| S.No | Question | Option A | Option B | Option C | Option D | Answer | Solution | Comments | Status | Action |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Density of an ideal fluid is always__________. | Zero | Constant | Increasing | Decreasing | b | Ideal fluid: A fluid, which is incompressible and is having no viscosity, is known as an ideal fluid. • Ideal fluid is only an imaginary fluid as all the fluids, which exist, have some viscosity. •Hence a fluid which has constant density and zero viscosity is known as an ideal fluid • Ideal fluid obeys the following two equations • Continuity equation • Bernoulli’s equation |
Comments | Active | |
| 2 | Which of the following devices is NOT used to measure flow rate or velocity of fluid? | Piezometer | Current and turbine meter | Wire anemometer | Pitot tube | a | Measures: Pressure head (specifically static pressure) in a fluid. Function: It's a simple vertical tube inserted into a pipe or vessel that shows the height to which a fluid will rise. Limitation: It cannot measure velocity or flow rate of fluid. |
Comments | Active | |
| 3 | Which type of pump is commonly used nowadays to force water into the boiler? | Centrifugal pump | Rotary pump | Duplex pump | Single-stage reciprocating pump | a | To force the water into the boiler, the pump must generate sufficient pressure to overcome the steam pressure developed by the boiler. This is usually accomplished through the use of a centrifugal pump. | Comments | Active | |
| 4 | ________is a gas-power cycle which consists of two isothermals connected by two constant volume processes. | Ericsson cycle | Brayton cycle | Stirling cycle | Atkinson cycle | c | The Ericsson cycle consists of two isothermal and two constant pressure processes While the Stirling cycle consists of two isothermal and two constant volume processes. 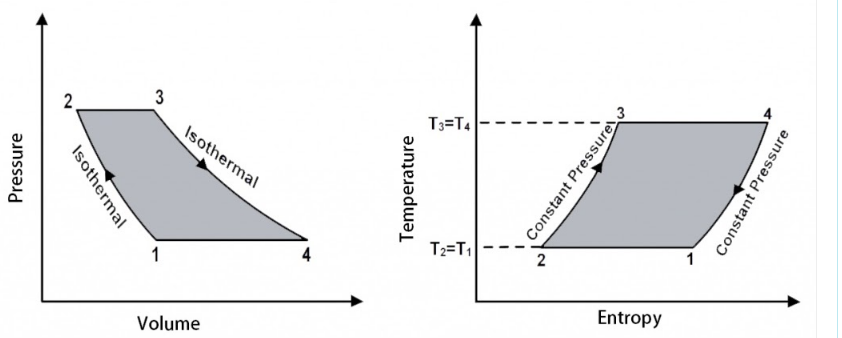 |
Comments | Active | |
| 5 | Which of the following is NOT applicable to fire-tube locomotive boilers? | They are externally fired | They are mobile in nature | They are multi-tubular | They are placed horizontally | a | A locomotive boiler is a multi-tubular, horizontal, internally fired, and mobile boiler. It consists of a shell or barrel having 1.5 m diameters and 4 m in length. | Comments | Active | |
| 6 | U type of configuration is possible in_________for pressure measurement. | Bourdon tube | Pirani gauge | Orifice meter | Manometer | d | Manometers are devices in which columns of a suitable liquid are used to measure the difference in pressure between two points or between a certain point and the atmosphere. • A manometer is needed for measuring large gauge pressures. It is basically the modified form of the piezo metric tube. •A common type of manometer is like a transparent "U-tube" as shown in Figure: 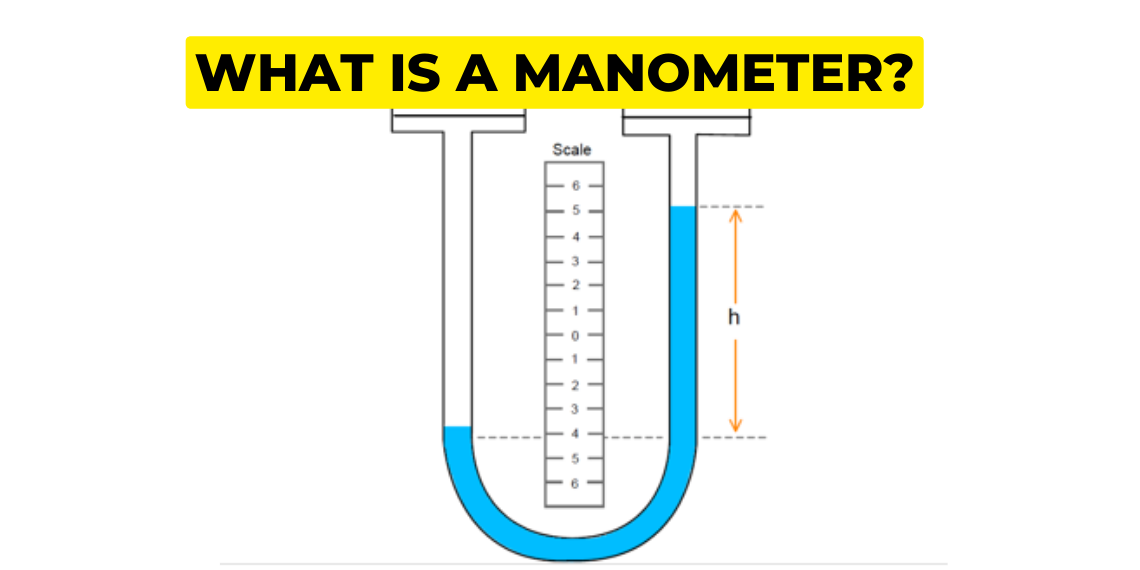 |
Comments | Active | |
| 7 | The degree of reaction of a turbine is defined as the ratio of ______drop to total energy transfer. | Kinetic energy | Dynamic energy | Static pressure | Velocity energy | c |  Degree of reaction or reaction ratio (R) is defined as the ratio of the static pressure drop/increase in the rotor (moving blade) to the static pressure drop/increase in the stage (both fixed blade and moving blade) or as the ratio of static enthalpy drop in the rotor to the static enthalpy drop in the stage. | Comments | Active | |
| 8 | Over a flat plate, thickness of turbulent boundary layer at a distance x from leading edge is________ | X2/5 | X3/4 | X4/5 | X5/4 | c | The Turbulent boundary layer for flat plate given by For turbulent flow \(5×10^{5} \(δ=x^{1-\frac{1}{5}}\) \(δ=x^{\frac{4}{5}}\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 9 | The_______part of the vapour compression cycle produces refrigeration effect. | Throttle valve | Condenser | Evaporator | Compressor | c | Evaporator or chiller or freezer: The refrigerant at very low pressure and temperature enters the evaporator or the freezer. • It is the coldest part of the refrigerator. • The refrigerant absorbs the heat from the substance to be cooled in the evaporator, gets evaporated and is then sucked by the compressor. |
Comments | Active | |
