turbine speed remains nearly constant, which is critical for applications like power generation where frequency stability is important. Reason (R): Throttle governing is a common method used in small steam turbines. It involves controlling the steam pressure and flow rate by throttling the steam before it enters the turbine. |
Comments | Active | |
| 106 | Calculate the depth of centre of pressure for the following body submerged in water.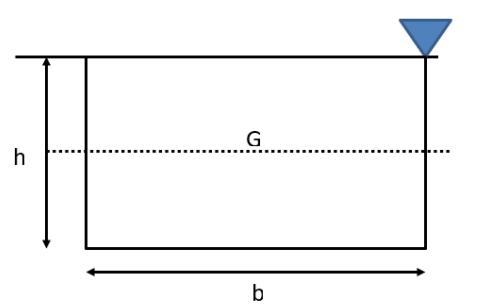 |
(2h) / 3 | (4h) / 3 | h/3 | (5h) / 3 | a | Surface C.G.( \(h)\) C.P.(P*) Rectangle  \(\frac{h}{3}\) \(\frac{2h}{3}\) Trapezium  \(\frac{a+2b}{a+b}.\frac{h}{3}\) \(\frac{a+3b}{a+2b}.\frac{h}{2}\) Triangle  \(\frac{2h}{3}\) \(\frac{h}{3}\) \(\frac{3h}{4}\) \(\frac{h}{2}\) Circle  \(\frac{D}{2}\) \(\frac{5D}{8}\) Semi-circle  \(\frac{2D}{3Ï€}\) \(\frac{3Ï€D}{32}\) Parabola  \(\frac{3h}{5}\) \(\frac{2h}{5}\) \(\frac{5h}{7}\) \(\frac{4h}{7}\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 107 | In ______, water flows parallel to the axis of the rotation of shaft. | Old Francis turbine | Francis turbine | Kaplan turbine | Pelton wheel | c | In a Kaplan turbine, water flows axially, meaning parallel to the axis of rotation of the shaft. It is an axial flow reaction turbine, commonly used for low-head, high Specific speed. |
Comments | Active | |
| 108 | The efficiency of Carnot cycle is expressed as | ratio of work done to amount of heat given | ratio of volume compressed to amount of heat given | ratio of work supplied to amount of work done | ratio of work done to pressure released | a | The efficiency of a Carnot cycle is defined as: η= \(\frac{Net work done by the engine}{Heat absorbed from the hot reservoir}\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 109 | Which of the following is NOT a type of boiler on the basis of its position? | Prone position boiler | Horizontal boiler | Inclined boiler | Vertical boiler | a | "Prone position boiler" is not a recognized classification in boiler terminology. | Comments | Active | |
| 110 | Identify which of the given statements are correct. Statements: A) A refrigerant should have high boiling point. B) A refrigerant should have high latent heat value. C) A refrigerant should have low freezing point. |
All A, B and C | Only A and C | Only B and C | Both A and B | c Solution  |
Comments | Active | ||
| 111 | Identify the thermodynamic device shown here.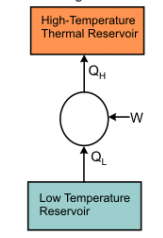 |
Refrigerator | Condenser | Compressor | Boiler | a | As we know that the work of refrigeration to absorb heat and transfer it to refrigerant as shown in figure.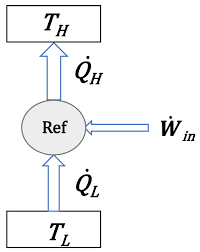 |
Comments | Active | |
| 112 | An air preheater is essentially a/an _____. | Heat exchanger | Cooler | Expander | Chiller | a | An air preheater is a device used to transfer heat from the flue gases to the incoming air before it enters the combustion chamber of a boiler or furnace. This increases thermal efficiency by preheating the combustion air, making it a type of heat exchanger. | Comments | Active | |
| 113 | Identify the correct pair on basis of types of components. | Venturimeter → Volume fan | Casing → Volute casing | Motor →Friction blades | Piston →Forward flow | b | A volute casing is a specific type of casing used in centrifugal pumps and compressors to collect and direct fluid flow efficiently. | Comments | Active | |
| 114 | Which of the following is NOT a classification of orifices? | Free discharging orifices | Drowned orifices | Submerged orifices | Blocked orifices | d | Blocked orifices is not a standard classification — a blocked orifice simply means it’s obstructed and not functional, not a recognized type of orifice in fluid mechanics. | Comments | Active | |
| 115 | ________ is done for keeping the steam turbine speed fairly same in-spite of load. | Positioning | Steering | Parting | Governing | d | Governing is the process used in steam turbines to maintain a nearly constant speed despite variations in the load. It involves controlling the steam flow to the turbine using a governor mechanism, which adjusts valves based on speed changes. | Comments | Active | |
| 116 | Identify the correct statement with respect to air standard cycle assumptions. | Water is a working fluid. | All processes in power cycles are internally irreversible. | Air is considered an ideal gas. | Steam is supplied at lower temperatures. | c | Air standard cycle assumptions: In the air standard cycle, we assume that the working fluid has a fixed mass. By assuming a closed system or fixed mass system, an ideal gas equation can be applied which makes the analysis easy. By assuming the fixed mass system we can use W = ∫Pdv because in closed system analysis swept volume is equal to displaced volume. The real open cycle is changed into a closed cycle by assuming that the gases being exhausted are fed back into the intake system. The working fluid is air which behaves as an ideal gas.  All the processes are internally reversible.  The specific heat of air remains constant during the cycle.  The combustion process is replaced by the heat addition process.  A cycle is assumed to be a closed cycle.  The exhaust process is modeled by a heat rejection process |
Comments | Active | |
| 117 | Negative gauge pressure is also known as | Barometric pressure | Atmospheric pressure | Vacuum pressure | Mercury pressure | c |  |
Comments | Active | |
| 118 | Identify the correct option based on the following statements pertaining to steam A: Condenser is a component of the refrigeration cycle. B: Throttling device is not a component of the refrigeration cycle. C: A compressor is a device of the refrigeration cycle. |
Only B and C are true | Only A and C are true | Both A and B are true | All A, B and C are true | b | An expansion valve (Throttling device) to regulate the flow of the refrigerant. So it is part of refrigeration cycle. | Comments | Active | |
| 119 | For which of the instrument out of given below, the coefficient of discharge is minimum? | Venturimeter | Orifice meter | Pirani gauge | Nozzle meter | b | Venturimeter: ~0.98 (highest, very efficient) Nozzle meter: ~0.95 Orifice meter: ~0.60 – 0.65 (lowest among flow meters listed) Pirani gauge: Not a flow-measuring device; it's used to measure low pressures (vacuum) using thermal conductivity – not applicable here |
Comments | Active | |
| 120 | Which of the following is true for stage efficiency for the steam turbines? | It is the product of blade efficiency and nozzle efficiency. | It is the addition of blade efficiency and nozzle efficiency. | It is the ratio of blade efficiency to nozzle efficiency. | It is the square of blade efficiency. | a | Stage Efficiency=Nozzle Efficiency×Blade Efficiency | Comments | Active | |
| 121 | Which of the following options is NOT true about viscosity? | It is caused by friction within a fluid. | Its unit is N-s/m². | It is the same as specific gravity. | It is an defined as the fluid's resistance to deformation at a given flow. | c | Specific Gravity is the density of any fluid w.r.t standard fluid i.e water, so it is simply ratio of densities and differ from viscosity. | Comments | Active | |
| 122 | Which of the following is NOT a type of clutch? | Cone clutch | Dry clutch | Cycloid clutch | Plate clutch | c | Cycloid clutch : Not a recognized type of clutch in mechanical systems. "Cycloid" typically refers to a type of gear profile (e.g., in cycloidal drives), not clutches. | Comments | Active | |
| 123 | Which of the following is NOT a component used in steam generation? | Evaporator | Governor | Boiler | Superheater | b | A governor is a mechanical or electronic device used to regulate the speed of a prime mover (such as a steam engine, diesel engine, or turbine) by controlling the fuel or steam input. | Comments | Active | |
| 124 | Which of the following is NOT an assumption made for Euler's equation of motion? | Frictional losses are zero. | Velocity of flow varies across the cross section. | Fluid is non-viscous. | Fluid is incompressible. | b | Velocity of flow varies across the cross section:- This is NOT an assumption of Euler's equation — it actually contradicts the assumptions, which treat the velocity as uniform across a cross-section along a streamline. | Comments | Active | |
| 125 | Identify the flow shown in the following figure.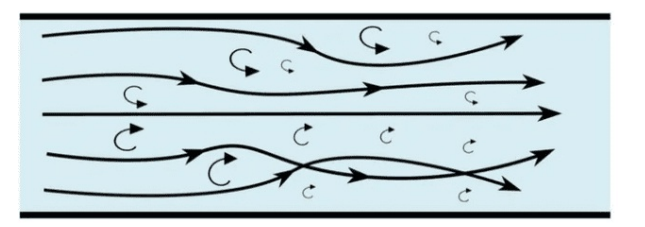 |
Turbulent flow | Laminar flow | Recoil flow | Transient flow | a | Turbulent flow is a type of fluid motion characterized by chaotic, irregular, and random fluctuations in velocity and pressure. | Comments | Active | |
| 126 | Which of the following is NOT a type of cam when classified according to follower movement? | Dwell-Rise-Dwell-Return-Dwell | Rise-Rise-Rise | Rise-Return-Rise | Dwell-Rise-Return-Dwell | b | Follower Movement (Reference – Theory of machine by SS Rattan – page No.-212)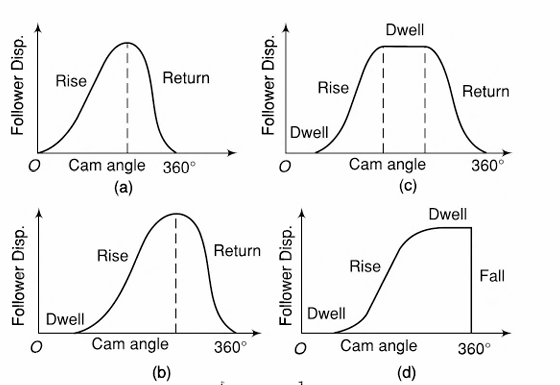 So, Rise-Rise-Rise is not any follower movement. |
Comments | Active | |
| 127 | ______ is a part of gas turbine fuel injector. | Plug | Screw gauge | Gun | Vaporiser | d | Vaporiser is a part of gas turbine fuel injector. | Comments | Active | |
| 128 | Identify the correct pair in terms of type of welding and the electrode used from the following options. | Tungsten electrode → TIG welding | Aluminium electrode → Laser welding | Monel electrode → Friction stir welding | Titanium electrode → Friction welding | a | Friction stir welding (FSW) is a solid-state process that does not use any electrodes or filler materials. Friction welding is another solid-state process that generates heat through mechanical friction. It does not use electrodes of any kind. Laser welding uses a high-energy laser beam to fuse materials. It does not use electrodes like traditional arc welding methods. | Comments | Active | |
| 129 | In a glass tube with water flowing, a liquid dye with the same specific weight is introduced. The resulting dye filament pattern is observed as shown in the figure. Identify the type of flow from the following options. |
Laminar flow | Recoil flow | Transient flow | Turbulent flow | d | Turbulent flow is a type of fluid motion characterized by chaotic, irregular, and random fluctuations in velocity and pressure. | Comments | Active | |
| 130 | Coefficient of friction depends on_____ | Density of the fluid | Surface roughness | Colour of the fluid | Weight of the fluid | b | Coefficient of fricition is simply the indication that how rough surface is . if this coefficient value is high then surface is rough and for smooth surface coefficient value will less and extremely smooth surface coefficient of friction value will very high. | Comments | Active | |
| 131 | Identify the correct option based on the given statements. A: Clearance ratio for a single stage reciprocating compressor is the ratio of clearance volume to swept volume. B: Clearance ratio for single stage reciprocating compressor is generally in the range of 2 to 10%. |
Both A and B are false | A is true, but B is false | Both A and B are true | A is false, but B is true | c | clearance Ratio = \(\frac{clearence Volume}{Swept Volume}\) The clearance ratio is typically in the range of 2% to 10% for single-stage compressors, depending on design and application. |
