| S.No | Question | Option A | Option B | Option C | Option D | Answer | Solution | Comments | Status | Action |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | The efficiency of any reversible engine operating between source reservoir and sink reservoir depends on | The nature of working fluid | The temperature of the source reservoir only | The temperatures of both reservoirs | The nature of working fluid and the temperatures of both reservoirs | c | It only depends on temperature limits. The efficiency of any reversible engine operating between source reservoir and sink reservoir depends on the temperatures of both reservoirs. | Comments | Active | |
| 2 | In which type of manometer, a reservoir having a large cross-sectional area (about 100 times) as compared to the area of the tube is connected to one of the limbs of the manometer? | U-tube differential manometer | Simple U-tube manometer | Single column manometer | Piezometer | c | Single column manometer: (i) Single column manometer is a modified form of a U-tube manometer in which one side is a large reservoir and the other side is a small tube, open to the atmosphere. (ii) In single column manometer there is a reservoir having a large cross-sectional area (about 100 times) as compared to the area of the tube connected to one of the limbs of the manometer. There are two types of single-column manometers: • Vertical single-column manometer. • Inclined single – column manometer. |
Comments | Active | |
| 3 | The Bell-Coleman cycle is an example of______ | Brayton cycle | vapour compression refrigeration cycle | vapour absorption refrigeration cycle | Air refrigeration cycle | d | Bell Coleman cycle is also known as Reversed Brayton cycle or Reversed Joule cycle. The working fluid of the Bell Coleman refrigeration cycle is Air. This system of refrigeration is used for Air Craft refrigeration and it has light weight. | Comments | Active | |
| 4 | Which of the following specification is generally measured in cubic centimeter for an internal combustion engine. | Swept volume of cylinder | Total volume of cooling water | Volume of exhaust gases | Volume of fuel inside tank | a | Cylinder block is the important part of the engine, where the reciprocating motion of the piston creates the moving boundary of the combustion system. The Boundaries are: Top Dead Centre: It is the centre where piston is farthest away from the crankshaft. It is denoted by TDC. Bottom Dead Centre: It is the dead centre where piston is nearest to the crankshaft. It is denoted by BDC. Swept Volume: It is the volume swept by the piston by travelling from one dead centre to another dead centre. It is denoted by Vs It is generally measured in cubic centimeter. Swept volume = Volume of cylinder at BDC (VBDC) – Volume of cylinder at TDC (VTDC) Clearance volume: It is the volume of the combustion chamber above the piston when it is a TDC. It is denoted by \(V_{c}\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 5 | The pressure of charge inducted through the inlet port inside the cylinder in the case of a two-stroke engine is. | Equal to atmospheric pressure | Less than atmospheric pressure | Equal to cylinder pressure | greater than atmospheric pressure | b | In engines, the pressure of charge inducted through the inlet port inside cylinder, during the intake stroke is below atmospheric pressure. | Comments | Active | |
| 6 | For a given impeller diameter, Power of the pump is proportional to: Where, N rotational speed in rpm | 1/N | N2 | N3 | N | c |  \(\frac{P_{1}}{P_{2}}=(\frac{N_{1}}{N_{2}})^{3}\) P \(âˆN^{3}D^{5}\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 7 | For H-S diagram of vapor compression refrigeration cycle, which of the following statements is FALSE? | The compression process is shown by a vertical line | The throttling process is shown by a horizontal line | The throttling process is shown by a curved line with a positive slope | The evaporation process is shown by a curved line with a negative slope | c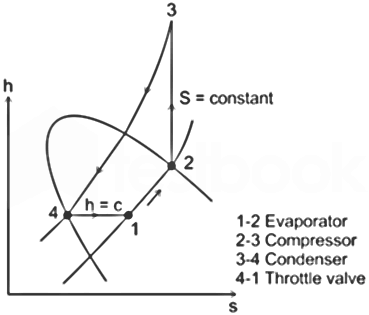 |
TdS = dh – vdp ( \(∴p=c)→TdS=dh\) \(→(\frac{dh}{dS})_{P}=T\) Temperature is constant during phase change Constant pressure lines have a constant slope in a 2-phase region (Inside the dome). So, 3rd statement is wrong as the process 4-1 is a straight horizontal line. |
Comments | Active | |
| 8 | In a horizontal pipe with a 100 mm diameter, the pressure head loss over a length of 5 metres Is found to be 0.85 m. If the coefficient of friction is 0.1, the flow velocity in the pipe will be | 0.5 m/sec | 2 m/sec | 0.91 m/sec | 1.5 m/sec | c | Head loss in a pipe is calculated by Darcy Weisbach equation: Where, f = coefficient of friction, L = length of pipe, V = average velocity of flowing fluid, g = acceleration due to gravity, and d = diameter of the pipe. Given: d = 100 mm f = 0.1 hf = 0.85 m L = 5 m \(V=\frac{2gdh_{f}}{4fL}=\frac{2×9.81×0.1×0.85}{4×0.1×5}=0.913 m/s.\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 9 | In order to increase the efficiency of Rankine cycle, Which one of the following statement is incorrect? | By decreasing condenser pressure | By superheating the steam | By increasing boiler pressure | By increasing condenser pressure | d | Methods for increasing the efficiency of Rankine cycle: Lowering the condenser pressure. Superheating the steam to high temperatures. Increasing the boiler pressure. |
Comments | Active | |
| 10 | The number of helical springs used in a spring loaded safety valve is | One | Four | Two | Three | a | In a spring-loaded safety valve, the force exerted by a single helical compression spring is used to keep the valve closed under normal operating pressure. When the pressure exceeds the set limit, the force of the steam overcomes the spring force, and the valve lifts to release excess pressure. Typically, only one helical spring is used to provide the required opposing force. This makes the mechanism simple, compact, and reliable. |
Comments | Active | |
| 11 | Oil of specific gravity 0.9 is flowing at the rate of 100 litres per second in a 0.30 m diameter pipe. If the pressure head at point P is 3 m of oil and this point P is 4 m above the datum line, then what will be the total energy at point P in metres of oil? Take g-10 m/s². | 8.1 m of oil | 7.1 m of oil | 7.4 m of oil | 7.8 m of oil | b | Total energy formula in terms of head, \(E_{total}=\frac{P}{Ïg}+Z+\frac{V^{2}}{2g}\) Given data, at a given point, Pressure head \((\frac{P}{Ïg})=3 m of oil\) Potential head (Z) = 4 m of oil Oil Flow (Q) = 100 liter/s We know, velocity (V) = Oil Flow (Q)/Cross section Area (A) Therefore V = \(\frac{Q}{(Ï€/4)×d^{2}}=\frac{100×10^{-3}}{Ï€/4×0.3^{2}}=1.41 m/s\) Velocity head \(\frac{V^{2}}{2×g}=\frac{1.41^{2}}{2×10}=0.09m~0.1m\) Therefore \(E_{total}=3+4+0.1=7.1 m of oil \) |
Comments | Active | |
| 12 | The pressure below atmospheric value is called | Vacuum pressure | Absolute pressure | Hydrostatic pressure | Gauge pressure | a | It can be measured with reference to any arbitrary datum. The common datum is Absolute zero pressure Local atmospheric pressure 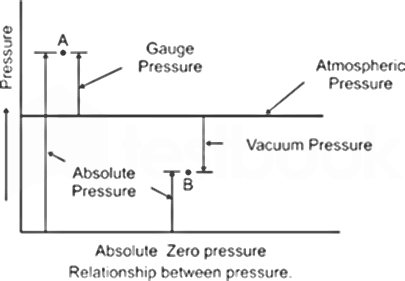 |
Comments | Active | |