| 10 | Which of the following processes generally does NOT occur during the heat treatment of steels? | Grain growth | Recovery | Rework | Recrystallisation | c | Recovery: Takes place during the early stages of annealing. It reduces dislocations and internal stresses without major changes in the grain structure. Recrystallization: New grains form without pre-existing stresses, restoring ductility after cold working. Grain growth: Occurs when steel is heated to high temperatures — grains become larger, which can reduce strength and toughness. |
Comments | Active | |
| 11 | Which of the following instruments is used for measuring ultra-high vacuum? | McLeod gauge | Cathode ray oscilloscope | Manometer | Bourdon tube | a | The McLeod gauge is a device used to measure very low pressures (high vacuum) — typically in the range of 10â»Â² to 10â»â¶ mm of Hg. | Comments | Active | |
| 12 | A car has a four-stroke in-line diesel engine whose compression ratio is 21: 1 and expansion ratio is 10: 1. What is the cut off ratio? | 2.8 | 3.2 | 210 | 2.1 | d | ∴ \( r_{c}×r_{e}=r\) \(r=21, r_{e}=10, r_{c}=?\) We know that, \(r_{c}×r_{e}=r\) \(r_{c}×10=21\) \(r_{c}=2.1\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 13 | ________boiler involves circulation of water by natural convention. | LaMont | Velox | Babcock-Wilcox | Benson | c | Babcock-Wilcox boiler: A continuous circulation of water from the drum to the water tubes and water tubes to the drum is maintained. The circulation of water is maintained by convective currents and is known as “natural circulationâ€. | Comments | Active | |
| 14 | Expansion of steam in Rankine cycle is assumed to be_______. | Isentropic | Hyperbolic | Polytropic | Isothermal | a | Rankine cycle is a reversible cycle which has two constant pressure and two isentropic processes. There are four processes in the Rankine cycle: Process 1 - 2: isentropic compressionWorking fluid is pumped from low to high pressure. Process 2 - 3: Isobaric heat additionthe high-pressure liquid enters a boiler where it is heated at constant pressure by an external heat source to become a dry saturated vapour. Process 3 - 4: isentropic expansionthe dry saturated vapour expands through a turbine, generating power. Process 4 - 1: Isobaric heat rejectionthe wet vapour then enters a condenser where it is condensed at constant pressure and temperature to become a saturated liquid. |
Comments | Active | |
| 15 | Oil spreads on the surface of water because_________. | Oil is lighter than water | Oil is heavier than water | Of surface tension effect | Oil has low vapour pressure | c | Surface tension: It is defined as the tensile force acting on the surface of a liquid in contact with a gas or on the surface between two immiscible liquids such that the surface under contact behaves like a membrane under tension. • Its unit in the SI system is N/m and in MKS it is kgf/m. The uncommon unit it has is J/m2 Mathematically it is given as \(σ=\frac{F}{L}\) The surface tension of the water is more than that of oil. Therefore, when oil is poured over water, the greater value of surface tension of water pulls oil in all directions, and as such it spreads on the water |
Comments | Active | |
| 16 | Cylinder and piston type flow meters are of_______type. | Variable area variable head | Variable head | Positive displacement | Variable area | c | Positive displacement flow meters: • These types of flow meters measure the volume filled with fluid, deliver it ahead and fill it again, which calculates the amount of fluid transferred. • It measures the actual flow of any fluid while all other types of flow meters measure some other parameter and convert the values into flow rate. • The output is directly related to the volume passing through the flow meter. • Positive displacement flow meters include cylinder-piston meters, oval- gear meters, mutating disk meters, rotary vane-type meters, etc. |
Comments | Active | |
| 17 | Due to the turbidity of the water in boiler feed water,_______is caused | Corrosion | Cracking | Embrittlement | Sludge | d | Less turbidity indicates clean water and high turbidity indicates contaminated water. Contaminated water contains suspended insoluble particles like mud, sand, sediments, etc. and during boiler operation, it settles down in the boiler which is called sludge. Turbidity ⇒ Suspended solids ⇒ Sludge |