Comments | Active | |
| 132 | Identify the correct statement with respect to hydroelectric power plant. | Net head is the water level before tail race. | Net head or effective head is the head available at the inlet of the turbine. | Gross head is the effective head after the water is delivered. | Gross head is the water level before head race. | B | Net head or effective head is the head available at the inlet of the turbine. | Comments | Active | |
| 133 | Match column A with column B Column A (Property) Column B (Definition) A. Flash point 1. Temperature at which vapours are given off from oil B. Pour point 2. Temperature at which lubricant is able to flow C. Fire point 3. Temperature at which oil catches fire |
A-1; B-2: C-3 | A-2: B-3: C-1 | A-2: B-1: C-3 | A-3: B-1: C-2 | a | Flash point: Temperature at which vapours are given off from oil Pour point: Temperature at which lubricant is able to flow Fire point: Temperature at which oil catches fire |
Comments | Active | |
| 134 | Bernoulli’s equation is applied on _______. | Tachometer | Manometer | Side bar | Orifice meter | d | Orifice meter – A flow measurement device that uses Bernoulli’s principle to calculate flow rate from pressure differences across an orifice. | Comments | Active | |
| 135 | Identity the correct option based on the following statements. A. Refrigerant should be affected by moisture. B. Refrigerants should be non-toxic. C. Refrigerants should be non-corrosive. |
Only B, and C are true | Only A, and C are true | Only A,B and C are true | Both A and C are true | a | Refrigerant should not affected by moisture.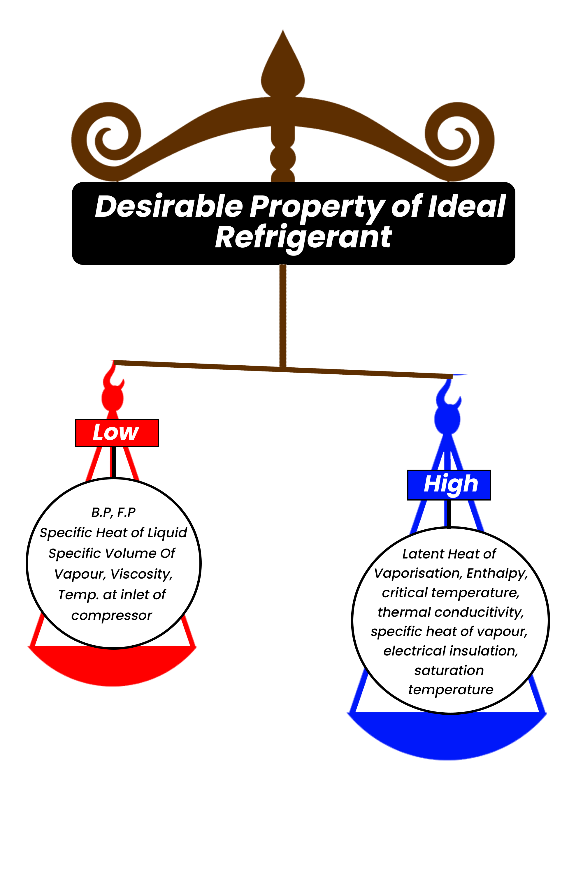 |
Comments | Active | |
| 136 | Which of the following fuels is LEAST/NEVER used in a boiler? | Gas | Mercury | Oil | Coal | b | Mercury is never used as a fuel in boilers. It is a toxic metal, not combustible, and does not release energy through combustion like other fuels do. | Comments | Active | |
| 137 | Cochran boiler is a ______, ________ and _______ type of boiler. | Fire tube; vertical; low pressure | Fire tube; horizontal; low pressure | Water tube; horizontal ; high pressure | Water tube; vertical; high pressure | a | Cochran boiler: fire tube; vertical; low pressure boiler.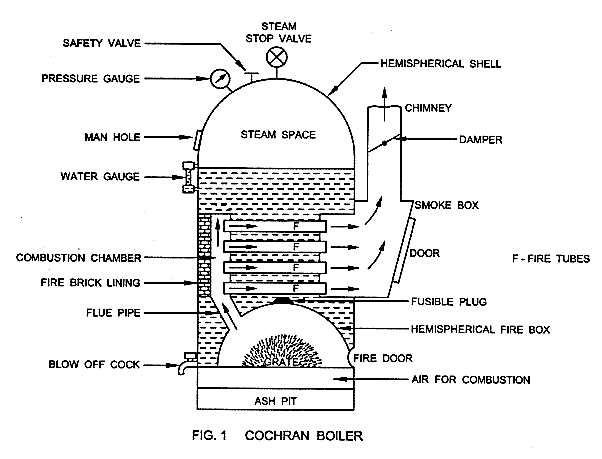 |
Comments | Active | |
| 138 | Refer to the given figure which shows Power (P) versus Discharge (Q) for a centrifugal pump and match the columns accordingly. Column A (Curve) Column B (Type of vane) A. Curve B 1. Forward vane B. Curve A 2. Backward vane C. Curve C 3. Radial vane |
A-2, B-3, C-1 | A-1, B-2, C-3 | A-1, B-3, C-2 | A-3, B-1, C-2 | d |  |
Comments | Active | |
| 139 | In ______ compressors, the compressor and the motor work on the same shaft and are housed in the same casing. | Hermetically sealed | Common cased | Ergonomically tabulated | Hydrophobically crafted | a | Comments | Active | ||
| 140 | Given in the options are terminologies related to the value timing diagram of an IC engine and their full forms. Identify the full form that is correctly paired with it short form. | FVO First Value operation \(→\) | TDC Top dead centre \(→\) | BDC Burden dead core \(→\) | IVC Intake valve corrosion \(→\) | b | FVO is not a standard term in IC engine valve timing diagrams, BDC stands for bottom dead center, IVC stands for Intake Valve Closing, part of the valve timing in an IC engine. | Comments | Active | |
| 141 | Which of the following is a 100% reaction turbine? | Hero's turbine | Rateau turbine | Curtis turbine | De-Laval turbine | a | 50 % reaction turbine : parson turbine , 100% reaction turbine : Hero's turbine | Comments | Active | |
| 142 | Which of the following is NOT a type of lathe machine? | Turret lathe | Tool room lathe | Boiler room lathe | Bench lathe | c | On the basis of their purpose, design, number of tools accommodated, degree of mechanisation and other factors, lathe-type machine tools may be classified as : 1. Limited or low-production Machines. The lathes included in this category are : engine lathe (centre lathe), bench lathe, tool room lathe and speed lathe. 2. Medium-production Machines. Turret lathes and duplicating (or tracer controlled) lathes. 3. High-production Machines. Semi automatic and automatic lathes. (Reference – A textbook of production technology by P.C. Sharma – page no.-449) |
Comments | Active | |
| 143 | Identify whether the given statements are true or false. Statements: A) Work done by a system on its surroundings is treated as a negative quantity. B) Energy transfer as heat to a system from its surroundings is treated as a positive quantity. |
Both A and B are true | A is true but B is false | A is false but B is true | Both A and B are false | c | Work done by the system is considered as positive work so option a is incorrect here. Remind sign work heat and work by this: 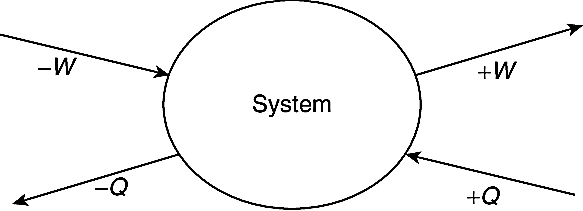 |
Comments | Active | |
| 144 | Calculate the depth of centre of pressure for the following body (circular plate) submerged in water (where D is diameter and G is centre of gravity).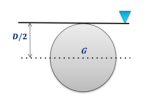 |
D/2 | D/3 | 5D/8 | 5D/4 | c | Surface C.G.( \(h)\) C.P.(P*) Rectangle  \(\frac{h}{3}\) \(\frac{2h}{3}\) Trapezium  \(\frac{a+2b}{a+b}.\frac{h}{3}\) \(\frac{a+3b}{a+2b}.\frac{h}{2}\) Triangle  \(\frac{2h}{3}\) \(\frac{h}{3}\) \(\frac{3h}{4}\) \(\frac{h}{2}\) Circle  \(\frac{D}{2}\) \(\frac{5D}{8}\) Semi-circle  \(\frac{2D}{3Ï€}\) \(\frac{3Ï€D}{32}\) Parabola  \(\frac{3h}{5}\) \(\frac{2h}{5}\) \(\frac{5h}{7}\) \(\frac{4h}{7}\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 145 | A______ is provided to remove the water from a steam-water mixture in a boiler. | Lever valve | Pin check | Fusible plug | Steam trap | d | steam trap: To "trap" steam in the system while removing condensate (water formed as steam cools down) and gases that can reduce efficiency or damage equipment. | Comments | Active | |
| 146 | Match column A with column B. Column A (Law of Thermodynamics) Column B (Concept) A. Zeroth law 1. Conservation of energy B. First law 2. Entropy C. Second law 3. Thermal equilibrium |
A-2; B-1; C-3 | A-1; B-3; C-2 | A-3; B-1: C-2 | A-2; B-3; C-1 | c | Zeroth Law of thermodynamics (Temperature Measurement) when a body A is in thermal equilibrium with a body B & also separately with a body C then body B & C will be in thermal equilibrium with each other. First Law of Thermodynamics (Law of Conversion of Energy)- Joule’s Experiment “It states that, a definite amount of mechanical work is needed to produce a definite amount of heat and vice versa i.e. “Heat and mechanical work are inter-convertibleâ€. Second Law of Thermodynamics : define entropy |
Comments | Active | |
| 147 | Based on the following P-V and T-s diagrams, identify the IC engine cycle.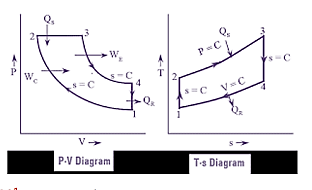 |
Brayton cycle | Diesel cycle | Otto cycle | Stirling cycle | b | 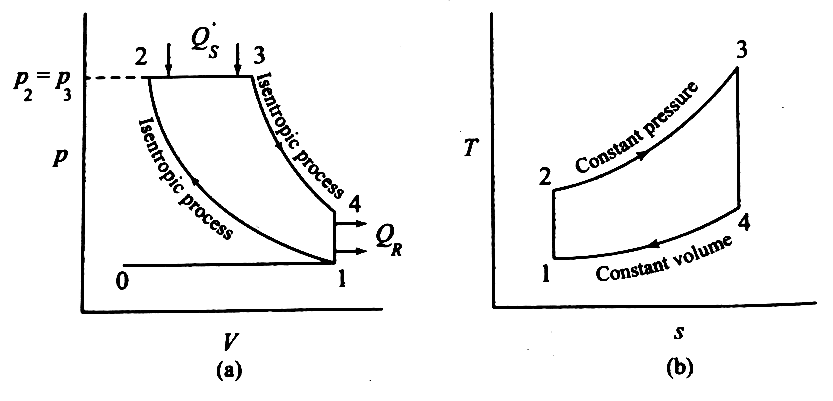 Diesel cycle: Isentropic Process 1-2 (compression) Isobaric Process 2-3 (heat addition) Isentropic Process 3-4 (expansion) Isochoric Process 4-1 (heat rejection) |
Comments | Active | |
| 148 | In order to grind material with high tensile strength abrasive is predominantly used on abrasive wheels. | Aluminium oxide | Sodium chloride | Manganese | Copper | a | Aluminium oxide it is extensively used for grinding materials of high tensile strength, such as, most steels, H.S.S., ferrous alloys, non-ferrous cast alloys and annealed malleable and ductile iron. (Reference – A textbook of production technology by P.C Sharma – page no.-532) |
Comments | Active | |
| 149 | The value of static friction is between___ and limiting friction. | 10 | 0 | 15 | 5 | b | As we can see in bleow diagram that between zero to limiting friction is reprenented by Static friction.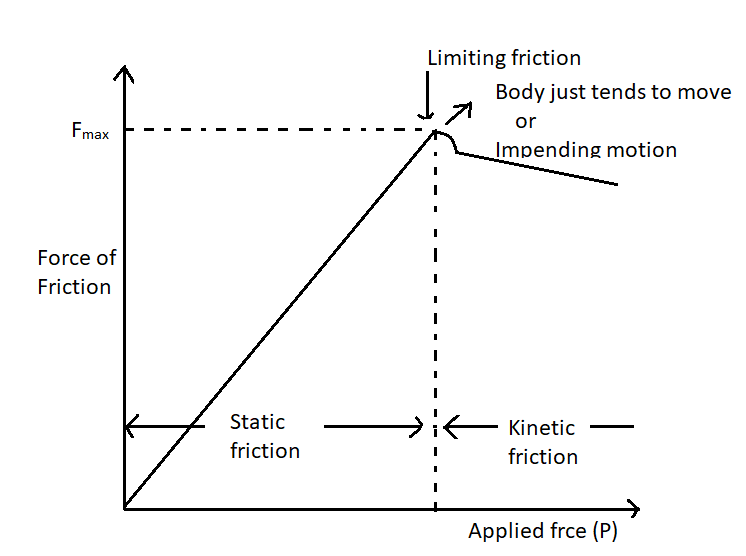 |
Comments | Active | |
| 150 | Archimedes principle discusses____ | viscosity | illuminance | potency | buoyancy | d | Archimedes Principle- Whenever a body is either partially or completely submerged in a fluid, it experiences a force in upward direction which is equal to the weight of the fluid displaced. So it discuss about buoyancy, option d will be correct answer. |
Comments | Active | |
| 151 | Identify point A in the following figure.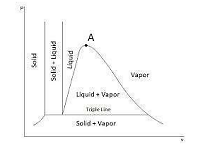 |
Critical point | Triple point | Saturation point | Superheated point | a | Point a represent the critical point .At this point solid directly convert into vapour. | Comments | Active | |
| 152 | In case of liquids, can be seen as cohesive forces between molecules of liquid | Adaptability | Transferability | Permeability | Viscosity | d | cohesive forces between molecules of liquid can be seen by viscosity. Dynamic viscosity: 10 poise \(\frac{N-s}{m^{2}}=Pa-s=\frac{kg}{m-s}=\) Kinematic viscosity: = m2/s \(ν=\frac{μ}{Ï}\) 1stoke = cm2/sec m2 / s = 104 stokes T \(↑\) \(μ\) ν Liquid \(↓\) \(↓\) Gases \(↑\) \(↑\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 153 | In a rotameter, the float position indicates____ | Weight | Viscosity | Density | Flow rate | d | Rotameter Operation principle: When fluid is entered into the tube, some of the fluid strikes the float & some pass by. This makes the float move upwards until the buoyant force is equal to the weight of the float. At this point, the float will stop to move upwards and the float position will indicate the flow rate. Annular space increasing upward, thus giving more area, more flow, more upward movement of the float & hence more flow rate.  |
Comments | Active | |
| 154 | An oil of specific gravity 0.9 flows through a 0.1 m diameter pipe under a pressure of 100 kPa. The centre line of the pipe is 5 m above the datum line and the total energy with respect to the datum is 0.04 kJ/N. Then the discharge of the oil through the pipe in litre per second is | 170 | 340 | 85 | 677 | a | Bernoulli equation \(\frac{p}{5g}+\frac{v^{2}}{2g}+z=H \) \(11.33+\frac{v^{2}}{2g}+5=40 \) \(v=464.28 ≈21.54 m/sec\) \(Q=A.v=0.007×21.54\) \(=169.2 Lites/sec\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 155 | Which of the following statements based on the given figure is/are correct?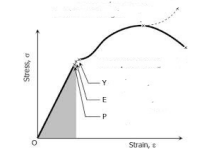 Statements: A) Point Y represents rupture strength. B) Point E represents elastic limit. C) Point P represents proportional limit. |
Only Statements B and C | Only Statement A | Only Statement C | Only Statement B | a A = Proportional limitB = Elastic limitC = Upper yield pointD = Lower yield pointF = Ultimate pointG = Breaking point A = Proportional limitB = Elastic limitC = Upper yield pointD = Lower yield pointF = Ultimate pointG = Breaking point Solution: |
Comments | Active | ||
| 156 | The work of a compressor in a vapour compression refrigeration system is to____ | Increase the volume of the refrigerant at constant entropy | Increase the temperature of the refrigerant at constant entropy | Increase the pressure of the refrigerant at constant entropy | Increase the velocity of the refrigerant at constant entropy | b | 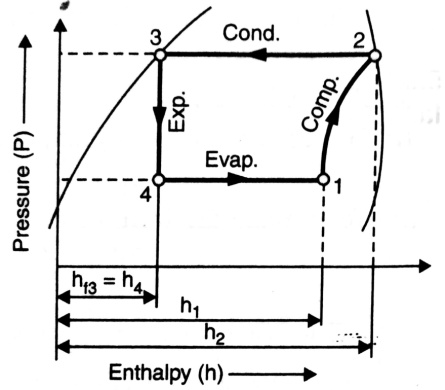 |
Comments | Active | |