| 13 | Dryness fraction is defined as | Ratio of mass of dry steam to total mass of wet steam | Ratio of total volume of wet steam to volume of dry steam | Ratio of volume of dry steam to total volume of wet steam | Ratio of total mass of wet steam to mass of dry steam | a | The dryness fraction (x) is a crucial parameter in steam engineering and thermodynamics, particularly when dealing with wet steam, which is a mixture of saturated liquid water and saturated vapor. It is defined as: \(x=\frac{mass of dry steam}{(Total mass of steam)}=\frac{(m_{g})}{m_{g}+m_{f}}\) \(m_{g}=mass of dry steam, m_{f}=mass of liquid\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 14 | The hydraulic efficiency of a hydraulic turbine is related to the overall efficiency of a turbine | m/o \(ɳ\) \(ɳ\) | o \(ɳ\) | o/m \(ɳ\) \(ɳ\) | о Х m \(ɳ\) \(ɳ\) | c | overall efficiency=hydraulic efficiency X mechanical efficiency  overall efficiency/ mechanical efficiency= hydraulic efficiency |
Comments | Active | |
| 15 | In a reciprocating compressor, the value of clearance volume has a direct impact on: | Piston speed | Volumetric efficiency | Thermal efficiency | Noise level | b | The volumetric efficiency of the reciprocating compressor is defined to account for the difference in the displacement volume or swept volume and the suction volume of the air to be compressed. The volumetric efficiency for reciprocating air compressors is about 65 to 85%. In a reciprocating compressor, the value of clearance volume "C" has a direct impact on volumetric efficiency. |
Comments | Active | |
| 16 | A cylinder contains 0.2 m³ of a gas at a pressure of 1 bar and temperature 27°C. If this gas is compressed to 0.02 m³ at a pressure of 20 bar, the temperature at the end of compression will be: | 540°C | 270°C | 327°C | 600°C | c | \(\frac{(P_{1}V_{1})}{T_{1}}= \frac{(P_{2}V_{2})}{T_{2}}\) \(T_{2}=\frac{2000×0.02×300}{100×0.2}=600K, 600-273=327℃\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 17 | Coefficient of performance is also called_______. | Refrigeration ratio | Performance ratio | Energy ratio | Heat ratio | c | This is the most technically accurate alternate name for COP because COP is a ratio of energy output to energy input (e.g., cooling provided vs. work done). | Comments | Active | |
| 18 | Which of the following statements is NOT correct? | The force of friction is not depending upon the roughness of the surfaces. | The magnitude of the force of friction is exactly equal to the force, which tends to move the body. | The force of friction is independent of the area of contact between the two surfaces. | The force of friction always acts in a direction, opposite to that in which the body tends to move, if the force of friction would have been absent. | a | The frictional force exits when two surfaces come in contact and it tries to stop the relative motion between the two surfaces. • The body can move relative to the surface when the external force applied to the body exceeds the frictional force. • The frictional force acts in the opposite direction of the motion of the body. F = N \(μ\) Where, F = frictional force (N), µ = coefficient of friction, N = normal force acting on the body (N) • The frictional force depends upon the coefficient of friction and normal force. • The coefficient of friction depends upon the nature of the surface in contact. • So, the frictional force also depends upon the nature of the surface in contact. • The coefficient of friction increases with an increase in the roughness of the surface, hence frictional force also increases accordingly. • Also, the frictional force doesn't depend upon the area of contact between the surfaces. |
Comments | Active | |
| 19 | A reaction turbine works at 420 rpm and its inlet diameter is 2m. Determine its tangential velocity. | 40 m/s | 28 m/s | 44 m/s | 36 m/s | c | Tangential velocity \(u_{1}= \frac{πD_{1}N}{60}\) \(N=420 rpm\) \(D_{1}=2m\) \(u_{1}=\frac{22}{7}×\frac{2×420}{60}=44m/s\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 20 | The average operating pressure of a Benson boiler is | 250 bar | 200 bar | 150 bar | 100 bar | a | The average operating pressure of a Benson boiler is 250 bar and can work up to 350 bar pressure and the water which is entered into the system is directly converted into steam because of Latent Heat. | Comments | Active | |
| 21 | Which among the following zone or part of piston is subjected to highest temperature due to combustion? | The center of the crown | Gudgeon pin | Bottom of the skirt | Piston outer surface | a | Crown or Head: It is the topmost portion of the piston. It is subjected to high pressure and temperature due to the combustion of the fuel. Skirt: It is the lowest portion of the piston. It works as a guide to the piston in the bore and enables the piston to move in a straight line. The skirt has the least clearance with the liner. Piston Rings: It is the outer grooves space made for compression and oil rings. |
Comments | Active | |
| 22 | When the compressor and motor operate on the same shaft and are enclosed in a common casing, then it is known as_______. | Hermetically sealed compressor | Screw compressor | Reciprocally sealed compressor | Centrifugal compressor | a | A hermetic compressor also houses both the motor and the compressor housing inside a shell. However, the steel shell is welded, which provides a true hermetic seal against the surroundings. | Comments | Active | |
| 23 | Specific heat at constant volume is | The ratio of the change in specific enthalpy to the corresponding change in temperature | The ratio of the change in specific internal energy to the corresponding change in temperature | The ratio of the change in pressure to the corresponding change in volume | The ratio of the change in volume to the corresponding change in pressure | b | Specific heat at constant volume means the amount of that is required to raise the temperature of unit mass of gas by 1 degree at constant volume. \(c_{v}=\frac{∂Q}{∆T}\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 24 | Variation in a specific volume of water if it is heated at 273 K: | Increases continuously | First increases then decreases | First decreases then increases | Depresses continuously | c | At 273 K (0°C), water is near its freezing point.  Water has anomalous expansion behavior near 0°C: As water is heated from 0°C to about 4°C, its volume decreases (specific volume decreases) because water contracts when heated in this range. Above 4°C, water behaves normally and specific volume increases with temperature.  So, when heated starting at 0°C (273 K), water's specific volume first decreases, reaches a minimum near 4°C, then increases with further heating. |
Comments | Active | |
| 25 | If the overall efficiency and mechanical efficiency of a centrifugal pump are 56% and 70%, respectively, then what will be its manometric efficiency? | 39.2% | 60% | 80% | 70% | c | \(η_{0}=56%=0.56\) \(η_{m}=70%=0.70\) \(η_{n}(Manometric efficiency)=\frac{η_{0}}{ η_{m}}=\frac{0.56}{0.70}=0.8\) Manometric efficiency = 80% |
Comments | Active | |