Comments | Active | |
| 18 | The degrees of freedom for a pure substance at the triple point is | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | d | Gibbs phase rule P+F=C+2, Where P = No. of phase, C=No. of components, F=Degree of freedom At Triple point P=3, C=1 P+F=C+2 3+F=1+2, F=0 |
Comments | Active | |
| 19 | _________gives an idea about the pressure in a static fluid | Pascal's law | Grashof's law | Weber's law | Newton's law | a | According to Pascal's Law, the pressure or intensity of pressure at a point in a static fluid is equal in all directions. This law is valid for the cases of fluid flow where shear stresses do not exist. The cases are • Fluid at rest • No relative motion exists between different fluid layers. For example, fluid at a constant linear acceleration in a container • Ideal fluid flow where viscous force is negligible. \(P=Ïgh\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 20 | The triple point of water is at_______mm of Hg. | 3.28 | 2.58 | 3.35 | 4.58 | d | The temperature and pressure at which a substance can exist in equilibrium in the liquid, solid, and gaseous states. The triple point of pure water is at 0.01 °C (273.16K) and 4.58 mm (611.2Pa) of mercury and is used to calibrate thermometers. | Comments | Active | |
| 21 | What is the use of a Hermetic sealed compressor? | It is used to supply air at low pressure in high volume applications such as air curtains. | It is used to supply air at constant low volume in high pressure applications such as in industrial operations. | It is used in aircraft engines to supply air to the cabin. | It is used in domestic refrigerators to prevent leakages of refrigerant. | d | A hermetic or sealed compressor is one in which both compressor and motor are confined in a single outer welded steel shell. The motor and compressor are directly coupled on the same shaft, with the motor inside the refrigeration circuit. Thus, hermetically sealed compressors and motor don't require the shaft seal and there is no problem of refrigerant leakage. Hermetically sealed compressors cannot be serviced due to being contained within the welded unit. | Comments | Active | |
| 22 | Lancashire boiler can also be classified as a________pass boiler. | Two | Three | Four | One | b | Lancashire boiler: It is a stationary fire tube type, internally fired, horizontal, and natural circulation boiler having two flue tubes and three passes. The maximum working pressure in a Lancashire boiler is 16 bar. | Comments | Active | |
| 23 | For a circular shaft under torsion, shear stress values at the centre of the shaft is | Maximum | Zero | Unity | Minimum | b | \(\frac{T}{J}=\frac{Ï„}{r}=\frac{Gθ}{l}=Ï„âˆr\) Hence the maximum shear stress occurs on the outer surface of the shaft where r = R and at the center the shear stress is zero. |
Comments | Active | |
| 24 | Shear stress for a fluid at rest is | Negative | Unpredictable | Positive | Zero | d | • A solid can resist shear stress by a static deformation; a fluid cannot resist. • Any shear stress applied to a fluid, no matter how small, will result in the motion of that fluid • The fluid moves and deforms continuously as long as the shear stress is applied • So, a fluid at rest must be in a state of zero shear stress |
Comments | Active | |
| 25 | If the back pressure is low enough and the throat is sonic, the Mach number is more than 1 in a/an______section during flow in a convergent-divergent nozzle. | Converging | Throat | Entry | Diverging | d | Mach number is less than 1(M<1) for converging section, M= 1 for throat and Mach number is greater than (M>1) for diverging section. | Comments | Active | |
| 26 | A water cooling system consists of a fan used to draw | Coolant | Water from the pump | Air through the radiator | Lubrication oil | c |  A water cooling system consists of a fan used to draw the air through the radiator. Provide drive to the water pump. Cool the engine by blowing air over it. | Comments | Active | |
| 27 | The Pressure-Volume diagram of an ideal reciprocating air compressor consists of ______Isobaric,______adiabatic and_____constant volume processes. | Two, two, zero | One, two, two | One, two, one | Two, one, one | d | You can see the process in the below diagram consists of 2 isobaric process, 1 adiabatic and 1 isochoric process.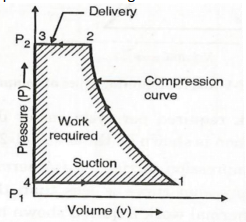 |