| 157 | Identify the correct statement with reference to definition of coefficient of discharge for a steam nozzle | Ratio of actual discharge to theoretical discharge. | Ratio of total discharge to leaked discharge. | Ratio of theoretical discharge to total discharge. | Ratio of theoretical discharge to actual discharge | a | Co-efficient of Discharge () is defined as the ratio of the actual discharge from an orifice to the theoretical discharge from the orifice. \(C_{d}\) \(C_{d}=\frac{Q}{Q_{th}}=\frac{Actual velocity× Actual area}{Theoretical velocity×Theoretical area} \) \(C_{d}=\frac{Actual velocity}{Theoretical velocity}×\frac{Actual area}{Theoretical area}= C_{v}× C_{c}\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 158 | Loss of head occurring due to bend in pipe during fluid flow is considered as___ | Minor loss | Resultant loss | Recording loss | Major loss | a | Loss of head occurring due to bend in pipe during fluid flow is considered as minor loss while fricition losses are considered as major loss. | Comments | Active | |
| 159 | The graphical representation of transformation of 1 kg of ice into 1 kg of superheated steam at constant pressure is known as ____ | u-v diagram | h-s diagram | p-v diagram | t-h diagram | d | The T-h diagram (Temperature vs. Enthalpy) clearly shows: Temperature plateaus during phase changes (melting and boiling) Sloped regions during sensible heating (solid, liquid, and superheated phases) It's ideal for representing processes involving heat addition and phase changes. |
Comments | Active | |
| 160 | Which of the following is NOT a minor energy (head) loss? | Loss due to enlargement | Loss due to obstruction in pipe | Loss due to friction | Loss due to contraction | c | Friction loss is considered as major loss in pipe flow. | Comments | Active | |
| 161 | Identify whether the given statements are true or false. Statements: A) In a double acting compressor, suction and expansion take place in two different strokes. B) In single acting compressors, both suction and expansion stroke take place in two different strokes. |
Both statements are false | Statement B is true but Statement A is false | Statement A is true but Statement B is false | Both statements are true | b | In a double-acting compressor, suction and compression occur simultaneously on opposite sides of the piston during each stroke. That means: On one side of the piston: suction takes place. On the other side of the piston: compression happens. There is no separate "expansion" stroke like in internal combustion engines. Instead, both sides of the piston are active during every stroke, which increases efficiency and output. |
Comments | Active | |
| 162 | Velocity potential function is a/an_____ | Infinite quantity | Vector quantity | Elemental quantity | Scalar quantity | b | (Reference -Fluid mechanics and machine by RK Bansal – page no .-181) Velocity Potential Function. It is defined as a scalar function of space and time such that its negative derivative with respect to any direction gives the fluid velocity in that direction. It is defined by ϕ (Phi). Mathematically, the velocity, potential is defined as ) for steady flow such that \(ϕ = f(x, y, z\) \(μ=-\frac{∂ϕ}{∂x} \) \(v =-\frac{∂ϕ}{∂y} \) \(w =-\frac{∂ϕ}{∂z}\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 163 | Identify the INCORRECT statement from the following options. | Stainless steels are a type of alloy steels. | Stainless steel contains chromium. | Stainless steels are a type of non-ferrous steels. | Stainless steels are resistant to corrosion. | c | Steel by definition is a ferrous alloy, meaning it is primarily composed of iron. Non-ferrous metals do not contain significant amounts of iron (e.g., aluminum, copper, titanium). |
Comments | Active | |
| 164 | Identify the correct option based on the given assertion and reason. Assertion (A): Hot tea kept in a thermos flask remains hot for a longer duration. Reason (R): A thermos flask is an example of a closed system. |
Both A and R are true | A is false but R is true | Both A and R are false | A is true but R is false | d | A thermos flask is designed to minimize heat loss through conduction, convection, and radiation. A closed system allows energy (heat or work) to cross the boundary, but not mass. A thermos flask ideally tries to minimize energy exchange (especially heat), so it is closer to an isolated system, although in practice, it's not perfectly isolated. So, A is true but R is false. |
Comments | Active | |
| 165 | Which of the following efficiencies is NOT related to turbines? | Mechanical efficiency | Hydraulic efficiency | Machine efficiency | Volumetric efficiency | c | Machine efficiency is NOT related to turbine.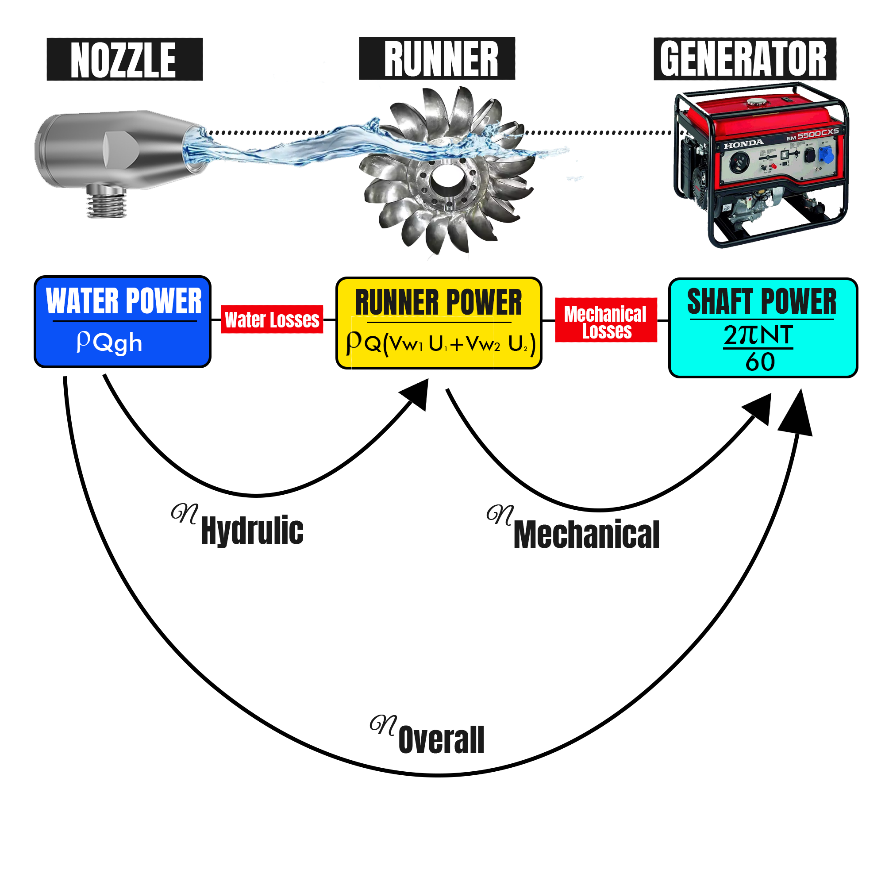 |
Comments | Active | |
| 166 | Two types of radiators used for IC engine systems are____and______ | Tubular core type, cellular core type | Tubular core type, reciprocating core type | Reciprocating core type, rotating core type | Rotating core type, cellular core type | a | 1. Tubular Core Type: Consists of tubes through which the coolant flows. Heat is transferred from the coolant to the fins attached to the tubes and then to the air. Common in older or simpler vehicles. 2. Cellular Core Type (also called honeycomb type): Made of numerous small air passages (cells) with coolant circulating around them. Offers a larger surface area for heat transfer. Common in modern vehicles due to better cooling efficiency. |
Comments | Active | |
| 167 | Identify which of the given statements related to IC engines is/are correct. Statements: A) Mechanical efficiency of a single-cylinder four-stroke engine is the ratio of brake power to indicated power. B) Volumetric efficiency of Sl engine is generally less than 30%. C) Volumetric efficiency of Cl engine is generally less than 30%. |
Only Statement C | Only Statement A | Only Statement B | Only Statements B and C | b | Volumetric efficiency of a Spark Ignition (SI) engine is typically in the range of 70% to 90% under normal operating conditions. Compression Ignition (CI) engines (diesel engines) often have volumetric efficiencies greater than 85%, sometimes even exceeding 100% due to turbocharging. | Comments | Active | |
| 168 | Barometric pressure is also known as____ | Fluid pressure | Volumetric pressure | Atmospheric pressure | Density | c | Barometer is the device used to measure the atmospheric pressure. | Comments | Active | |
| 169 | Match column A with column B. Column A (Boiler) Column B (Pressure) A. Cochran boiler 1. Medium pressure B. Babcock and Wilcox boiler 2. Low pressure C. Locomotive 3. High pressure boilers |
A-2: B-3: C-1 | A-1; B-2; C-3 | A-2: B-1: C-3 | A-1; B-3; C-2 | c | Cochran boiler: Low pressure (6.7 bar) Babcock and Wilcox boiler: Medium pressure (11.5 – 17.5 bar) Locomotive: High pressure boilers (20-25 bar) |
Comments | Active | |
| 170 | Identify whether the given statements related to IC engines are true or false. Statements: A) SI engine does not consist of a spark plug. B) CI engine does not consist of a spark plug. |
Both statements are true | Statement B is true but Statement A is false | Both statements are false | Statement A is true but Statement B is false | b | SI stands for spark ignition i.e petrol engine . we use spark plug to ignite fuel here so a is incorrect. | Comments | Active | |
| 171 | The temperature at which liquid droplets just appear when moist air is cooled continuously is called, | Flash point temperature | Fire temperature | Pour point temperature | Dew point temperature | d | Dry Bulb Temperature: Actual temperature of gas or mixture of gases. Wet-bulb temperature: Temperature obtained by an accurate thermometer having a wick moistened with distilled water. Dew point temperature: Temperature at which the liquid droplets just appear when the moist air is cooled continuously. |
Comments | Active | |
| 172 | Identify the correct statement with respect to centrifugal pumps. | Forward curved vanes can handle high flow rates. | Forward curved vanes have concave side of curvature facing direction of fluid flow. | In radial vanes, the fluid does not flow radially outward/inward from centre of rotation. | Backward curved vanes can handle high flow rates. | a | Forward curved vanes can handle high flow rates. | Comments | Active | |
| 173 | According to the Darcy-Weisbach equation for flow through pipe, head loss due to friction is inversely proportional to which of the following pipe parameters? | Diameter of the pipe | Material type of the pipe | Colour of the pipe | Weight of the pipe | a | According to the Darcy-Weisbach equation for flow through pipe, head loss due to friction is inversely proportional to Diameter of the pipe. According to the Darcy-Weisbach equation: \(h_{f}=\frac{f. L.V^{2}}{2g.D}\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 174 | Identify the part of the flywheel indicated as 'A' in the following figure.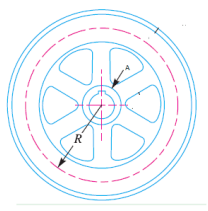 |
Hub | Frame | Spoke | Rim | a | A indicate hub of the flywheel. | Comments | Active | |
| 175 | Match the columns. Column A (Compressor) Column B (Feature) A. Screw compressor 1. Compressor and motor operate on same shaft B. Hermetically sealed compressor 2. Uses piston assembly C. Reciprocating compressor 3. Rotary type |
A-3; B-1; C-2 | A-2; B-3; C-1 | A-2; B-1; C-3 | A-1; B-3; C-2 | a | Screw compressor: Rotary type Hermetically sealed compressor: Compressor and motor operate on same shaft Reciprocating compressor: Uses piston assembly |
Comments | Active | |
| 176 | _____ is also known as the principle of transmission of fluid pressure. | Buoyancy law | Pascal's law | Newton's law | Archimedes' principle | b | Pascal law: In a static fluid pressure at point is equal in all directioon.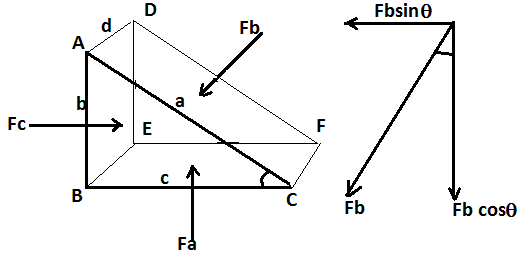 |
Comments | Active | |
| 177 | ____ is a vertical boiler | Cochran boiler | Locomotive boiler | Babcock and Wilcox boiler | Lancashire boiler | a | 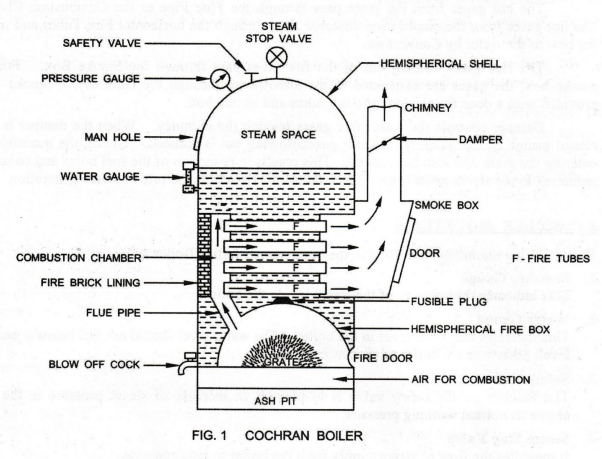 |
Comments | Active | |
| 178 | Identify the correct expression from the following options. | Brake power = Indicated power + Friction power | Brake power = Indicated power/Friction power | Brake power = Indicated power* Friction power | Brake power = Indicated power - Friction power | d | \(HA/sec=m_{f}(Cv)_{f}\) \(H.RI.P(At Piston) \) \(-F.P⟶due to mechanical arrangement B.P=τ×w(At engine shaft)\) | Comments | Active | |
| 179 | Which of the following statements is correct with respect to definition of sensible heat factor? | It is a ratio of sensible heat to total heat of the system. | It is a ratio of total heat to usable heat of the system. | It is a ratio of total heat to sensible heat of the system. | It is a ratio of total heat to available heat of the system | a | Sensible heat factor (S.H.F) The sensible heat factor is the ration of sensible heat to total heat. \(SHF=\frac{SH}{SH+LH}=\frac{S.H}{T.H}\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 180 | Match the given stages of the valve timing diagram for four-stroke petrol engines with their respective positions Column A (Stages) Column B (Position) A. Exhaust valve opens 1. 10°-20° before top dead centre B. Exhaust valve closes 2. 30°-50° before bottom dead centre C. Inlet valve opens 3. 10"-15" after top dead centre |