| 26 | Which of the following statements is true about sensible heat? | It is the amount of energy given to a system to increase its enthalpy. | It is the molecular energy of a system stored in it because of random motion of the molecules of the system | It is the amount of energy needed to increase or decrease the temperature of refrigerant | It is the amount of energy required to convert liquid refrigerant into vapour refrigerant. | c | Sensible Heat: When an object is heated, its temperature rises as heat is adde(d) The increase in heat is called sensible heat. Similarly, when heat is removed from an object and its temperature falls, the heat removed is also called sensible heat. Heat that causes a change in temperature in an object is called sensible heat. Latent Heat : All pure substances in nature are able to change their state. Solids can become liquids (ice to water) and liquids can become gases (water to vapor) but changes such as these require the addition or removal of heat. The heat that causes these changes is called latent heat. |
Comments | Active | |
| 27 | Compared to Air cooling system of an engine the compressed Water cooled engine has | Higher fuel consumption | No effect on fuel consumption | Lower fuel consumption | Same fuel consumption | c | In air cooled engine, forced/compressed air is used for cooling engine components as well as lube oils. While in the case of water cooled systems, pressurized water is used for engine cooling. Water has a much higher heat capacity and a higher heat transfer coefficient than air. This means that for a given amount of cooling, the surface area required for a water cooler is much less than for an air cooler. In other words, for the same amount of cooling, high airflow is required which would result in higher power consumption of compressed air. Therefore, water – cooled systems are more efficient and thus require lower fuel consumption. However, air – cooled systems are used for smaller, lightweight engines which require less maintenance. Bikes, Scooters are examples of air cooled systems whereas, in cars, and trucks, water – cooled engines are used. |
Comments | Active | |
| 28 | Two pressure lines in the superheated region on the T-S diagram of a Rankine cycle are: | Diverged to each other | Perpendicular to each other | Converged to each other | Parallel to each other | d | In the T-S (Temperature-Entropy) diagram for water/steam: Pressure lines represent isobars (constant pressure). In the superheated region (right of the saturated vapor line), the isobars (constant pressure lines) are almost parallel and almost vertical but slightly inclined. As pressure increases, these lines tend to become closer together (since superheated steam at higher pressure has less entropy at the same temperature). However, generally, pressure lines in the superheated region are approximately parallel. |
Comments | Active | |
| 29 | Choose the correct answer from the following four options. S1: High load on engine requires high viscosity lubricating oil. S2: High speed engine requires low viscosity oil. |
S1 and S2 both are correct | S1 is incorrect but S2 is correct | S1 is correct but S2 is incorrect | S1 and S2 both are incorrect | b | For high loads, the engine requires a higher viscosity lubricating oil to maintain an adequate lubricating film and prevent wear under heavy pressure.For high-speed engines, lower viscosity oil is preferred because it reduces fluid friction and allows the oil to circulate more easily at high RPMs.Therefore, both S1 and S2 are correct. | Comments | Active | |
| 30 | Fluids undergo volumetric change under the action of external forces due to | Bulk modulus | Compressibility | Incompressibility | Capillarity | b | Compressibility is defined as the variation of volume (V) or density With respect to pressure with constant mass (m). If variation of volume with respect to pressure is high then compressibility is high. Liquids are generally incompressible whereas gases are generally highly compressible. Fluids change the volume under external pressure due to the compressibility of the fluid. For an incompressible fluid, the density remains constant for a constant mass of fluid, as a result of which volume does not change. |
Comments | Active | |
| 31 | Which of the following statements is true about entropy is? | All adiabatic processes are isentropic processes, | Entropy of an isolated system may increase or decrease according to the value of internal irreversibility. | Entropy of the universe always increases for all practical processes: | Entropy of a system is intrinsic property. | c | The entropy of the universe increases because energy never flows uphill spontaneously. If in any process, if the entropy of the universe decreases, then the process will be an impossible process, so for any process which exists the entropy of the universe is always increasing. Entropy of a system is intrinsic property. |
Comments | Active | |
| 32 | The machining time for drilling process is calculated by: (Where L = Length of axial travel in mm; N = rpm of the drill; f = feed per rev in mm) |
T = L2/(Nxf) | T = L/(Nxf) | T = f/(NXL) | T = (Nxf)/L | b | Machining time for drilling: \(T_{m}=\frac{L}{f×N}\) D = diameter, N = speed in rpm of the drill, L = Length of axial travel in mm, f = feed |
Comments | Active | |
| 33 | The amount of heat required to convert water at a given temperature and pressure into steam at the same temperature and pressure is known as: | Superheated steam | Latent heat of water | Sensible heat of water | Enthalpy of wet steam | b | The latent heat is the amount of heat transfer required to cause a phase change per unit mass of a substance at constant pressure and temperature. | Comments | Active | |
| 34 | The change in vertical height (in mm) of a Watt governor when it changes its speed from 50 rpm to 51 rpm is approximately equal to: | 8 | 5 | 16 | 14 | d | Given \(N_{1}=50 rpm\) \(N_{2}=51 rpm\) \(h_{1}-h_{2}=895(\frac{1}{N22}-\frac{1}{N12})\) =-0.0139m = 14mm \(=895(\frac{1}{50^{2}}-\frac{1}{51^{2}})\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 35 | The property of the material by which the material recovers its original shape after the removal of load is known as: | Plasticity | Ductility | Elasticity | Hardness | c | Elasticity is the property of the material by which the material recovers its original shape after the removal of load. | Comments | Active | |
| 36 | Choose the correct answer from the following four options? S1: Open cycle Gas turbine is a rotary internal combustion engine. S2: Steam engine is a reciprocation external combustion engine. |
S1 and S2 both are incorrect. | S1 is correct and S2 is incorrect. | S1 is incorrect and S2 is correct | S1 and S2 both are correct | d | An open cycle gas turbine is a rotary internal combustion engine where air is compressed, mixed with fuel, and combusted continuously inside the engine. The resulting high-temperature gases expand through the turbine to produce work. The steam engine is a reciprocating external combustion engine where steam generated outside the cylinder is used to drive pistons in a reciprocating motion. |
Comments | Active | |