Comments | Active | |
| 28 | The steam expansion process in a nozzle can be approximated as a process. | Free expansion | Throttling | Adiabatic | polytropic | c | No heat is supplied or rejected by the steam during flow through a nozzle. Therefore it is considered as an adiabatic flow, and the corresponding expansion is considered as an adiabatic expansion. | Comments | Active | |
| 29 | __________Irreversibility is due to the friction in the system. | Chemical | Frictional | Rotary | Internal | d | Internal irreversibility: Irreversibility caused by properties of the working fluid in a process like throttling or free expansion, friction within the system etc. When a gas expands, it uses its internal energy to do so. | Comments | Active | |
| 30 | Which of the following forces does NOT act on fluid which is at rest? | Surface tension | Gravity | Viscous | Hydrostatic | c | Static fluid: Static fluid, fluid at rest has no shear stress. • Consequently, any force developed is only due to normal stresses i.e., pressure. • The fluid is to be at rest if there is no relative movement between the adjacent particles of the fluid i.e. no shear stress is acting on the fluid. • Hence, the viscous force is inconsiderable in this case. • However, fluid particles are always acted upon by external pressure and their own self-weight. • Surface tension acts only for fluid at rest condition. |
Comments | Active | |
| 31 | In a laminar flow_______ can be applied | Fresnel law | Newton's law of viscosity | Snell's law | Grashof's law | b | Reynolds number is given by \(Re=\frac{Ï×V×D}{μ}\) Where, = Density of fluid, V = velocity of fluid, D = Diameter of pipe, µ = Dynamic viscosity of the fluid \(Ï\) In the case of pipe flow, • If Re≤ 2000 then flow is laminar • 2000 ≤ Re≤ 4000 then flow is transitional • Re≥ 4000 then flow is turbulent From the formula, Re V \(âˆ\) Re 1/μ \(âˆ\) The dynamic viscosity is obtained by Newton's law of viscosity i.e., thus, \(μ=\frac{Ï„}{\frac{du}{dy}}\) Newton's law of viscosity is of importance for calculating Reynold's number i.e. for Laminar flow. |
Comments | Active | |
| 32 | ____property is stated by first law of thermodynamics. | Pressure | Temperature | Entropy | Internal energy | d | The equation for the first law of thermodynamics is given as where, \(∂Q=∆U+ ∂W \) ΔU = Change in internal energy of the system = Algebraic sum of heat transfer between system and surroundings \(∂Q\) = Work interaction of the system with its surroundings \(∂W\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 33 | __________is closely related to working of hydraulic turbines. | Newton's second law | Bragg's law | Faraday's law | Charles' law | a | The hydraulic turbine works on the principle of Newton's second law of motion. The hydraulic turbine blades are moved against the flow of water, causing the water's momentum to vary. As the momentum changes, a pressure force is created, which causes the turbine to rotate. | Comments | Active | |
| 34 | Which of the following cycles incorporates two isothermal processes? | Diesel cycle | Otto cycle | Dual cycle | Carnot cycle | d | The Carnot cycle consists of 4 processes 1 – 2 Isothermal heat addition 2 – 3 reversible adiabatic expansion 3 – 4 isothermal heat rejection 4 – 1 reversible adiabatic compression A cycle is said to be reversible only when each process in a cycle is reversible. The Carnot cycle consist of 2 isothermal and 2 adiabatic processes. An isothermal process is a very slow process and the adiabatic process is a very fast process and the combination of a slow process and fast process are very difficult. So a Carnot cycle is also known as an impractical cycle. It is used only to compare other actual cycle. |
Comments | Active | |