A-3; B-1; C-2 | A-2; B-3; C-1 | A-2; B-1; C-3 | A-1; B-3; C-2 | b | (Reference: Internal combustion engine by V ganeshan – page no.-140 )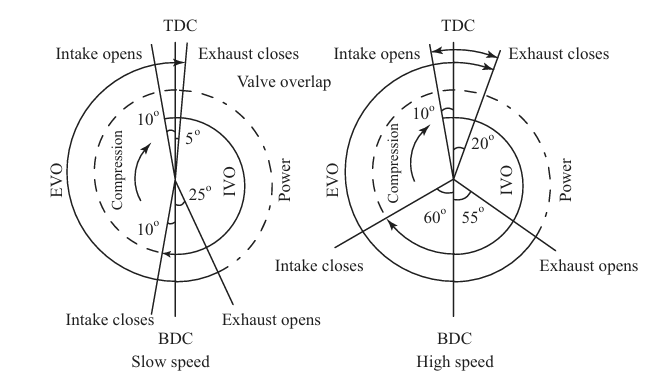 |
Comments | Active | |
| 181 | Natural draught for exhaust gases is provided during the working of a steam generator by….. | Feed valves | Chimneys | Conductors | Compressors | b | In a steam generator (boiler) system, natural draught is the flow of air and exhaust gases due to natural convection, created by the difference in density between the hot gases inside the chimney and the cooler outside air. Chimneys create this pressure difference, allowing the exhaust gases to rise and escape naturally without the use of fans or compressors. |
Comments | Active | |
| 182 | Steam tables are available either on…. Or….. basis | Temperature, velocity | Pressure, dryness | Pressure, temperature | Velocity, dryness | c | "Steam tables are available either on pressure or temperature basis." | Comments | Active | |
| 183 | Identify the correct option based on following statements pertaining to steam. A: At a given pressure, the capacity of superheated steam to do work will be comparatively higher. B: Dryness fraction is a term related to quality of steam. C: Wet steam does not exists. |
Both A and B are true | Only C is true | Only A is true | Both A and C are true | a | Superheated steam contains more energy (enthalpy) than saturated steam at the same pressure. This extra energy can be converted to work, especially in turbines, making it more efficient. Dryness fraction indicates the proportion of vapor in wet steam. It is used to measure the quality of steam. Wet steam does exist and is a common state in steam systems. It is a mixture of saturated liquid water and saturated steam. |
Comments | Active | |
| 184 | Calculate the depth of the centre of pressure for the following body submerged in water. |
h/4 | h/3 | h | h/2 | d | Surface C.G.( \(h)\) C.P.(P*) Rectangle  \(\frac{h}{3}\) \(\frac{2h}{3}\) Trapezium  \(\frac{a+2b}{a+b}.\frac{h}{3}\) \(\frac{a+3b}{a+2b}.\frac{h}{2}\) Triangle  \(\frac{2h}{3}\) \(\frac{h}{3}\) \(\frac{3h}{4}\) \(\frac{h}{2}\) Circle  \(\frac{D}{2}\) \(\frac{5D}{8}\) Semi-circle  \(\frac{2D}{3Ï€}\) \(\frac{3Ï€D}{32}\) Parabola  \(\frac{3h}{5}\) \(\frac{2h}{5}\) \(\frac{5h}{7}\) \(\frac{4h}{7}\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 185 | Identify the correct pair in terms of type of process and the temperatures they are carried out from the following options. | Brazing → Below 300°C | Soldering → Above 1500°C | Brazing → Above 1500°C | Soldering → Below 300°C | d | Brazing: the brazing process can be define as the process to join two metal pieces heated to suitable temperature by using a filler metal having a liquidus above 427 and below the solidus of the base metals. \(℃\) Soldering: in soldering, two parts are joined by the use of a molten filler metal whose melting point is below the solidus (melting point of the base metals) and in all cases below 427 . \(℃\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 186 | Coefficient of performance for vapour compression refrigeration is proportional to evaporator temperature and proportional to condenser temperature. | Inversely, inversely | Directly, directly | Directly, inversely | Inversely, directly | c | The coefficient of performance (COP) of a vapour compression refrigeration cycle is directly proportional to the evaporator temperature and inversely proportional to the condenser temperature. | Comments | Active | |
| 187 | Which of the following statements is correct with respect to the Cochran boiler? | It has high rate of steam generation. | It requires high floor area. | High room head is required for its installation due to the vertical design | It has high initial installation cost. | c |  Cochran boiler: high room head required for its installation due to the vertical design. |
Comments | Active | |
| 188 | Tensile forces on the arms of a flywheel are due to the | Kinetic forces | Lateral deviation | Longitudinal variation | Centrifugal forces | d | Flywheel The rotating rim of a flywheel is subjected to a uniformly distributed centrifugal force Pc , which acts in a radially outward direction. This includes a tensile force P in the cross-section of the rim acting in the tangential direction and a bending moment M. 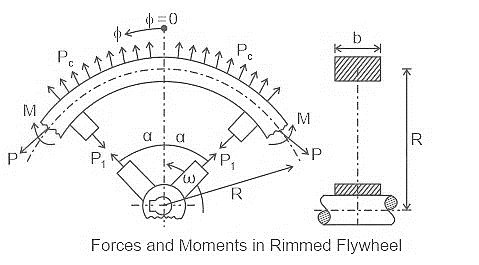 From the above diagram we can observe that the tensile forces on the arms of a flywheel are due to centrifugal force Pc. |
Comments | Active | |
| 189 | Relative density is also termed as…… | Buoyancy | Floatability | Acceleration | Specific gravity | d | Relative density is the density of any fluid w.r.t another fluid if this other fluid is standard fluid i.e water then this relative density is called as specific gravity. | Comments | Active | |
| 190 | Identify the correct pair from the following. | Secondary refrigerant : R12 | Secondary refrigerant : R1150 | Secondary refrigerant : Brine | Secondary refrigerant :R11 | c | Primary Refrigerant - These are the refrigerants or working substance which are directly used for cooling purpose. These refrigerants undergo a cyclic process and produce lower temperature. There is a latent heat transformation for the refrigerants. For e.g. R-11, R-12, R-22, R-134a, R-1150, Ammonia etc. Secondary Refrigerant - These are the working fluids or working substance which are first cooled by primary refrigerant and then used for cooling at the desired place.eg, H2O , Brine, Ethylene glycol. Uses of different refrigerants R-11 – Large central air conditioning plant R-12- Domestic refrigerator, water cooler etc. R-22- Window AC NH3 - Cold storage or Icing plants CO2 - Transportation of dry ice Air- Air-craft refrigeration system Brine- Milk chilling plants |
Comments | Active | |
| 191 | Match the columns.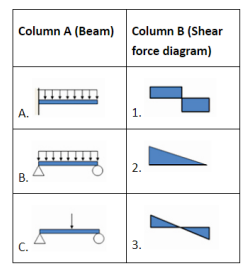 |
A-2; B-3; C-1 | A-2; B-1; C-3 | A-1; B-3; C-2 | A-3; B-1; C-2 | a | Beam A: Cantiliver beam having UDL over the entire length , then SFD will be Triangle Beam B: simply supported beam having UDL over the entire length , then SFD will be diag.3, at middle point shear force will zero and B.M have maximum value at that point. Beam C: Simply supported beam having point load at mid point then SFD Will be diag.1, at middle point shear force will zero and B.M have maximum value at that point. |
Comments | Active | |
| 192 | Which of the following is NOT a safety valve used in a boiler? | Pin safety valve | Dead weight safety valve | Lever safety valve | Spring loaded safety valve | a | Safety valves The function is to release the excess steam when the pressure of steam inside the boiler exceeds the rated pressure. Types of safety valves: Deadweight safety valve Lever safety valve Spring-loaded safety valve High steam and low water safety valve. |
Comments | Active | |
| 193 | Which of the following statements related to the efficiency of a roots blower is correct? | It is a ratio of actual work done to ideal work done. | It is a ratio of actual volume to ideal volume required | It is a ratio of ideal volume to actual volume required. | It is a ratio of isentropic work done to actual work done. | d | Isentropic Efficiency = \(\frac{Isentropic Work}{Actual Work}\) | Comments | Active | |
| 194 | Identify the correct pair from the following. | Otto cycle: Petrol engines | Diesel engines: Electric vehicles | Carnot cycle: Compressors | Brayton cycle: Chillers | a | Ic engine cycle: otto cycle – petrol engine , diesel cycle – CI engine , lenior cycle – jet engine | Comments | Active | |
| 195 | Identify Point A in the given figure.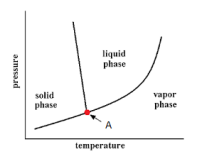 |
Triple point | Saturation point | Critical point | Superheated point | a |  |
Comments | Active | |
| 196 | Thermo-siphon type of IC engine cooling system | Does not use a pump for water circulation | Uses a condenser for cooling | Uses grease as working fluid | Uses a compressor for water circulation | a | A thermo-siphon cooling system works based on the principle of natural convection. In this system: Hot water from the engine rises naturally due to decreased density. It flows to the radiator, where it cools down. The cooler, denser water then sinks and returns to the engine. This cycle happens without any pump, relying purely on the difference in density due to temperature changes. |
Comments | Active | |
| 197 | Identify the correct option based on the given assertion and reason. Assertion (A): While tensile testing of gold, necking phenomenon occurred. Reason (R): Gold is a brittle material. |
A is true but R is false | Both A and R are true | A is false but R is true | Both A and R are false | a | As we know that gold have good ductility and meleable so reason is false. | Comments | Active | |
| 198 | Identify the cycle on the basis of its P-h diagram. |
Stirling cycle | Vapour compression refrigerant cycle | Brayton cycle | mollier cycle | b | Given P-h diagram shows VCRS cycle. |
Comments | Active | |
| 199 | Identify the measuring set-up shown in the following figure.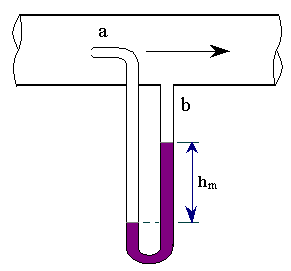 |
Pitot tube | Diaphragm gauge | Bernoulli's tube | Switch gauge | a | A pitot tube is a simple glass tube bent at an angle of 90° that is used to measure the velocity of flow.It is based on principle of conversion of kinetic head into pressure head. The point at which velocity reduces to zero is called stagnation point. Used to measure velocity of flow. The point at which velocity of flow tends to zero – stagnation point ( velocity in open channels) \(V_{th}=2gh= \frac{2g(p_{s}-p_{o})}{Ïg}\) Vact = Cv \(2gh\) Coefficeint of velocity (0.98) \(C_{v}=\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 200 | While deaerating the steam, when water is heated to 100 another steam is introduced known as \(℃ \) | Scorching steam | Pegging steam | Charging steam | Monochrome steam | b | In deaeration, the process aims to remove dissolved gases (especially oxygen and carbon dioxide) from feedwater in steam systems, which can cause corrosion. When the water is heated to 100°C, it reaches its boiling point at atmospheric pressure. To drive off the remaining dissolved gases, additional steam is introduced. This introduced steam is known as pegging steam. |
Comments | Active | |
| 201 | Identify the pressure indicated by C in the following figure.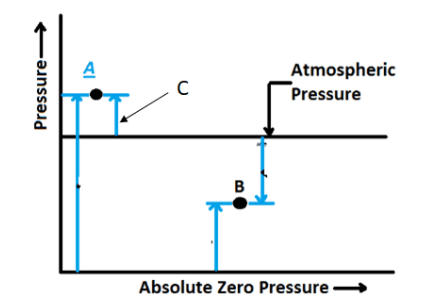 |
Vacuum pressure | Absolute pressure | Gauge pressure | Barometric pressure | c | 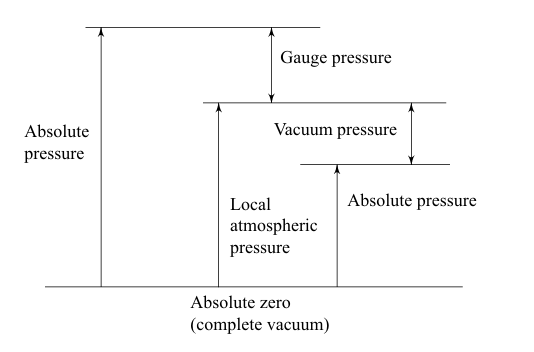 |
Comments | Active | |
| 202 | The Sl unit of couple is: | Kg-S | N-S | Pa-m | N-m | d | A couple in physics refers to a pair of equal and opposite forces whose lines of action do not coincide, creating a rotational effect (torque) but no resultant force. The magnitude of a couple (or torque) is calculated as: Torque=Force×Perpendicular distance between the forces Force is measured in newtons (N) Distance is measured in meters (m) So SI unit will N-m. |
Comments | Active | |
| 203 | Which of the following processes DOES NOT constitute in the Carnot cycle?" | Reversible Isothermal Heat Addition | Reversible Adiabatic Expansion | Reversible Isobaric Condensation | Reversible Isothermal Heat Rejection | c | 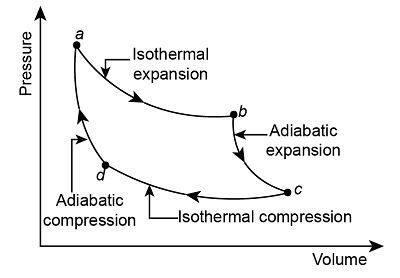 There is no process of Reversible Isobaric Condensation. |
Comments | Active | |