| 37 | In a refrigeration system, the work input is 20 kJ/kg while 80 kJ/kg of heat is rejected out of the system. The COP of the system will be: | 4 | 3 | 0.25 | 5 | b | Given \(W_{R}=20 kJ/kg\) \(Q_{2}=80 KJ/kg\) \(Q_{2}=Q_{1}+W_{R}\) \(Q_{1}=80-20=60 KJ/kg\) \(COP=\frac{Q_{1}}{W_{R}}=\frac{60}{20}=3\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 38 | The purpose of using fins in intercooler is to reduce: | Pressure | Temperature | Volume | Entropy | b | The purpose of an intercooler is to reduce the intake air temperature using fins. It can do so up to a few hundred degrees Fahrenheit before it enters the intake manifold. Decreasing air temperature increases the density of the pressurized air and improves engine efficiency. | Comments | Active | |
| 39 | When a fluid comes into contact with a surface, the force exerted by the fluid on the surface is referred to as_____. | Total pressure | Normal pressure | Weight of the liquid | Total force | a | Whenever a static mass of fluid comes into contact with a surface, the fluid exerts a force upon that surface. The magnitude of these forces exerted on the surface is known as hydrostatic resultant force or pressure force or total pressure. | Comments | Active | |
| 40 | Which of the following is NOT a property of the thermodynamic system? | Temperature | Heat | Internal energy | Pressure | b | Thermodynamic properties describe the state of a system and depend only on the current state, not on the path taken. Examples include pressure, temperature, internal energy, density, etc. Heat, however, is not a property; it is a form of energy transfer and depends on the path of the process, so it is a path function, not a state property. | Comments | Active | |
| 41 | Convergent part, divergent part and throat are the used to construct which of the following devices? | Orifice meter | Rota meter | Venturi meter | Pitot tube | c | Venturimeter: Venturimeter is a device used for finding out the discharge of a fluid flowing through a pipeline. • It consists of a converging tube, a small throat section, and a divergent tube. • The inlet and outlet diameters are the same as the diameter of the pipe in which it is to be installed. |
Comments | Active | |
| 42 | Which of the following high pressure boilers has a unique characteristic of absence of steam separating drum? | Velox boiler | Loeffler boiler | Lamont boiler | Benson boiler | d | The Benson boiler is a high-pressure forced circulation boiler that operates at supercritical pressure and hence does not have a steam separating drum. This unique feature distinguishes it from other high-pressure boilers that use steam drums for phase separation. | Comments | Active | |
| 43 | The dimensional formula of Volumetric Discharge is given by: | L2T-2 | L3T-1 | L1T-2 | L37-2 | b | Discharge = Cross –sectional area of pipe velocity \(×\) The unit of volumetric discharge is m3/sec Hence, the dimension of Q = L3T-1 |
Comments | Active | |
| 44 | Cross-flow turbines are devices for converting the kinetic energy of the wind or water currents to | Hydraulic energy | Pressure energy | Rotational mechanical energy | Chemical energy | c | Cross-flow turbines convert the kinetic energy of water into rotational mechanical energy. They are typically used for medium to low head applications (usually up to about 30–40 m). | Comments | Active | |
| 45 | Supersaturated expansion of steam through the nozzle results in: | Decrease in entropy and decrease in dryness fraction | Increase in entropy and increase in dryness fraction | Increase in entropy and decrease in dryness fraction | Decrease in entropy and increase in dryness fraction | b | During rapid expansion through the nozzle, steam may become supersaturated as condensation is delayed due to insufficient time for droplet formation. This causes the steam to have higher dryness fraction than equilibrium saturated steam. The rapid, irreversible process increases entropy. | Comments | Active | |
| 46 | If a turbine develops a power of 2.515 MW at 240 rpm, then the torque developed in the turbine shaft is: | 10 kNm | 200 kNm | 100 kNm | 20 kNm | c | \(P=2.515 MW,\)  \( N=240 rpm \) \(=2.515 KW\) \(P=\frac{2πNT}{60}, T=\frac{(60×2.515×10^{3}}{(2×3.14×240)}\) \(T=100 KNm.\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 47 | External work of evaporation is defined as______. | Heat expended in overcoming the internal molecular resistance to change in state from saturated water to dry steam | Heat expended in overcoming the external resistance to change in volume | Heat required for complete conversion of saturated liquid to dry saturated vapour | Heat required for complete conversion of ice to water | b | The amount of heat absorbed due to the increase in volume when water is converted into steam is called external work done during evaporation. | Comments | Active | |
| 48 | Which of the following characteristics decides that the Lancashire boiler is a fire tube boiler? | All around brick-work setting for the circulation of hot gases | Use of two flue tubes through which flow of hot gases and water is kept around the tubes | Coal firing | Horizontal erection | b | The Lancashire Boiler is the internal fire tube boiler in which flue gases are located in the tube and surrounded by water. It is a type of shell and tube heat exchanger where the flue gases are flowing in the tubes and water flowing in the shell. The heat transfer from flue gases to the water is by convection mode. There is use of two flue tubes through which flow of hot gases and water is kept around the tubes. | Comments | Active | |
| 49 | The heat acquired or released during a phase change is called | Latent heat | Specific heat | Enthalpy | Sensible heat | a | The heat given to the substance during the phase change is called latent heat. It can be either the latent heat of fusion or the latent heat of vaporization depending upon the phase change. | Comments | Active | |
| 50 | A fully insulated and completely empty tank is being filled with some fluid with negligible fluid velocity. Which of the following is correct? | Specific enthalpy of entering fluid is equal to final specific internal energy of fluid in the charged tank | Specific enthalpy of entering fluid is equal to final specific potential energy of fluid in the charged tank. | Nothing can be said about specific enthalpy. | Specific enthalpy of entering fluid is equal to final specific kinetic energy of fluid in the charged tank. | a | This is the case of an unsteady state. Energy associated with entering fluid = (m2 – m1) \((h_{1}+\frac{V12}{2})\) Q = heat transfer of the control volume, then (m1 – m2) \((h_{1}+\frac{V12}{2})+Q=m_{2}u_{2}-m_{1}u_{1}\) The tank is fully insulated so Q = 0, then \((m_{2}-m_{1})(h_{1}+\frac{v12}{2})=m_{2}u_{2}-m_{1}u_{1}\) Also, the tank is initially empty so m1 = 0 \(m_{2}(h_{1}+\frac{V12}{2})=m_{2}u_{2}\) The velocity of entering fluid is negligible, so V1 = 0 The final result is, \(h_{1}=u_{2}\) So, the specific enthalpy of entering fluid is equal to final specific internal energy of fluid in the charged tank. |
Comments | Active | |
| 51 | Which type of condenser is used for small installations of refrigeration systems (up to 30 kW)? | Shell and coil type | Double tube type | Shell and tube type | Forced convection type | b | Double tube type condensers are used for small capacity refrigeration systems (up to around 30–35 kW). These consist of an inner tube carrying refrigerant and an outer tube carrying cooling water in counterflow. Due to their compact design and sufficient heat transfer for small loads, they are ideal for such installations. | Comments | Active | |
| 52 | The product of specific volume and density is: | 1.0 | 2.5 | 0.5 | 1.5 | a | The SI unit of mass density is kg/m3. • The density is the mass per unit of volume. \(Ï=m/V\) • The specific volume is the volume per unit of mass. v = V/M \(Ïv=1\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 53 | The CGS unit of mass density is | Gram per cubic centimeter | Kilogram per cubic meter | Gram per cubic meter | Kilogram per cubic centimeter | a | •The SI unit of mass density is kg/m3. • The CGS unit of mass density is g/cm3. • The density of the material is its mass per unit of volume. |
Comments | Active | |
| 54 | Point X is 10 m below the free surface of a liquid and point Y is 12 m below the free surface of the same liquid. The correct relationship for the pressure at points X and Y is____. | Pressure at point X < Pressure at point Y | Pressure at point X = Pressure at point Y = 0 | Pressure at point X > Pressure at point Y | Pressure at point X = Pressure at point Y | a | \(h_{X}=10m, h_{Y}=12m\) \(ÏX=ÏY \) So, \(P_{absX}=P_{atm}+Ï_{X}gh_{X}=P_{atm}+Ï_{X}g(10)\) Similarly, \(P_{abs_{Y}}=P_{atm}+Ï_{Y}g(12)\) The absolute pressure depends upon the distance of the point from the free surface. \(∴P_{absY}>P_{absX}\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 55 | In which boiler is forced circulation of water required? | Lancashire | Benson | Locomotive | Babcock and Wilcox | b | Benson boiler is one of the high-pressure boilers having the unique feature of producing steam at supercritical pressure, which means it operates at a pressure and temperature above the critical point of water, resulting in improved thermodynamic efficiency and power generation capabilities. | Comments | Active | |
| 56 | In a simple vapour compression refrigeration cycle, the enthalpy at point 1, 2 and 4 are 260 kJ/kg, 60 kJ/kg and 180 kJ kg, respectively, as shown in the figure. If 2 kg of refrigerant is used to cool the system, then COP of the refrigerator will be: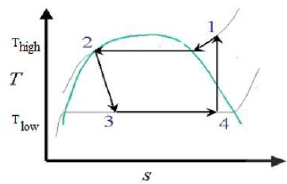 |
2.25 | 3.5 | 3 | 1.5 | d | Given \(h_{1}=260 kJ/kg, h_{4}=180 kJ/kg\) \(h_{2}=60 kJ/kg\) \(h_{3}=h_{2}=60 kJ/kg\) \(COP=\frac{Refrigeration Effect}{Work Input}\) \(COP=\frac{h_{4}-h_{3}}{h_{1}-h_{4}}\) \(=\frac{180-60}{260-180}\) COP = 1.5 |
Comments | Active | |
| 57 | Which velocity is kept as a common reference in both inlet and outlet velocity triangle for drawing the velocity diagram of a steam turbine? | Radial velocity | Whirl velocity | Relative velocity | Blade velocity | d |  Referring to the velocity triangle of the Steam turbine, we can say that the blade velocity "u" is kept as a common reference in both the inlet and outlet velocity triangle for drawing the velocity diagram of a steam turbine. |
Comments | Active | |
| 58 | In a mist lubricating system, mist of lubricating oil forms when: | Only fuel vaporises | Neither oil nor fuel vaporises | Both oil and fuel vaporise | Only oil vaporises | a | Mist lubrication system: In two – stroke engines, mist lubrication is used where crankcase lubrication is not suitable. In a two – stroke engine, as the charge is compressed in the crankcase, it is not possible to have the lubricating oil in the sump. Hence, mist lubrication is adopted in practice. In such engines, the lubricating oil is mixed with the fuel, the usual rating being 3% to 6%. The oil and fuel mixture is inducted through the carburettor. The fuel is vaporized and the oil (mist form) goes through the crankcase into the engine cylinder. The mist from the oil strikes the crankcase walls, lubricates connecting rod bearings, and the remaining oil lubricates the piston, piston rings, and the cylinder. |
Comments | Active | |
| 59 | In a heat pump, the processes of the cycle are carried out in such a manner that the sequence of processes on the p-V diagram | is the same as in a heat engine | is in anticlockwise direction | depends on the processes | is in clockwise direction | b | A heat pump working on a reversed Carnot cycle so the processes of the cycle are carried out in such a manner that the sequence of processes on the p-V diagram is counter clockwise or anticlockwise direction. | Comments | Active | |
| 60 | Double helical gears are also known as: | Mitres | Helical bevel gears | Herring bone gears | Spur gears | c | The double-helical gear, also referred to as the herringbone gear, is used for transmitting power between parallel shafts. It was developed to overcome the disadvantage of the high-end thrust that is present with single-helical gears. |
Comments | Active | |
| 61 | Water is flowing through a circular pipe of diameter 20 cm at the rate of 2 meter cube per second. What will be the velocity of water in the pipe? | 0.00324 cm/s | 32.4 m/s | 0.00637 cm/s | 63.7 m/s | d | \(Q=\frac{2m^{3}}{s}, d=20 cm=0.2 m\) As we know Q = AV \(V=\frac{Q}{A}\) We know, Area (A) = \(\frac{πd^{2}}{4}\) Area (A) = \(\frac{π×0.2^{2}}{4}=0.0314\) \(V=\frac{2}{0.0314}=63.67 m/s\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 62 | If the thermal efficiency of a Carnot engine is 0.5, then the coefficient of performance of the carnot refrigerator will be: | 2 | 0.5 | 0 | 1 | d | Given \(η_{c}=0.5\) \(COP_{HP}=\frac{1}{η_{c}}=\frac{1}{0.5}\) \(COP_{HP}=2\) We know \(COP_{Ref}=COP_{HP}-1\) \(=2-1\) \(COP_{Ref}=1\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 63 | For a laminar flow through a circular pipe of diameter 400 mm, the maximum velocity is 2 m/s. What will be the velocity at 8 cm from the wall of the pipe? | 1.1 m/s | 2.2 m/s | 1.28 m/s | 1.2 m/s | c | When a flow is fully developed steady laminar flow of an incompressible fluid in a pipe (circular). Then velocity profile at any radius r: \(U=-\frac{1}{4μ}(\frac{dP}{dx})(R^{2}-r^{2})\) For r = 0 \(u(r)=u_max(1-\frac{r^{2}}{R^{2}})\) r = R/2; u = ? at r = 200 – 80 = 120 mm (radial distance from the central line), umax = 2 m/s \(u(r)=2(1-\frac{120^{2}}{200^{2}})=1.28 m/s\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 64 | An engine cylinder has clearance volume of 20 cc and compression ratio of 14. The mechanical and volumetric efficiencies are 88% and 80%, respectively. The actual volume of charge in cc inducted per stroke is: | 264 | 208 | 164 | 124 | b | Volumetric efficiency: it is defined as the ratio of the actual volume of charge inducted per stroke to the actual volume displaced by the system. Volumetric efficiency \((η_{v})=\frac{Actual volume intake}{Swept volume}\) Compression ratio: It is defined as the ratio of the total volume of the cylinder to the clearance volume of the cylinder. Compression ratio (r) = \(\frac{Total volume}{Clearance volume}=\frac{V_{s}+V_{c}}{V_{c}}=\frac{V_{s}}{V_{c}}+1\) Total volume = swept volume + Clearance volume \((V_{s})\) \((V_{c})\) \(V_{c}=20 cc, r=14, η_{v}=80%, η_{m}=88%\) \(r=\frac{V_{s}}{20}+1⇒V_{s}=260 cc\) \(η_{v}=\frac{Actual volume intake}{V_{s}}⇒0.8=\frac{Actual volume intake}{260}\) \(∴Actual volume intake=260×0.8=208 cc.\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 65 | High pressure low water safety valve CANNOT be used on | Locomotive boiler | Cornish boiler | Cochran boiler | Lancashire boiler | a | High steam and low water safety valve is not suitable for locomotive and marine engines. It is designed such that when the steam pressure exceeds a certain pressure limit or when the water level falls below a certain limit the valve opens and the steam is released to the atmosphere. | Comments | Active | |