| 204 | Which of the following turbines is correctly paired with its type? | Mixed flow turbine → Francis turbine | Radial flow turbine→ Kaplan turbine | Reaction turbine→ Pelton wheel turbine | Inward flow turbine → Fourneyron turbine | a | Francis turbine is a mixed flow turbine, meaning water flows both radially and axially through the runner. The Kaplan turbine is an axial flow turbine, not radial. Water flows parallel to the axis of rotation. The Pelton wheel is an impulse turbine, not a reaction turbine. Reaction turbines involve pressure change across the runner, which is not the case for Pelton wheels. The Fourneyron turbine is an outward flow turbine, not inward. | Comments | Active | |
| 205 | Identify the correct option based on the given assertion and reason. Assertion (A): Steam turbines operate at fairly the same speed regardless of the load due to governing. Reason (R): Throttle governing is often done in small steam turbines. |
A is true but R is false | Both A and R are true | Both A and R are false | A is false but R is true | b | Assertion (A): Steam turbines are equipped with governing mechanisms that adjust the steam supply based on the load. This ensures that the turbine speed remains nearly constant, which is critical for applications like power generation where frequency stability is important. Reason (R): Throttle governing is a common method used in small steam turbines. It involves controlling the steam pressure and flow rate by throttling the steam before it enters the turbine. |
Comments | Active | |
| 206 | Calculate the depth of centre of pressure for the following body submerged in water. |
(2h) / 3 | (4h) / 3 | h/3 | (5h) / 3 | a | Surface C.G.( \(h)\) C.P.(P*) Rectangle  \(\frac{h}{3}\) \(\frac{2h}{3}\) Trapezium 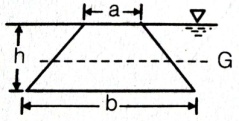 \(\frac{a+2b}{a+b}.\frac{h}{3}\) \(\frac{a+3b}{a+2b}.\frac{h}{2}\) Triangle  \(\frac{2h}{3}\) \(\frac{h}{3}\) \(\frac{3h}{4}\) \(\frac{h}{2}\) Circle 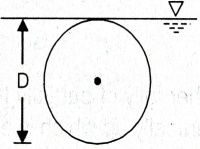 \(\frac{D}{2}\) \(\frac{5D}{8}\) Semi-circle  \(\frac{2D}{3Ï€}\) \(\frac{3Ï€D}{32}\) Parabola  \(\frac{3h}{5}\) \(\frac{2h}{5}\) \(\frac{5h}{7}\) \(\frac{4h}{7}\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 207 | In ______, water flows parallel to the axis of the rotation of shaft. | Old Francis turbine | Francis turbine | Kaplan turbine | Pelton wheel | c | In a Kaplan turbine, water flows axially, meaning parallel to the axis of rotation of the shaft. It is an axial flow reaction turbine, commonly used for low-head, high Specific speed. |
Comments | Active | |
| 208 | The efficiency of Carnot cycle is expressed as | ratio of work done to amount of heat given | ratio of volume compressed to amount of heat given | ratio of work supplied to amount of work done | ratio of work done to pressure released | a | The efficiency of a Carnot cycle is defined as: η= \(\frac{Net work done by the engine}{Heat absorbed from the hot reservoir}\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 209 | Which of the following is NOT a type of boiler on the basis of its position? | Prone position boiler | Horizontal boiler | Inclined boiler | Vertical boiler | a | "Prone position boiler" is not a recognized classification in boiler terminology. | Comments | Active | |
| 210 | Identify which of the given statements are correct. Statements: A) A refrigerant should have high boiling point. B) A refrigerant should have high latent heat value. C) A refrigerant should have low freezing point. |
All A, B and C | Only A and C | Only B and C | Both A and B | c Solution 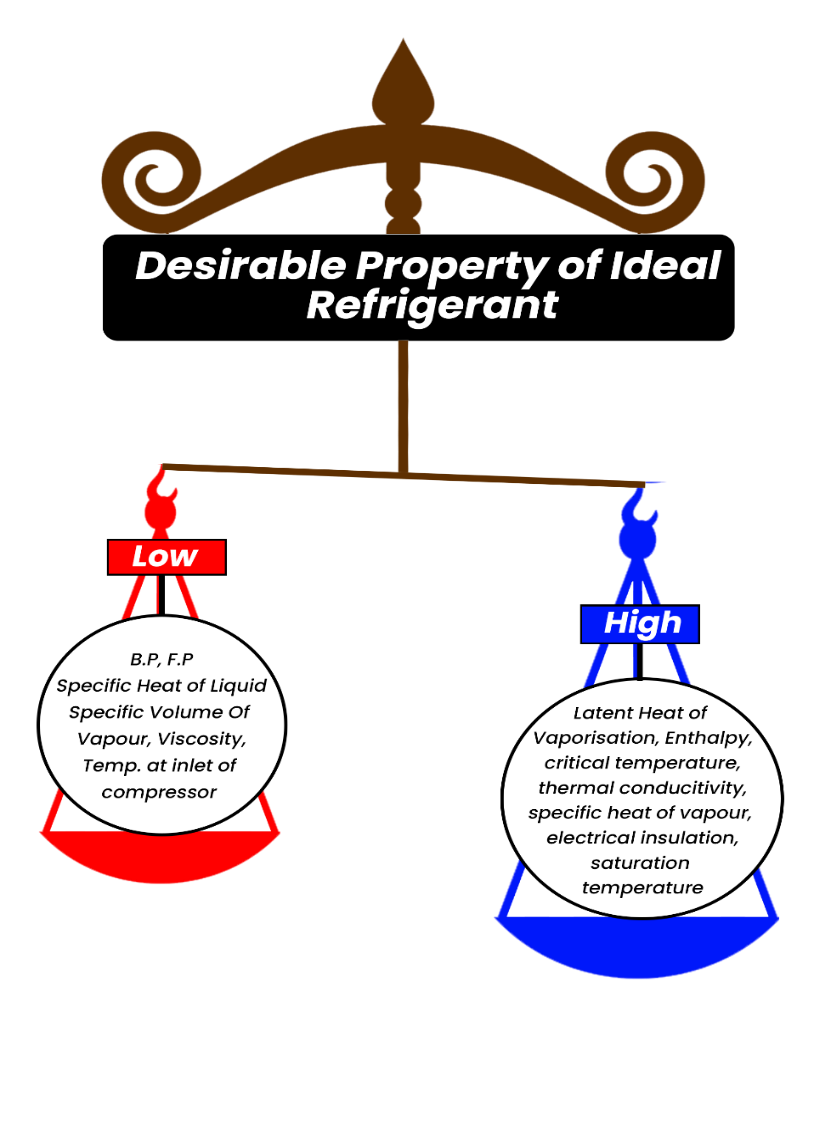 |
Comments | Active | ||
| 211 | Identify the thermodynamic device shown here.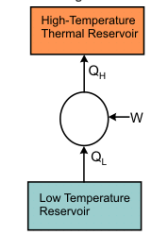 |
Refrigerator | Condenser | Compressor | Boiler | a | As we know that the work of refrigeration to absorb heat and transfer it to refrigerant as shown in figure. |
Comments | Active | |
| 212 | An air preheater is essentially a/an _____. | Heat exchanger | Cooler | Expander | Chiller | a | An air preheater is a device used to transfer heat from the flue gases to the incoming air before it enters the combustion chamber of a boiler or furnace. This increases thermal efficiency by preheating the combustion air, making it a type of heat exchanger. | Comments | Active | |
| 213 | Identify the correct pair on basis of types of components. | Venturimeter → Volume fan | Casing → Volute casing | Motor →Friction blades | Piston →Forward flow | b | A volute casing is a specific type of casing used in centrifugal pumps and compressors to collect and direct fluid flow efficiently. | Comments | Active | |
| 214 | Which of the following is NOT a classification of orifices? | Free discharging orifices | Drowned orifices | Submerged orifices | Blocked orifices | d | Blocked orifices is not a standard classification — a blocked orifice simply means it’s obstructed and not functional, not a recognized type of orifice in fluid mechanics. | Comments | Active | |
| 215 | ________ is done for keeping the steam turbine speed fairly same in-spite of load. | Positioning | Steering | Parting | Governing | d | Governing is the process used in steam turbines to maintain a nearly constant speed despite variations in the load. It involves controlling the steam flow to the turbine using a governor mechanism, which adjusts valves based on speed changes. | Comments | Active | |
| 216 | Identify the correct statement with respect to air standard cycle assumptions. | Water is a working fluid. | All processes in power cycles are internally irreversible. | Air is considered an ideal gas. | Steam is supplied at lower temperatures. | c | Air standard cycle assumptions: In the air standard cycle, we assume that the working fluid has a fixed mass. By assuming a closed system or fixed mass system, an ideal gas equation can be applied which makes the analysis easy. By assuming the fixed mass system we can use W = ∫Pdv because in closed system analysis swept volume is equal to displaced volume. The real open cycle is changed into a closed cycle by assuming that the gases being exhausted are fed back into the intake system. The working fluid is air which behaves as an ideal gas.  All the processes are internally reversible.  The specific heat of air remains constant during the cycle.  The combustion process is replaced by the heat addition process.  A cycle is assumed to be a closed cycle.  The exhaust process is modeled by a heat rejection process |
Comments | Active | |
| 217 | Negative gauge pressure is also known as | Barometric pressure | Atmospheric pressure | Vacuum pressure | Mercury pressure | c |  |
Comments | Active | |
| 218 | Identify the correct option based on the following statements pertaining to steam A: Condenser is a component of the refrigeration cycle. B: Throttling device is not a component of the refrigeration cycle. C: A compressor is a device of the refrigeration cycle. |
Only B and C are true | Only A and C are true | Both A and B are true | All A, B and C are true | b | An expansion valve (Throttling device) to regulate the flow of the refrigerant. So it is part of refrigeration cycle. | Comments | Active | |
| 219 | For which of the instrument out of given below, the coefficient of discharge is minimum? | Venturimeter | Orifice meter | Pirani gauge | Nozzle meter | b | Venturimeter: ~0.98 (highest, very efficient) Nozzle meter: ~0.95 Orifice meter: ~0.60 – 0.65 (lowest among flow meters listed) Pirani gauge: Not a flow-measuring device; it's used to measure low pressures (vacuum) using thermal conductivity – not applicable here |
Comments | Active | |
| 220 | Which of the following is true for stage efficiency for the steam turbines? | It is the product of blade efficiency and nozzle efficiency. | It is the addition of blade efficiency and nozzle efficiency. | It is the ratio of blade efficiency to nozzle efficiency. | It is the square of blade efficiency. | a | Stage Efficiency=Nozzle Efficiency×Blade Efficiency | Comments | Active | |
| 221 | Which of the following options is NOT true about viscosity? | It is caused by friction within a fluid. | Its unit is N-s/m². | It is the same as specific gravity. | It is an defined as the fluid's resistance to deformation at a given flow. | c | Specific Gravity is the density of any fluid w.r.t standard fluid i.e water, so it is simply ratio of densities and differ from viscosity. | Comments | Active | |
| 222 | Which of the following is NOT a type of clutch? | Cone clutch | Dry clutch | Cycloid clutch | Plate clutch | c | Cycloid clutch : Not a recognized type of clutch in mechanical systems. "Cycloid" typically refers to a type of gear profile (e.g., in cycloidal drives), not clutches. | Comments | Active | |
| 223 | Which of the following is NOT a component used in steam generation? | Evaporator | Governor | Boiler | Superheater | b | A governor is a mechanical or electronic device used to regulate the speed of a prime mover (such as a steam engine, diesel engine, or turbine) by controlling the fuel or steam input. | Comments | Active | |
| 224 | Which of the following is NOT an assumption made for Euler's equation of motion? | Frictional losses are zero. | Velocity of flow varies across the cross section. | Fluid is non-viscous. | Fluid is incompressible. | b | Velocity of flow varies across the cross section:- This is NOT an assumption of Euler's equation — it actually contradicts the assumptions, which treat the velocity as uniform across a cross-section along a streamline. | Comments | Active | |
| 225 | Identify the flow shown in the following figure. |
Turbulent flow | Laminar flow | Recoil flow | Transient flow | a | Turbulent flow is a type of fluid motion characterized by chaotic, irregular, and random fluctuations in velocity and pressure. | Comments | Active | |
| 226 | Which of the following is NOT a type of cam when classified according to follower movement? | Dwell-Rise-Dwell-Return-Dwell | Rise-Rise-Rise | Rise-Return-Rise | Dwell-Rise-Return-Dwell | b | Follower Movement (Reference – Theory of machine by SS Rattan – page No.-212)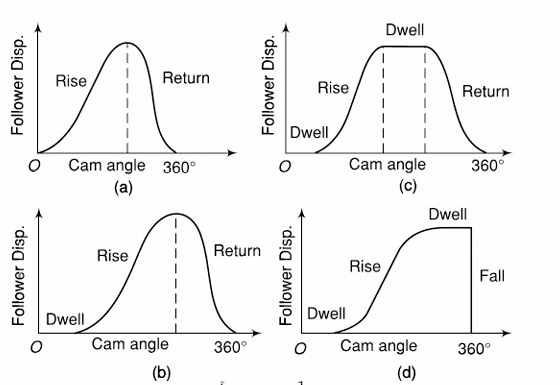 So, Rise-Rise-Rise is not any follower movement. |
Comments | Active | |
| 227 | ______ is a part of gas turbine fuel injector. | Plug | Screw gauge | Gun | Vaporiser | d | Vaporiser is a part of gas turbine fuel injector. | Comments | Active | |
| 228 | Identify the correct pair in terms of type of welding and the electrode used from the following options. | Tungsten electrode → TIG welding | Aluminium electrode → Laser welding | Monel electrode → Friction stir welding | Titanium electrode → Friction welding | a | Friction stir welding (FSW) is a solid-state process that does not use any electrodes or filler materials. Friction welding is another solid-state process that generates heat through mechanical friction. It does not use electrodes of any kind. Laser welding uses a high-energy laser beam to fuse materials. It does not use electrodes like traditional arc welding methods. | Comments | Active | |
| 229 | In a glass tube with water flowing, a liquid dye with the same specific weight is introduced. The resulting dye filament pattern is observed as shown in the figure. Identify the type of flow from the following options.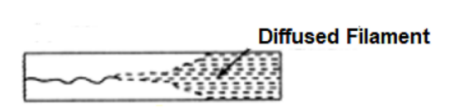 |