| 66 | Which of the following is NOT an advantage of water tube boiler in comparison with fire tube boiler? | Less immune to failure in feed water supply | High evaporation rate | Easy transport and quick erection at site | All parts easily accessible for cleaning, inspection and repairing | a | Water Tube Boiler Advantages over Fire Tube Boiler: High evaporation capacity and can operate at high pressures. Quick steam generation, as water is inside the tubes. Lightweight and hence easy to transport and erect. Easier to clean and inspect internal parts, especially tubes. |
Comments | Active | |
| 67 | The frictional torque transmitted in a conical pivot bearing with assumption of uniform wear is_____ as compared to uniform pressure theory. | More | Less | Equal when bearing is new | Always equal | b | For conical pivot bearing, , \(T_{UPT}=\frac{2}{3,}μWRcosecα\) \(T_{UWT}=\frac{1}{2}μWcosecα\) | Comments | Active | |
| 68 | For a velocity compounded impulse turbine, which of the following statements is correct? | Pressure drops only in moving blades | Pressure drops both in nozzle and moving blades | Pressure drops neither in moving blades nor in nozzle | Pressure drops only in nozzle | d | Velocity compounding involves a progressive reduction in the velocity of steam across multiple stages. This method comprises several key components, including a single set of nozzles in the initial stage, sets of moving blades attached to a rotor, and sets of fixed blades mounted within the casing. The total enthalpy drop and hence pressure drop occur in the nozzles so that the pressure remains constant in all three rows of blades. | Comments | Active | |
| 69 | An IC engine gives an output of 4 KW when the input is 10000 J/S, and the thermal efficiency is_______. | 66.6% | 60% | 40% | 30% | c | \(W_{out}=4kW=4000 J/s, Q_{input}=1000 J/s\) The thermal efficiency of a IC engine is defined as: \((η)\) \(η=\frac{W_{output}}{W_{input}}\) \(η=\frac{4000}{10000}×100=40%\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 70 | A body floats in a static fluid. It is found that the metacentre coincides with the centre of gravity of the body. The body will be in______ equilibrium. | Unstable | Neither stable nor unstable | Neutral | Stable | d | GM > 0 (Metacentre is above centre of Gravity) Stable equlibrium GM = 0 (Metacentre is above centre of Gravity) Neutral equilibrium GM = 0 (Metacentre coinciding with centre of Gravity) Unstable equilibrium |
Comments | Active | |
| 71 | A boiler produces steam at a rate of 10/9 kg per second at 20 bar and 400°C. The efficiency of the boiler is 80 and the feed-water temperature is 50°C. The calorific value of the fuel used is 44500 kJ/kg. Enthalpy of steam at 20 bar and 400°C is 3245.5 kJ/kg, and enthalpy of feed-water at 50°C is 209.3kJ/kg. The fuel burning rate in kg/h is: | 341.15 | 34.115 | 150 | 3411.5 | a | \(η_{boiler}=80%\) \(m_{s}=\frac{10}{9}kg/s\) \(h_{s}=3245.5 KJ/Kg\) \(h_{f}=209.3 KJ/Kg\) \(CV=44500 KJ/Kg\) \(η_{boiler}=\frac{m_{s}(h_{s}-h_{f})}{m_{f}×CV}\) \(=\frac{\frac{10}{9}×(3245.5-209.3)}{0.8×44500}×3600\) \(=341.15 Kg/h.\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 72 | The range of flow ratio value for a Francis turbine is: | 0.40 to 0.75 | 0.75 to 1.25 | 0.15 to 0.25 | 0.10 to 0.40 | c | Â The flow ratio of Francis turbine is defined as the ratio of the velocity of flow at the inlet to the theoretical jet velocity. \(flow Ratio=\frac{V_{f}_{1}}{2gH}\) In the case of Francis turbine, Flow ratio varies from 0.15 to 0.3 Speed ratio varies from 0.6 to 0.9 |
Comments | Active | |
| 73 | In a reciprocating compressor, the swept volume is 8/9 times the maximum volume. The clearance ratio will be equal to_______. | 0.11 | 0.1 | 0.125 | 0.89 | c | Since the maximum volume] \(=V_{s}+V_{c}\) The swept volume is 8/9 times the maximum volume. \(=V_{s}=8/9 (V_{s}+V_{c})\) \(=\frac{V_{c}}{V_{s}}=\frac{1}{8}\) Clearance ratio = \(\frac{V_{c}}{V_{s}}=0.125\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 74 | Water is flowing through a circular pipe under pressure. If the total energy per unit weight of the water at a cross-section is 30 m and the piezometric head at that section is 29.4 m, then what will be the kinetic head at that section? | 0.3 cm | 0.3m | 0.6m | 0.6 cm | c | Total head = 30 m, Piezometric head = 29.4 m. Total head = Piezometric head + Kinetic head 30 = 29.4 + Kinetic head Kinetic head = 0.6m. |
Comments | Active | |
| 75 | The discharge velocity in the orifice meter is measured by using which of the following? | Rota meter | Pitot tube | Ventura meter | Elbow meter | b | Pitot Tube is a device that is used to measure velocity at a particular point. Basic Principle: When we insert a pitot tube at any point • The velocity of flow at that point reduces to zero, which is called the stagnation point (No motion). • Kinetic Energy at that point is converted into Pressure Energy, and by measuring the pressure energy at this point, the velocity of flow can be calculated. |
Comments | Active | |
| 76 | In Electrode Discharge Machining (EDM) process, the gap between the tool and work piece should be: | 0.1 mm to 0.3 mm | 0.025 mm to 0.05 mm | 0.25 mm to 0.5 mm | 0.015 mm to 0.025 mm | b | Electro-Discharge Machining (EDM): Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM) is a manufacturing process whereby a desired shape is obtained by using electrical discharges (sparks). • Material is removed from the work piece by a series of rapidly recurring current discharges between two electrodes, separated by a dielectric liquid that controls spark discharges and is subjected to an electric voltage. • In EDM, the work piece is connected to the positive terminal, and the tool is connected to the negative terminal. • EDM machines are equipped with a servo control mechanism that automatically maintains a constant gap of approximately 0.02 to 0.05 mm between the tool and work piece. • EDM has the lowest specific power requirement and can achieve sufficient accuracy. |
Comments | Active | |
| 77 | Which of the following is NOT an assumption taken in the Bernoulli theorem? | The fluid is inviscid | The flow is rotational. | The flow is incompressible. | The flow is steady | b | The following are the assumptions made in the derivation of Bernoulli's equation: The fluid is ideal i.e. viscosity is zero The flow is steady The flow is incompressible The flow is irreversible The fluid is ideal So, "The flow is rotational" is not an assumption taken in the Bernoulli theorem. |
Comments | Active | |
| 78 | In P-H diagram of vapour compression refrigeration cycle, the compression process is shown by a: | Straight line with positive slope | Straight line with negative slope | Horizontal line | Curved line with positive slope | a |  Referring to the above diagram, the P-H diagram of the vapour compression refrigeration cycle, the compression process is shown by a straight line with a positive slope. |