Laminar flow | Recoil flow | Transient flow | Turbulent flow | d | Turbulent flow is a type of fluid motion characterized by chaotic, irregular, and random fluctuations in velocity and pressure. | Comments | Active | |
| 230 | Coefficient of friction depends on_____ | Density of the fluid | Surface roughness | Colour of the fluid | Weight of the fluid | b | Coefficient of fricition is simply the indication that how rough surface is . if this coefficient value is high then surface is rough and for smooth surface coefficient value will less and extremely smooth surface coefficient of friction value will very high. | Comments | Active | |
| 231 | Identify the correct option based on the given statements. A: Clearance ratio for a single stage reciprocating compressor is the ratio of clearance volume to swept volume. B: Clearance ratio for single stage reciprocating compressor is generally in the range of 2 to 10%. |
Both A and B are false | A is true, but B is false | Both A and B are true | A is false, but B is true | c | clearance Ratio = \(\frac{clearence Volume}{Swept Volume}\) The clearance ratio is typically in the range of 2% to 10% for single-stage compressors, depending on design and application. |
Comments | Active | |
| 232 | Identify the correct statement with respect to hydroelectric power plant. | Net head is the water level before tail race. | Net head or effective head is the head available at the inlet of the turbine. | Gross head is the effective head after the water is delivered. | Gross head is the water level before head race. | B | Net head or effective head is the head available at the inlet of the turbine. | Comments | Active | |
| 233 | Match column A with column B Column A (Property) Column B (Definition) A. Flash point 1. Temperature at which vapours are given off from oil B. Pour point 2. Temperature at which lubricant is able to flow C. Fire point 3. Temperature at which oil catches fire |
A-1; B-2: C-3 | A-2: B-3: C-1 | A-2: B-1: C-3 | A-3: B-1: C-2 | a | Flash point: Temperature at which vapours are given off from oil Pour point: Temperature at which lubricant is able to flow Fire point: Temperature at which oil catches fire |
Comments | Active | |
| 234 | Bernoulli’s equation is applied on _______. | Tachometer | Manometer | Side bar | Orifice meter | d | Orifice meter – A flow measurement device that uses Bernoulli’s principle to calculate flow rate from pressure differences across an orifice. | Comments | Active | |
| 235 | Identity the correct option based on the following statements. A. Refrigerant should be affected by moisture. B. Refrigerants should be non-toxic. C. Refrigerants should be non-corrosive. |
Only B, and C are true | Only A, and C are true | Only A,B and C are true | Both A and C are true | a | Refrigerant should not affected by moisture.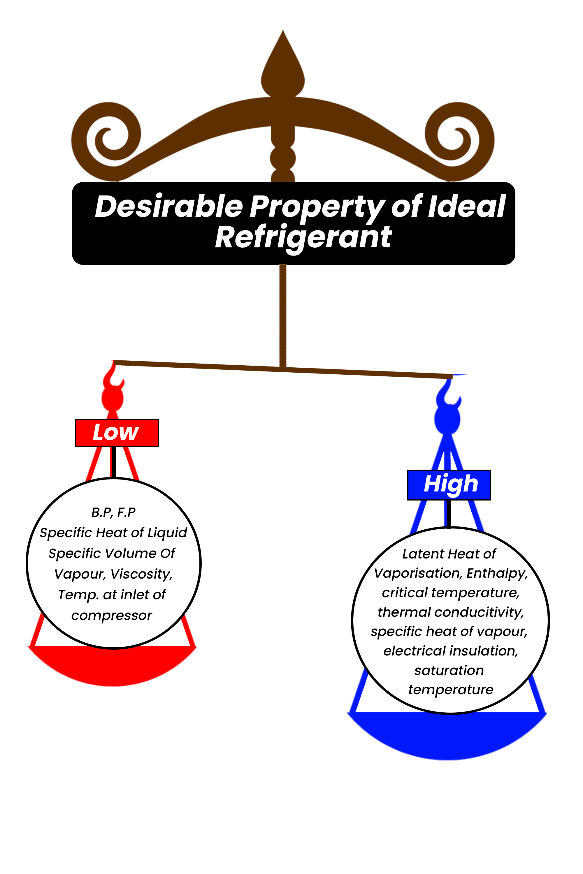 |
Comments | Active | |
| 236 | Which of the following fuels is LEAST/NEVER used in a boiler? | Gas | Mercury | Oil | Coal | b | Mercury is never used as a fuel in boilers. It is a toxic metal, not combustible, and does not release energy through combustion like other fuels do. | Comments | Active | |
| 237 | Cochran boiler is a ______, ________ and _______ type of boiler. | Fire tube; vertical; low pressure | Fire tube; horizontal; low pressure | Water tube; horizontal ; high pressure | Water tube; vertical; high pressure | a | Cochran boiler: fire tube; vertical; low pressure boiler.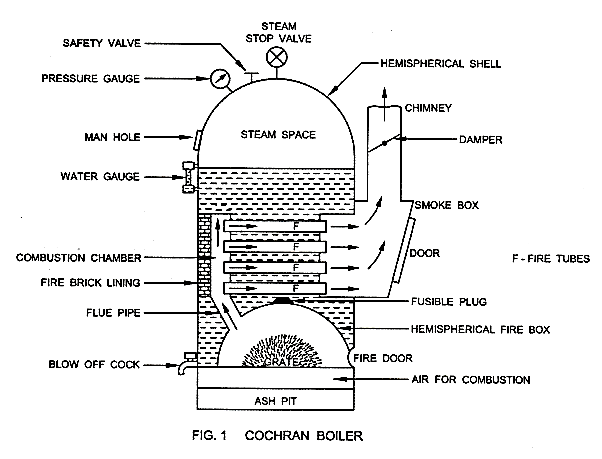 |
Comments | Active | |
| 238 | Refer to the given figure which shows Power (P) versus Discharge (Q) for a centrifugal pump and match the columns accordingly.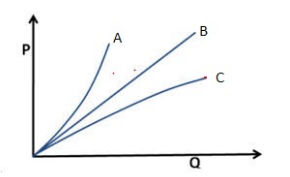 Column A (Curve) Column B (Type of vane) A. Curve B 1. Forward vane B. Curve A 2. Backward vane C. Curve C 3. Radial vane |
A-2, B-3, C-1 | A-1, B-2, C-3 | A-1, B-3, C-2 | A-3, B-1, C-2 | d | 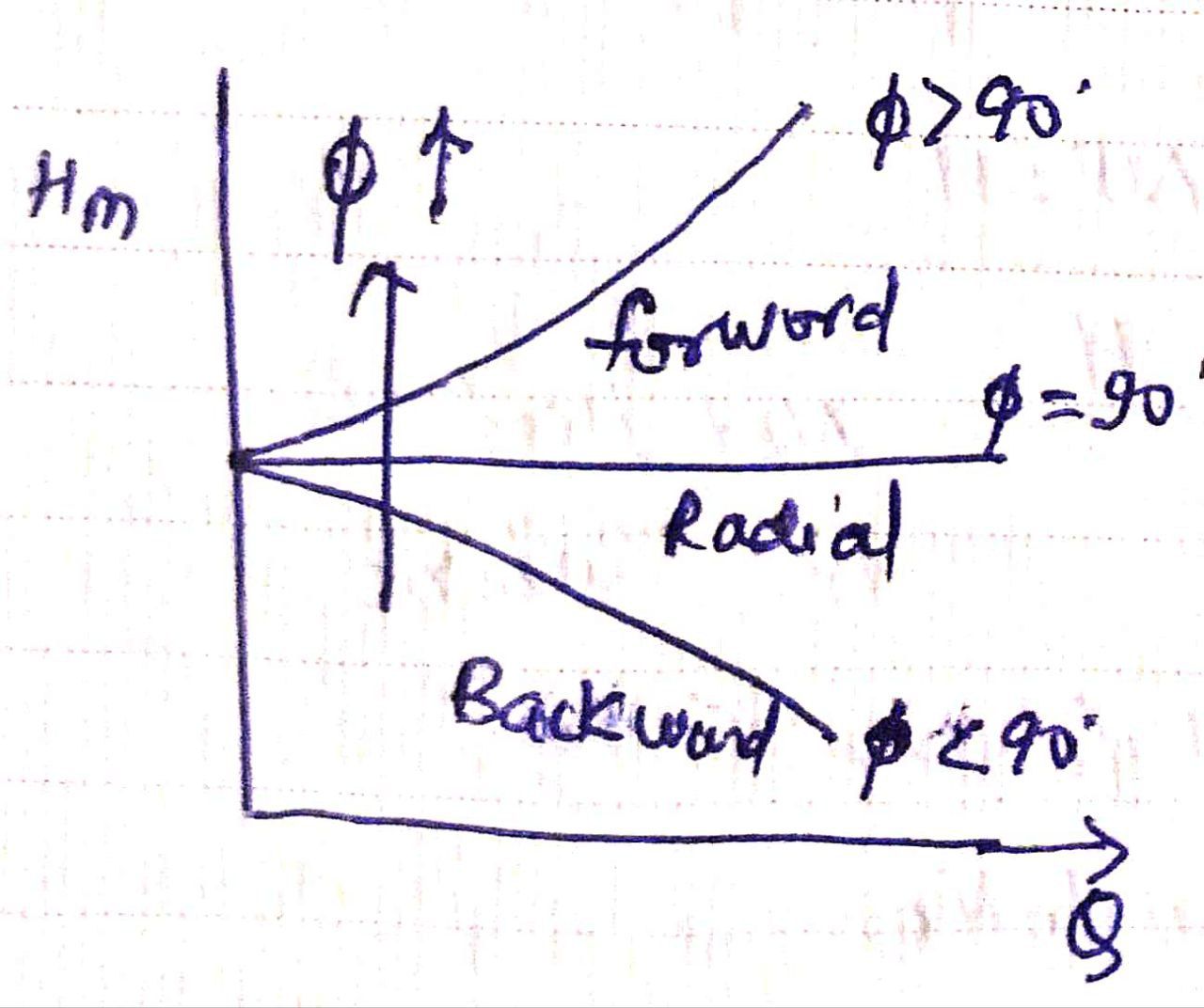 |
Comments | Active | |
| 239 | In ______ compressors, the compressor and the motor work on the same shaft and are housed in the same casing. | Hermetically sealed | Common cased | Ergonomically tabulated | Hydrophobically crafted | a | Comments | Active | ||
| 240 | Given in the options are terminologies related to the value timing diagram of an IC engine and their full forms. Identify the full form that is correctly paired with it short form. | FVO First Value operation \(→\) | TDC Top dead centre \(→\) | BDC Burden dead core \(→\) | IVC Intake valve corrosion \(→\) | b | FVO is not a standard term in IC engine valve timing diagrams, BDC stands for bottom dead center, IVC stands for Intake Valve Closing, part of the valve timing in an IC engine. | Comments | Active | |
| 241 | Which of the following is a 100% reaction turbine? | Hero's turbine | Rateau turbine | Curtis turbine | De-Laval turbine | a | 50 % reaction turbine : parson turbine , 100% reaction turbine : Hero's turbine | Comments | Active | |
| 242 | Which of the following is NOT a type of lathe machine? | Turret lathe | Tool room lathe | Boiler room lathe | Bench lathe | c | On the basis of their purpose, design, number of tools accommodated, degree of mechanisation and other factors, lathe-type machine tools may be classified as : 1. Limited or low-production Machines. The lathes included in this category are : engine lathe (centre lathe), bench lathe, tool room lathe and speed lathe. 2. Medium-production Machines. Turret lathes and duplicating (or tracer controlled) lathes. 3. High-production Machines. Semi automatic and automatic lathes. (Reference – A textbook of production technology by P.C. Sharma – page no.-449) |
Comments | Active | |
| 243 | Identify whether the given statements are true or false. Statements: A) Work done by a system on its surroundings is treated as a negative quantity. B) Energy transfer as heat to a system from its surroundings is treated as a positive quantity. |
Both A and B are true | A is true but B is false | A is false but B is true | Both A and B are false | c | Work done by the system is considered as positive work so option a is incorrect here. Remind sign work heat and work by this:  |
Comments | Active | |
| 244 | Calculate the depth of centre of pressure for the following body (circular plate) submerged in water (where D is diameter and G is centre of gravity). |
D/2 | D/3 | 5D/8 | 5D/4 | c | Surface C.G.( \(h)\) C.P.(P*) Rectangle  \(\frac{h}{3}\) \(\frac{2h}{3}\) Trapezium  \(\frac{a+2b}{a+b}.\frac{h}{3}\) \(\frac{a+3b}{a+2b}.\frac{h}{2}\) Triangle  \(\frac{2h}{3}\) \(\frac{h}{3}\) \(\frac{3h}{4}\) \(\frac{h}{2}\) Circle  \(\frac{D}{2}\) \(\frac{5D}{8}\) Semi-circle  \(\frac{2D}{3Ï€}\) \(\frac{3Ï€D}{32}\) Parabola  \(\frac{3h}{5}\) \(\frac{2h}{5}\) \(\frac{5h}{7}\) \(\frac{4h}{7}\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 245 | A______ is provided to remove the water from a steam-water mixture in a boiler. | Lever valve | Pin check | Fusible plug | Steam trap | d | steam trap: To "trap" steam in the system while removing condensate (water formed as steam cools down) and gases that can reduce efficiency or damage equipment. | Comments | Active | |
| 246 | Match column A with column B. Column A (Law of Thermodynamics) Column B (Concept) A. Zeroth law 1. Conservation of energy B. First law 2. Entropy C. Second law 3. Thermal equilibrium |
A-2; B-1; C-3 | A-1; B-3; C-2 | A-3; B-1: C-2 | A-2; B-3; C-1 | c | Zeroth Law of thermodynamics (Temperature Measurement) when a body A is in thermal equilibrium with a body B & also separately with a body C then body B & C will be in thermal equilibrium with each other. First Law of Thermodynamics (Law of Conversion of Energy)- Joule’s Experiment “It states that, a definite amount of mechanical work is needed to produce a definite amount of heat and vice versa i.e. “Heat and mechanical work are inter-convertibleâ€. Second Law of Thermodynamics : define entropy |
Comments | Active | |
| 247 | Based on the following P-V and T-s diagrams, identify the IC engine cycle.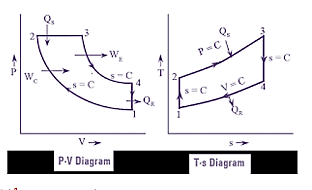 |
Brayton cycle | Diesel cycle | Otto cycle | Stirling cycle | b |  Diesel cycle: Isentropic Process 1-2 (compression) Isobaric Process 2-3 (heat addition) Isentropic Process 3-4 (expansion) Isochoric Process 4-1 (heat rejection) |
Comments | Active | |
| 248 | In order to grind material with high tensile strength abrasive is predominantly used on abrasive wheels. | Aluminium oxide | Sodium chloride | Manganese | Copper | a | Aluminium oxide it is extensively used for grinding materials of high tensile strength, such as, most steels, H.S.S., ferrous alloys, non-ferrous cast alloys and annealed malleable and ductile iron. (Reference – A textbook of production technology by P.C Sharma – page no.-532) |
Comments | Active | |
| 249 | The value of static friction is between___ and limiting friction. | 10 | 0 | 15 | 5 | b | As we can see in bleow diagram that between zero to limiting friction is reprenented by Static friction.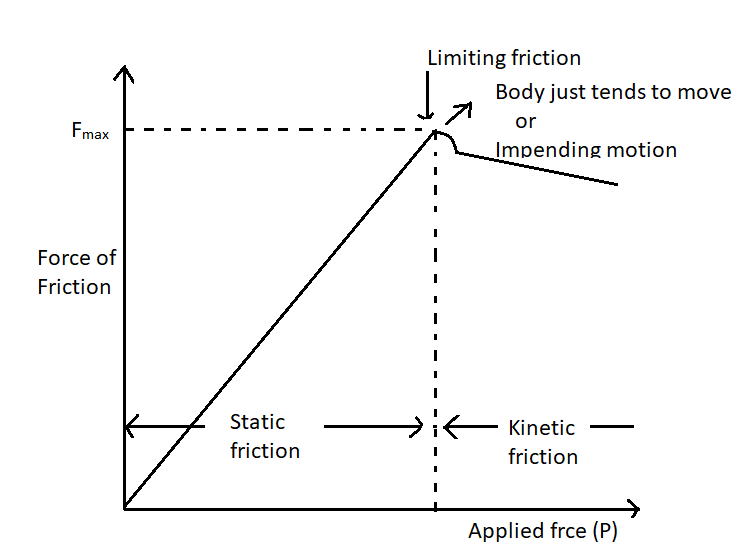 |
Comments | Active | |
| 250 | Archimedes principle discusses____ | viscosity | illuminance | potency | buoyancy | d | Archimedes Principle- Whenever a body is either partially or completely submerged in a fluid, it experiences a force in upward direction which is equal to the weight of the fluid displaced. So it discuss about buoyancy, option d will be correct answer. |
Comments | Active | |
| 251 | Identify point A in the following figure.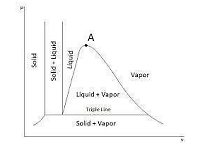 |
Critical point | Triple point | Saturation point | Superheated point | a | Point a represent the critical point .At this point solid directly convert into vapour. | Comments | Active | |
| 252 | In case of liquids, can be seen as cohesive forces between molecules of liquid | Adaptability | Transferability | Permeability | Viscosity | d | cohesive forces between molecules of liquid can be seen by viscosity. Dynamic viscosity: 10 poise \(\frac{N-s}{m^{2}}=Pa-s=\frac{kg}{m-s}=\) Kinematic viscosity: = m2/s \(ν=\frac{μ}{Ï}\) 1stoke = cm2/sec m2 / s = 104 stokes T \(↑\) \(μ\) ν Liquid \(↓\) \(↓\) Gases \(↑\) \(↑\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 253 | In a rotameter, the float position indicates____ | Weight | Viscosity | Density | Flow rate | d | Rotameter Operation principle: When fluid is entered into the tube, some of the fluid strikes the float & some pass by. This makes the float move upwards until the buoyant force is equal to the weight of the float. At this point, the float will stop to move upwards and the float position will indicate the flow rate. Annular space increasing upward, thus giving more area, more flow, more upward movement of the float & hence more flow rate. 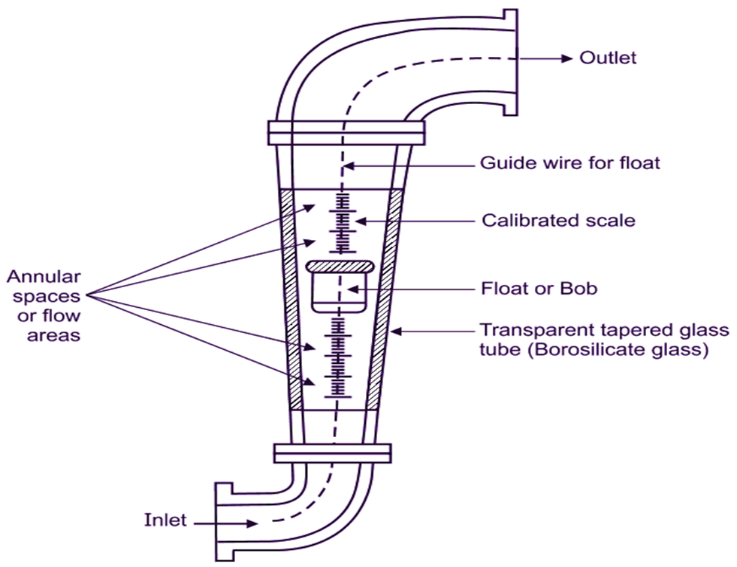 |
Comments | Active | |
| 254 | An oil of specific gravity 0.9 flows through a 0.1 m diameter pipe under a pressure of 100 kPa. The centre line of the pipe is 5 m above the datum line and the total energy with respect to the datum is 0.04 kJ/N. Then the discharge of the oil through the pipe in litre per second is | 170 | 340 | 85 | 677 | a | Bernoulli equation \(\frac{p}{5g}+\frac{v^{2}}{2g}+z=H \) \(11.33+\frac{v^{2}}{2g}+5=40 \) \(v=464.28 ≈21.54 m/sec\) \(Q=A.v=0.007×21.54\) \(=169.2 Lites/sec\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 255 | Which of the following statements based on the given figure is/are correct?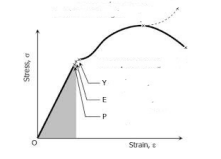 Statements: A) Point Y represents rupture strength. B) Point E represents elastic limit. C) Point P represents proportional limit. |