Comments | Active | |
| 79 | The equations of equilibrium for non-concurrent force system are: | ΣFy = 0 | ΣFx = 0, ΣFy = 0 | ΣFx = 0 | ΣFx = 0, ΣFy = 0 and ΣM=0 | d | Equations of equilibrium for Non-concurrent force System: A non- concurrent force system will be in equilibrium if the resultant of all forces and moments is zero. • ΣFx, = 0, ΣFy = 0 and ΣM = 0 Equations of equilibrium for concurrent force System: For the concurrent forces, the lines of action of all forces met at a point and hence the moment of those forces about that point will be zero or ΣM = 0 automatically. • ΣFx, = 0, and ΣFy = 0 |
Comments | Active | |
| 80 | If cut-off ratio in air standard dual cycle approaches to unity, then this lead to which among the following cycles? | Diesel cycle | Brayton cycle | Rankine cycle | Otto cycle | D | The air standard dual cycle (also called the mixed cycle or limited pressure cycle) combines features of both Otto and Diesel cycles.  It has two heat addition processes: Constant volume heat addition (like Otto cycle) Constant pressure heat addition (like Diesel cycle)  Cut-off ratio (r_c) is the ratio of cylinder volume after combustion to the volume before combustion during the constant pressure heat addition process.  When the cut-off ratio approaches unity (r_c → 1), it means the constant pressure heat addition process disappears, and all heat addition occurs at constant volume.  Therefore, the dual cycle degenerates into an Otto cycle (which has constant volume heat addition only). |
Comments | Active | |
| 81 | Austempering is a process where______of steam temperature happens. | Increment | Reduction | Reduction or increment | No change | b | Austempering is a heat treatment process used to improve mechanical properties (like toughness and strength) of steel and cast iron.  The process involves: Heating the steel to the austenitizing temperature to form austenite. Then quenching the steel rapidly into a bath held at an intermediate temperature (usually between 250°C and 400°C), which is lower than the austenitizing temperature but above the martensite start temperature. Holding it isothermally at this temperature to allow the formation of ausferrite (a mixture of bainitic ferrite and retained austenite) instead of martensite.  This treatment results in a reduction of temperature during the process (from austenitizing temperature to austempering bath temperature). |
Comments | Active | |
| 82 | For spring loaded safety valve the pressure required to lift the valve is the pressure required to open it fully. | Equal to | More than | May be more or less than | Less than | d | A spring loaded safety valve is designed so that the valve just starts to lift at a certain pressure, called the cracking pressure. ï‚· The pressure required to lift the valve slightly (cracking pressure) is less than the pressure required to open it fully. ï‚· Reason: At the initial lift, the fluid pressure overcomes the spring force and causes the valve to start moving (lift). As the valve lifts further, the effective area on which the fluid pressure acts increases (due to the shape of the valve seat and valve disc geometry). This increased area means the fluid pressure exerts more force, so the valve requires a higher pressure to open fully. ï‚· Therefore, the pressure to open fully is greater than the pressure required to just start lifting the valve. |
Comments | Active | |
| 83 | Which of the following is NOT a type of radiator core arrangement? | Syphon | Honey comb | Cellular | Tubular | a | The radiator in an engine cooling system removes heat from the hot coolant (water or water-antifreeze mixture) by passing it through a large surface area exposed to airflow. ï‚· The radiator core is the central part of the radiator where heat exchange happens, consisting of many small passages (tubes or cells) to maximize heat transfer. ï‚· The common types of radiator core arrangements are: Tubular core: Made of multiple tubes for coolant flow with fins attached to increase the heat transfer surface. Cellular core: Consists of many small square or rectangular cells (similar to honeycomb but generally with square cells) to increase cooling surface area. Honeycomb core: Comprises hexagonal cells, similar in purpose to cellular cores, enhancing heat dissipation by maximizing surface area and airflow. ï‚· Syphon is not a type of radiator core arrangement; it refers to a fluid transport principle used elsewhere, unrelated to radiator core design. |
Comments | Active | |
| 84 | Pressure at any point in a liquid depends upon | Depth of the free surface | Height of the free surface above the measured point | Area of the free surface | Force exerted on the free surface | b | The pressure inside a liquid is given by: \(P=Ïgh\) Therefore the Pressure inside the liquid at a point depends on- the density of the liquid \(Ï \) the depth of the liquid form the free surface or height of the free surface above the measured point \(h \) the acceleration due to gravity. \(g\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 85 | In a Hydroelectric power plant, the electric power is obtained from the_____. | Chemical energy | Nuclear energy | Potential energy | Energy of water | d | In a Hydroelectric power plant, the electric power is obtained from the energy of water. • The amount of electrical energy that can be generated by a hydroelectric power plant is given as • The amount of electrical energy that can be generated by a hydroelectric power plant depends upon the quantity of water that would be most appropriate. |
Comments | Active | |
| 86 | For a system operating in a cycle, the network transfer is equal to | Change in internal energy | Change in enthalpy | Net heat transfer | Zero | C | For a cyclic process, the system returns to its initial state after completion of the cycle. Since internal energy U is a state function, the change in internal energy over a complete cycle is zero: ΔU=0 From the first law of thermodynamics for a cycle: ΔU=Q−W Since ΔU=0 for the cycle, it follows: 0=Q−W  ⟹  W=Q So, network transfer (work output) equals the net heat transfer into the system during the cycle. |
Comments | Active | |
| 87 | The Hydraulic Gradient Line will be having zero in case of______. | Non-uniform velocity | Uniform velocity | Non-uniform pressure | Uniform pressure | d | • Hydraulic gradient Line (H.G.L) – Line representing the sum of pressure head and datum head. • Total energy line (T.E.L) – Line representing the sum of pressure head, datum head, and velocity head. • IF there is no variation of pressure and constant datum then the Hydraulic Gradient Line will be having zero in case of uniform pressure. |
Comments | Active | |
| 88 | During phase change process of water______ | Only pressure remains constant | Both pressure and temperature remain constant | Only temperature remains constant | Neither pressure nor temperature remains constant | b | The latent heat is the amount of heat transfer required to cause a phase change per unit mass of a substance at constant pressure and temperature. | Comments | Active | |
| 89 | Which of the following expressions give the Thoma's cavitation factor (o), which is basically used to determine whether cavitation will occur in any portion of the turbine? Where, H, atmospheric pressure head, H, vapour pressure head, H, suction pressure head, H = working head of turbine. |