Only Statements B and C | Only Statement A | Only Statement C | Only Statement B | a A = Proportional limitB = Elastic limitC = Upper yield pointD = Lower yield pointF = Ultimate pointG = Breaking point A = Proportional limitB = Elastic limitC = Upper yield pointD = Lower yield pointF = Ultimate pointG = Breaking point Solution: |
Comments | Active | ||
| 256 | The work of a compressor in a vapour compression refrigeration system is to____ | Increase the volume of the refrigerant at constant entropy | Increase the temperature of the refrigerant at constant entropy | Increase the pressure of the refrigerant at constant entropy | Increase the velocity of the refrigerant at constant entropy | b |  |
Comments | Active | |
| 257 | Identify the correct statement with reference to definition of coefficient of discharge for a steam nozzle | Ratio of actual discharge to theoretical discharge. | Ratio of total discharge to leaked discharge. | Ratio of theoretical discharge to total discharge. | Ratio of theoretical discharge to actual discharge | a | Co-efficient of Discharge () is defined as the ratio of the actual discharge from an orifice to the theoretical discharge from the orifice. \(C_{d}\) \(C_{d}=\frac{Q}{Q_{th}}=\frac{Actual velocity× Actual area}{Theoretical velocity×Theoretical area} \) \(C_{d}=\frac{Actual velocity}{Theoretical velocity}×\frac{Actual area}{Theoretical area}= C_{v}× C_{c}\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 258 | Loss of head occurring due to bend in pipe during fluid flow is considered as___ | Minor loss | Resultant loss | Recording loss | Major loss | a | Loss of head occurring due to bend in pipe during fluid flow is considered as minor loss while fricition losses are considered as major loss. | Comments | Active | |
| 259 | The graphical representation of transformation of 1 kg of ice into 1 kg of superheated steam at constant pressure is known as ____ | u-v diagram | h-s diagram | p-v diagram | t-h diagram | d | The T-h diagram (Temperature vs. Enthalpy) clearly shows: Temperature plateaus during phase changes (melting and boiling) Sloped regions during sensible heating (solid, liquid, and superheated phases) It's ideal for representing processes involving heat addition and phase changes. |
Comments | Active | |
| 260 | Which of the following is NOT a minor energy (head) loss? | Loss due to enlargement | Loss due to obstruction in pipe | Loss due to friction | Loss due to contraction | c | Friction loss is considered as major loss in pipe flow. | Comments | Active | |
| 261 | Identify whether the given statements are true or false. Statements: A) In a double acting compressor, suction and expansion take place in two different strokes. B) In single acting compressors, both suction and expansion stroke take place in two different strokes. |
Both statements are false | Statement B is true but Statement A is false | Statement A is true but Statement B is false | Both statements are true | b | In a double-acting compressor, suction and compression occur simultaneously on opposite sides of the piston during each stroke. That means: On one side of the piston: suction takes place. On the other side of the piston: compression happens. There is no separate "expansion" stroke like in internal combustion engines. Instead, both sides of the piston are active during every stroke, which increases efficiency and output. |
Comments | Active | |
| 262 | Velocity potential function is a/an_____ | Infinite quantity | Vector quantity | Elemental quantity | Scalar quantity | b | (Reference -Fluid mechanics and machine by RK Bansal – page no .-181) Velocity Potential Function. It is defined as a scalar function of space and time such that its negative derivative with respect to any direction gives the fluid velocity in that direction. It is defined by ϕ (Phi). Mathematically, the velocity, potential is defined as ) for steady flow such that \(ϕ = f(x, y, z\) \(μ=-\frac{∂ϕ}{∂x} \) \(v =-\frac{∂ϕ}{∂y} \) \(w =-\frac{∂ϕ}{∂z}\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 263 | Identify the INCORRECT statement from the following options. | Stainless steels are a type of alloy steels. | Stainless steel contains chromium. | Stainless steels are a type of non-ferrous steels. | Stainless steels are resistant to corrosion. | c | Steel by definition is a ferrous alloy, meaning it is primarily composed of iron. Non-ferrous metals do not contain significant amounts of iron (e.g., aluminum, copper, titanium). |
Comments | Active | |
| 264 | Identify the correct option based on the given assertion and reason. Assertion (A): Hot tea kept in a thermos flask remains hot for a longer duration. Reason (R): A thermos flask is an example of a closed system. |
Both A and R are true | A is false but R is true | Both A and R are false | A is true but R is false | d | A thermos flask is designed to minimize heat loss through conduction, convection, and radiation. A closed system allows energy (heat or work) to cross the boundary, but not mass. A thermos flask ideally tries to minimize energy exchange (especially heat), so it is closer to an isolated system, although in practice, it's not perfectly isolated. So, A is true but R is false. |
Comments | Active | |
| 265 | Which of the following efficiencies is NOT related to turbines? | Mechanical efficiency | Hydraulic efficiency | Machine efficiency | Volumetric efficiency | c | Machine efficiency is NOT related to turbine. |
Comments | Active | |
| 266 | Two types of radiators used for IC engine systems are____and______ | Tubular core type, cellular core type | Tubular core type, reciprocating core type | Reciprocating core type, rotating core type | Rotating core type, cellular core type | a | 1. Tubular Core Type: Consists of tubes through which the coolant flows. Heat is transferred from the coolant to the fins attached to the tubes and then to the air. Common in older or simpler vehicles. 2. Cellular Core Type (also called honeycomb type): Made of numerous small air passages (cells) with coolant circulating around them. Offers a larger surface area for heat transfer. Common in modern vehicles due to better cooling efficiency. |
Comments | Active | |
| 267 | Identify which of the given statements related to IC engines is/are correct. Statements: A) Mechanical efficiency of a single-cylinder four-stroke engine is the ratio of brake power to indicated power. B) Volumetric efficiency of Sl engine is generally less than 30%. C) Volumetric efficiency of Cl engine is generally less than 30%. |
Only Statement C | Only Statement A | Only Statement B | Only Statements B and C | b | Volumetric efficiency of a Spark Ignition (SI) engine is typically in the range of 70% to 90% under normal operating conditions. Compression Ignition (CI) engines (diesel engines) often have volumetric efficiencies greater than 85%, sometimes even exceeding 100% due to turbocharging. | Comments | Active | |
| 268 | Barometric pressure is also known as____ | Fluid pressure | Volumetric pressure | Atmospheric pressure | Density | c | Barometer is the device used to measure the atmospheric pressure. | Comments | Active | |
| 269 | Match column A with column B. Column A (Boiler) Column B (Pressure) A. Cochran boiler 1. Medium pressure B. Babcock and Wilcox boiler 2. Low pressure C. Locomotive 3. High pressure boilers |
A-2: B-3: C-1 | A-1; B-2; C-3 | A-2: B-1: C-3 | A-1; B-3; C-2 | c | Cochran boiler: Low pressure (6.7 bar) Babcock and Wilcox boiler: Medium pressure (11.5 – 17.5 bar) Locomotive: High pressure boilers (20-25 bar) |
Comments | Active | |
| 270 | Identify whether the given statements related to IC engines are true or false. Statements: A) SI engine does not consist of a spark plug. B) CI engine does not consist of a spark plug. |
Both statements are true | Statement B is true but Statement A is false | Both statements are false | Statement A is true but Statement B is false | b | SI stands for spark ignition i.e petrol engine . we use spark plug to ignite fuel here so a is incorrect. | Comments | Active | |
| 271 | The temperature at which liquid droplets just appear when moist air is cooled continuously is called, | Flash point temperature | Fire temperature | Pour point temperature | Dew point temperature | d | Dry Bulb Temperature: Actual temperature of gas or mixture of gases. Wet-bulb temperature: Temperature obtained by an accurate thermometer having a wick moistened with distilled water. Dew point temperature: Temperature at which the liquid droplets just appear when the moist air is cooled continuously. |
Comments | Active | |
| 272 | Identify the correct statement with respect to centrifugal pumps. | Forward curved vanes can handle high flow rates. | Forward curved vanes have concave side of curvature facing direction of fluid flow. | In radial vanes, the fluid does not flow radially outward/inward from centre of rotation. | Backward curved vanes can handle high flow rates. | a | Forward curved vanes can handle high flow rates. | Comments | Active | |
| 273 | According to the Darcy-Weisbach equation for flow through pipe, head loss due to friction is inversely proportional to which of the following pipe parameters? | Diameter of the pipe | Material type of the pipe | Colour of the pipe | Weight of the pipe | a | According to the Darcy-Weisbach equation for flow through pipe, head loss due to friction is inversely proportional to Diameter of the pipe. According to the Darcy-Weisbach equation: \(h_{f}=\frac{f. L.V^{2}}{2g.D}\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 274 | Identify the part of the flywheel indicated as 'A' in the following figure.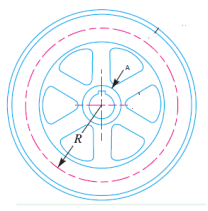 |
Hub | Frame | Spoke | Rim | a | A indicate hub of the flywheel. | Comments | Active | |
| 275 | Match the columns. Column A (Compressor) Column B (Feature) A. Screw compressor 1. Compressor and motor operate on same shaft B. Hermetically sealed compressor 2. Uses piston assembly C. Reciprocating compressor 3. Rotary type |
A-3; B-1; C-2 | A-2; B-3; C-1 | A-2; B-1; C-3 | A-1; B-3; C-2 | a | Screw compressor: Rotary type Hermetically sealed compressor: Compressor and motor operate on same shaft Reciprocating compressor: Uses piston assembly |
Comments | Active | |
| 276 | _____ is also known as the principle of transmission of fluid pressure. | Buoyancy law | Pascal's law | Newton's law | Archimedes' principle | b | Pascal law: In a static fluid pressure at point is equal in all directioon. |
Comments | Active | |
| 277 | ____ is a vertical boiler | Cochran boiler | Locomotive boiler | Babcock and Wilcox boiler | Lancashire boiler | a | 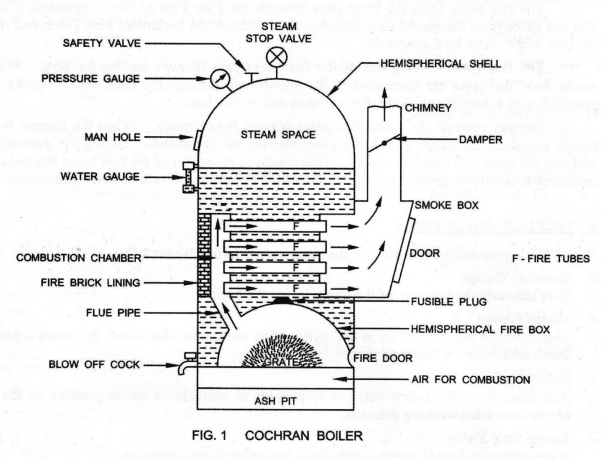 |
Comments | Active | |
| 278 | Identify the correct expression from the following options. | Brake power = Indicated power + Friction power | Brake power = Indicated power/Friction power | Brake power = Indicated power* Friction power | Brake power = Indicated power - Friction power | d | \(HA/sec=m_{f}(Cv)_{f}\) \(H.RI.P(At Piston) \) \(-F.P⟶due to mechanical arrangement B.P=τ×w(At engine shaft)\) | Comments | Active | |