(Ha+Hv - Hs)/H | (Ha -Hs)/H | (Hv -Hs)/H | (Ha -Hv -Hs)/H | d |  Thoma’s cavitation factor: Thoma’s cavitation parameter: It is the ratio of the Net Positive Suction Head (NPSH) to the total head. \((σ)\) NPSH: It is defined as the net head developed at the suction port of the pump, is excess of the head due to the vapor pressure of the liquid at the temperature in the pump. From the definition of \(σ_{Thomas}\) \(σ_{Thoma}= \frac{H_{a}-H_{vp}-H_{s}}{H}\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 90 | Identify the option that completes the given statement with respect to stress. Factor of safety is the: | Product of ultimate stress to the working stress | Ratio of ultimate stress to the working stress | Square root of ratio of ultimate stress to the working stress | Ratio of working stress to ultimate stress | b | The factor of safety: It is the ratio of Ultimate (or maximum) stress to the permissible or working stress of a structure | Comments | Active | |
| 91 | According to___________the rate of Increase in pressure along the depth is equal to | Weight density, hydrostatic law | Hydrostatic law, weight density | Hydrostatic law, mass density | Pascal's law, weight density | b | According to Hydrostatic Law, the rate of increase of pressure in a vertical direction is equal to the weight density of the fluid at that point when the fluid is stationary. The pressure at any point in a fluid at rest is obtained by the Hydrostatic Law which states that the rate of increase of pressure in a vertically downward direction must be equal to the specific weight of the fluid at that point. |
Comments | Active | |
| 92 | The first law of thermodynamics is based on | Joule's law | The principle of conservation of mass | The principle of conservation of energy | Zeroth law of thermodynamics | c | The first law of thermodynamics is based on the law of conservation of energy, which states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, but can be transferred from one form to another. | Comments | Active | |
| 93 | Equivalent evaporation is defined as the amount of water evaporated from | 0°C to wet and saturated steam at 100°C | 0°C to dry and saturated steam at 100°C | 100°C to wet and saturated steam at 100°C | 100°C to dry and saturated steam at 100°C | d | Equivalent evaporation is the quantity of water evaporated from water at 100°C to dry saturated steam at 100°C under standard atmospheric pressure (1.01325 bar). It is used as a standard basis to compare the performance of boilers.†| Comments | Active | |
| 94 | A flywheel is used to control___. | Variation in power during each cycle of an engine | Variation of power of a punching press | Variation in speed during each cycle of an engine | Variation of fuel supply of an engine during running | c | A flywheel is used to control the speed variation caused by the fluctuations of energy during each cycle of operation. | Comments | Active | |
| 95 | In an air standard Diesel cycle the efficiency depends on: | Cut off ratio, compression ratio and ratio of specific heats | Cut off ratio only | Ratio of specific heats only | Pressure ratio only | a | Otto cycle/Brayton cycle: \(η_{otto}=1-\frac{1}{r^{γ-1}}\) Diesel cycle: \(η_{diesel}=1-\frac{1}{r^{γ-1}} \frac{Ï^{γ}-1}{γ(Ï-1)}\) Where r = compression ratio, α = pressure ratio and Ï = cut – off ratio. Thus, it can be seen that the efficiency of diesel cycle depends upon compression ratio and cut off ratio both. |
Comments | Active | |
| 96 | Knocking takes place in compression ignition engine____. | At the start of the combustion | At the end of the combustion | During combustion | At the start as well as the end of the combustion | a | The ignition delay or delay period in a diesel engine is defined as the time interval between the start of injection and the start of combustion. The pressure reached during the second stage of combustion is dependent on the duration of the delay period. More delay leads to more increase in pressure and leads to knocking. Hence, shorter ignition delays are preferred. Difference in the knocking phenomenon of the SI and CI engine. In SI engines, detonation occurs near the end of combustion whereas, in CI engines, detonation occurs near the beginning of combustion. The detonation in SI engines of a homogeneous charge cause a very high rate of pressure rise and very high maximum pressure. In the CI engine, the fuel and air are imperfectly mixed and hence the rate of pressure rise is normally lower than that in the detonating part of the charge in the SI engine. In the CI engine, the fuel is injected into the cylinder only at the end of the compression stroke, there is no question of pre – ignition as in SI engine. The rate of pressure rise in diesel knock is lower than in detonation in SI engines. \((P_{max})_{CI}=1.3 to 1.4×(P_{max})_{SI}\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 97 | If the density of the fluid does NOT vary during the flow, then the fluid is said to be: | Non-uniform | Uniform | Compressible | Incompressible | d | Compressible flow: The flow in which the density of the fluid changes from point to point or the density is not constant for the fluid. Mathematically, for compressible flow \(Ï≠Constant\) Incompressible flow: The flow in which the density is constant for the fluid flow. Liquids are generally incompressible and gases are compressible. Mathematically, for Incompressible flow \(Ï=Constant \) |
Comments | Active | |
| 98 | The function of a steam trap is, | To automatically drain away the superheated steam from the steam pipes, steam jackets | To automatically collect condensed steam from the steam pipes, steam jackets without permitting it to escape | To automatically drain away the saturated steam from the steam pipes, steam jackets | To automatically drain away the condensed steam from the steam pipes, steam jackets without permitting it to escape | d | A Steam Trap is an automatic drain valve which distinguishes between steam and condensate. A steam trap holds back steam & discharges condensate under varying pressures or loads. | Comments | Active | |
| 99 | If water is flowing through a circular pipe of diameter d (in m) and has a velocity of V (in m/s), the quantity of water (in litres per sec) is given by | V litres/second \(\frac{π}{4}d^{2}\) | V*1000 litres/second \(\frac{π}{4}d^{2}\) | V*100 litres/second \(\frac{π}{4}d^{2}\) | V*10 litres/second \(\frac{π}{4}d^{2}\) | b | Diameter = d m, Velocity = V (in m/s), the quantity of water (in litres per sec) is given by_____. \(∵1 m^{3}=1000 liters\) \(Q=(π/4)×d^{2}×V m^{3}/s\) \(Q=(π/4)×d^{2}×V ×1000 liters/second\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 100 | The mathematical expression for centre of pressure when the surface is inclined and immersed in the liquid is given by. | = \(h\) \(\frac{I_{G}sin^{2}Xθ}{Ax}+2X\) | = \(h\) \(\frac{I_{G}sin^{2}θ}{2Ax}+X\) | = \(h\) \(\frac{I_{G}sin^{2}θ}{Ax}+X\) | = \(h\) \(\frac{I_{G} sinθ}{Ax}=X\) | c | \(h^{*}=\frac{I_{G}sin^{2}θ}{Ah}+h\) For vertical plane surface: \(θ=90°\) \(h^{*}=\frac{I_{G}}{Ah}+h\) |
Comments | Active |