| 279 | Which of the following statements is correct with respect to definition of sensible heat factor? | It is a ratio of sensible heat to total heat of the system. | It is a ratio of total heat to usable heat of the system. | It is a ratio of total heat to sensible heat of the system. | It is a ratio of total heat to available heat of the system | a | Sensible heat factor (S.H.F) The sensible heat factor is the ration of sensible heat to total heat. \(SHF=\frac{SH}{SH+LH}=\frac{S.H}{T.H}\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 280 | Match the given stages of the valve timing diagram for four-stroke petrol engines with their respective positions Column A (Stages) Column B (Position) A. Exhaust valve opens 1. 10°-20° before top dead centre B. Exhaust valve closes 2. 30°-50° before bottom dead centre C. Inlet valve opens 3. 10"-15" after top dead centre |
A-3; B-1; C-2 | A-2; B-3; C-1 | A-2; B-1; C-3 | A-1; B-3; C-2 | b | (Reference: Internal combustion engine by V ganeshan – page no.-140 ) |
Comments | Active | |
| 281 | Natural draught for exhaust gases is provided during the working of a steam generator by….. | Feed valves | Chimneys | Conductors | Compressors | b | In a steam generator (boiler) system, natural draught is the flow of air and exhaust gases due to natural convection, created by the difference in density between the hot gases inside the chimney and the cooler outside air. Chimneys create this pressure difference, allowing the exhaust gases to rise and escape naturally without the use of fans or compressors. |
Comments | Active | |
| 282 | Steam tables are available either on…. Or….. basis | Temperature, velocity | Pressure, dryness | Pressure, temperature | Velocity, dryness | c | "Steam tables are available either on pressure or temperature basis." | Comments | Active | |
| 283 | Identify the correct option based on following statements pertaining to steam. A: At a given pressure, the capacity of superheated steam to do work will be comparatively higher. B: Dryness fraction is a term related to quality of steam. C: Wet steam does not exists. |
Both A and B are true | Only C is true | Only A is true | Both A and C are true | a | Superheated steam contains more energy (enthalpy) than saturated steam at the same pressure. This extra energy can be converted to work, especially in turbines, making it more efficient. Dryness fraction indicates the proportion of vapor in wet steam. It is used to measure the quality of steam. Wet steam does exist and is a common state in steam systems. It is a mixture of saturated liquid water and saturated steam. |
Comments | Active | |
| 284 | Calculate the depth of the centre of pressure for the following body submerged in water.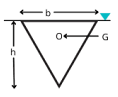 |
h/4 | h/3 | h | h/2 | d | Surface C.G.( \(h)\) C.P.(P*) Rectangle  \(\frac{h}{3}\) \(\frac{2h}{3}\) Trapezium  \(\frac{a+2b}{a+b}.\frac{h}{3}\) \(\frac{a+3b}{a+2b}.\frac{h}{2}\) Triangle  \(\frac{2h}{3}\) \(\frac{h}{3}\) \(\frac{3h}{4}\) \(\frac{h}{2}\) Circle  \(\frac{D}{2}\) \(\frac{5D}{8}\) Semi-circle  \(\frac{2D}{3Ï€}\) \(\frac{3Ï€D}{32}\) Parabola  \(\frac{3h}{5}\) \(\frac{2h}{5}\) \(\frac{5h}{7}\) \(\frac{4h}{7}\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 285 | Identify the correct pair in terms of type of process and the temperatures they are carried out from the following options. | Brazing → Below 300°C | Soldering → Above 1500°C | Brazing → Above 1500°C | Soldering → Below 300°C | d | Brazing: the brazing process can be define as the process to join two metal pieces heated to suitable temperature by using a filler metal having a liquidus above 427 and below the solidus of the base metals. \(℃\) Soldering: in soldering, two parts are joined by the use of a molten filler metal whose melting point is below the solidus (melting point of the base metals) and in all cases below 427 . \(℃\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 286 | Coefficient of performance for vapour compression refrigeration is proportional to evaporator temperature and proportional to condenser temperature. | Inversely, inversely | Directly, directly | Directly, inversely | Inversely, directly | c | The coefficient of performance (COP) of a vapour compression refrigeration cycle is directly proportional to the evaporator temperature and inversely proportional to the condenser temperature. | Comments | Active | |
| 287 | Which of the following statements is correct with respect to the Cochran boiler? | It has high rate of steam generation. | It requires high floor area. | High room head is required for its installation due to the vertical design | It has high initial installation cost. | c | 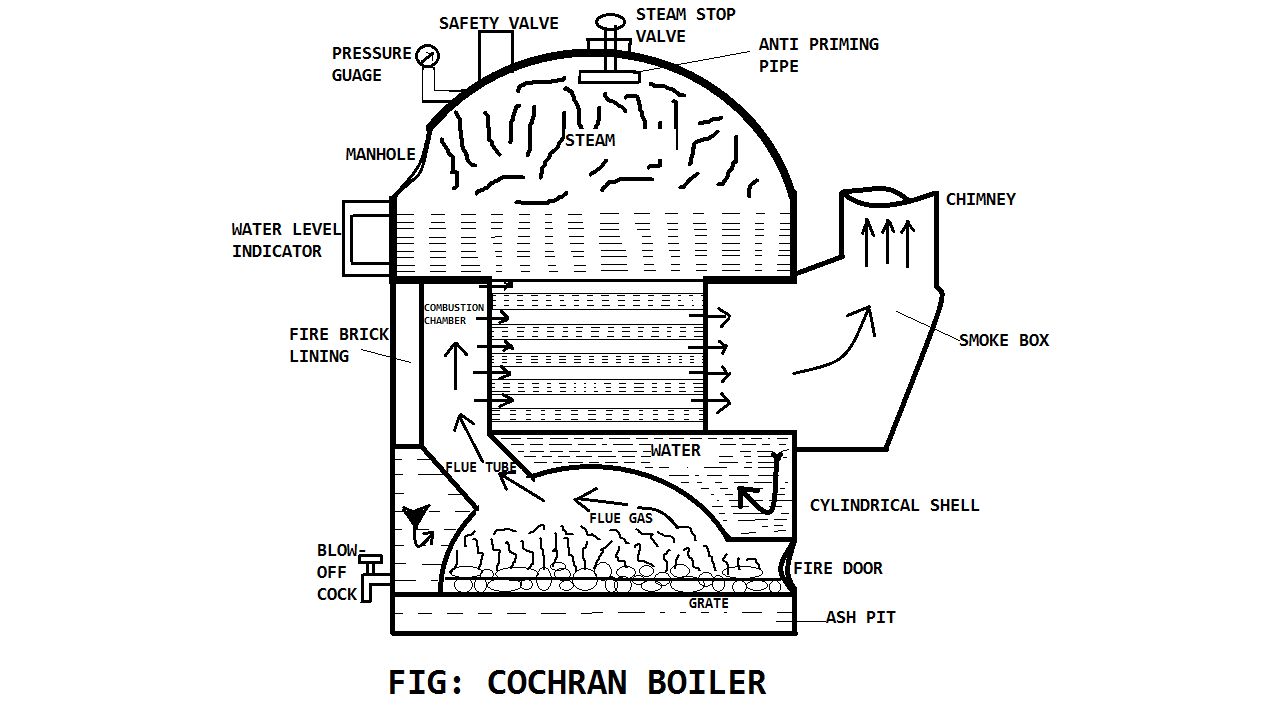 Cochran boiler: high room head required for its installation due to the vertical design. |
Comments | Active | |
| 288 | Tensile forces on the arms of a flywheel are due to the | Kinetic forces | Lateral deviation | Longitudinal variation | Centrifugal forces | d | Flywheel The rotating rim of a flywheel is subjected to a uniformly distributed centrifugal force Pc , which acts in a radially outward direction. This includes a tensile force P in the cross-section of the rim acting in the tangential direction and a bending moment M.  From the above diagram we can observe that the tensile forces on the arms of a flywheel are due to centrifugal force Pc. |
Comments | Active | |
| 289 | Relative density is also termed as…… | Buoyancy | Floatability | Acceleration | Specific gravity | d | Relative density is the density of any fluid w.r.t another fluid if this other fluid is standard fluid i.e water then this relative density is called as specific gravity. | Comments | Active | |
| 290 | Identify the correct pair from the following. | Secondary refrigerant : R12 | Secondary refrigerant : R1150 | Secondary refrigerant : Brine | Secondary refrigerant :R11 | c | Primary Refrigerant - These are the refrigerants or working substance which are directly used for cooling purpose. These refrigerants undergo a cyclic process and produce lower temperature. There is a latent heat transformation for the refrigerants. For e.g. R-11, R-12, R-22, R-134a, R-1150, Ammonia etc. Secondary Refrigerant - These are the working fluids or working substance which are first cooled by primary refrigerant and then used for cooling at the desired place.eg, H2O , Brine, Ethylene glycol. Uses of different refrigerants R-11 – Large central air conditioning plant R-12- Domestic refrigerator, water cooler etc. R-22- Window AC NH3 - Cold storage or Icing plants CO2 - Transportation of dry ice Air- Air-craft refrigeration system Brine- Milk chilling plants |
Comments | Active | |
| 291 | Match the columns.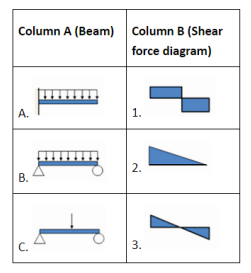 |
A-2; B-3; C-1 | A-2; B-1; C-3 | A-1; B-3; C-2 | A-3; B-1; C-2 | a | Beam A: Cantiliver beam having UDL over the entire length , then SFD will be Triangle Beam B: simply supported beam having UDL over the entire length , then SFD will be diag.3, at middle point shear force will zero and B.M have maximum value at that point. Beam C: Simply supported beam having point load at mid point then SFD Will be diag.1, at middle point shear force will zero and B.M have maximum value at that point. |
Comments | Active | |
| 292 | Which of the following is NOT a safety valve used in a boiler? | Pin safety valve | Dead weight safety valve | Lever safety valve | Spring loaded safety valve | a | Safety valves The function is to release the excess steam when the pressure of steam inside the boiler exceeds the rated pressure. Types of safety valves: Deadweight safety valve Lever safety valve Spring-loaded safety valve High steam and low water safety valve. |
Comments | Active | |
| 293 | Which of the following statements related to the efficiency of a roots blower is correct? | It is a ratio of actual work done to ideal work done. | It is a ratio of actual volume to ideal volume required | It is a ratio of ideal volume to actual volume required. | It is a ratio of isentropic work done to actual work done. | d | Isentropic Efficiency = \(\frac{Isentropic Work}{Actual Work}\) | Comments | Active | |
| 294 | Identify the correct pair from the following. | Otto cycle: Petrol engines | Diesel engines: Electric vehicles | Carnot cycle: Compressors | Brayton cycle: Chillers | a | Ic engine cycle: otto cycle – petrol engine , diesel cycle – CI engine , lenior cycle – jet engine | Comments | Active | |
| 295 | Identify Point A in the given figure. |
Triple point | Saturation point | Critical point | Superheated point | a |  |
Comments | Active | |
| 296 | Thermo-siphon type of IC engine cooling system | Does not use a pump for water circulation | Uses a condenser for cooling | Uses grease as working fluid | Uses a compressor for water circulation | a | A thermo-siphon cooling system works based on the principle of natural convection. In this system: Hot water from the engine rises naturally due to decreased density. It flows to the radiator, where it cools down. The cooler, denser water then sinks and returns to the engine. This cycle happens without any pump, relying purely on the difference in density due to temperature changes. |
Comments | Active | |
| 297 | Identify the correct option based on the given assertion and reason. Assertion (A): While tensile testing of gold, necking phenomenon occurred. Reason (R): Gold is a brittle material. |
A is true but R is false | Both A and R are true | A is false but R is true | Both A and R are false | a | As we know that gold have good ductility and meleable so reason is false. | Comments | Active | |
| 298 | Identify the cycle on the basis of its P-h diagram.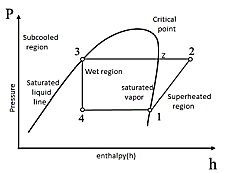 |
Stirling cycle | Vapour compression refrigerant cycle | Brayton cycle | mollier cycle | b | Given P-h diagram shows VCRS cycle. |
Comments | Active | |
| 299 | Identify the measuring set-up shown in the following figure. |
Pitot tube | Diaphragm gauge | Bernoulli's tube | Switch gauge | a | A pitot tube is a simple glass tube bent at an angle of 90° that is used to measure the velocity of flow.It is based on principle of conversion of kinetic head into pressure head. The point at which velocity reduces to zero is called stagnation point. Used to measure velocity of flow. The point at which velocity of flow tends to zero – stagnation point ( velocity in open channels) \(V_{th}=2gh= \frac{2g(p_{s}-p_{o})}{Ïg}\) Vact = Cv \(2gh\) Coefficeint of velocity (0.98) \(C_{v}=\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 300 | While deaerating the steam, when water is heated to 100 another steam is introduced known as \(℃ \) | Scorching steam | Pegging steam | Charging steam | Monochrome steam | b | In deaeration, the process aims to remove dissolved gases (especially oxygen and carbon dioxide) from feedwater in steam systems, which can cause corrosion. When the water is heated to 100°C, it reaches its boiling point at atmospheric pressure. To drive off the remaining dissolved gases, additional steam is introduced. This introduced steam is known as pegging steam. |
Comments | Active |