| 35 | Heat rejection in vapour absorption refrigerator occurs in: | Absorber only | Condenser and absorber | Generator only | Condenser only | b | Heat is added at the high-pressure generator from a gas burner, steam, hot water or hot gases The added heat causes the refrigerant to desorb from the absorbent and vaporize The vapours flow to a condenser, where heat is rejected and condense to a high-pressure liquid The liquid is then throttled through an expansion valve to the lower pressure in the evaporator where it evaporates by absorbing heat and provides useful cooling The remaining liquid absorbent, in the generator, passes through a valve, where its pressure is reduced, and then is recombined with the low-pressure refrigerant vapours returning from the evaporator so the cycle can be repeated |
Comments | Active | |
| 36 | If suction compression and delivery of the air takes place on one side of the piston only then the compressor is known as: | Single acting | Double acting | Single stage | Multistage | a | Single-acting compressor: Suction, compression, and delivery of the air take place on one side of the piston only in the single-acting compressor. | Comments | Active | |
| 37 | _______is a type of anti-frictional bearing. | Needle bearing | Hydrostatic bearing | Collar bearing | Pedestal bearing | a | • The antifriction bearing consists of rolling elements, races, and cage. • Rolling elements are available in different shapes such as balls, parallel rollers, taper rollers, barrels, and needles. • They are made of chromium or chrome-nickel steel with ground or polished surface. • The load of the rotating member is carried by the rolling elements. • Example: Ball bearing, Roller bearings, Needle bearing |
Comments | Active | |
| 38 | The increase in entropy of a system represents ______of energy. | Degradation | Up gradation | Generation | Preservation | a | Entropy is a measure of the energy of a system that is unavailable for doing useful work. Increase in entropy of a system leads to increase in randomness and degradation of energy. Since entropy is a point function that depends only on states i.e. independent of the path followed. |
Comments | Active | |
| 39 | An increase in the efficiency of Rankine cycle can be expected with _____. | Increase in temperature of heat rejection | Decrease in exhaust pressure | Increase in exhaust pressure | Decrease in temperature of heat addition | b | On Decreasing the condenser pressure: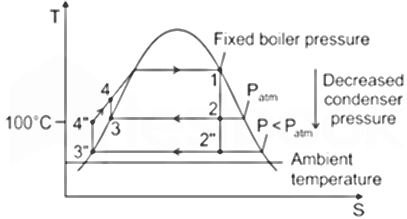 Lowering the condenser pressure will increase the area enclosed by the cycle on a T-S diagram which indicates that the net-work will increase. Thus, the thermal efficiency of the cycle will be increased. |
Comments | Active | |
| 40 | Mitre gears are generally used for _____. | Minimum axial thrust | Speed reduction | Minimum backlash | Change in direction without effecting speed | d | Mitre Gears are paired together and used to change the direction of power transmission.They are primarily used to change the direction of the shaft rotation by 90 degrees without changing the speed or torque. | Comments | Active | |
| 41 | _______technique uses wear particles analysis using lubricating oil for predicting the impending failures of machine components. | Ferrography | Waveform analysis | Envelope analysis | Spectrography | a | Ferrography: It is a technique for isolating wear particle debris from lubricating and hydraulic oils, the presence of which carry with them a history of the wear processes in the machine. • Thus, the technique has fundamental application in machine condition monitoring and failure prevention. • The wear particles are significant in the metal type that are present in the particle distribution as an indication of the wearing machine components and in the particle size distribution and morphology which indicated the severity of wear in the system. |
Comments | Active | |
| 42 | In a vapour compression cycle, the refrigerant exists in a superheated vapour state _______. | After leaving the evaporator | After passing through the condenser | At the exit of the compressor | After leaving the expansion valve | c | In refrigeration cycle, the vapors leaving the evaporator are in saturated vapor state. These vapors are compressed in the compressor and their temperature and pressure increases. These vapors are in the superheated state at the exit of compressor or at the entrance of condenser. | Comments | Active | |
| 43 | Which of the following statements about a principal plane is true? | No shear stress is present | It has maximum shear stress | It has no normal stress. | Shear stress can have any value. | a | 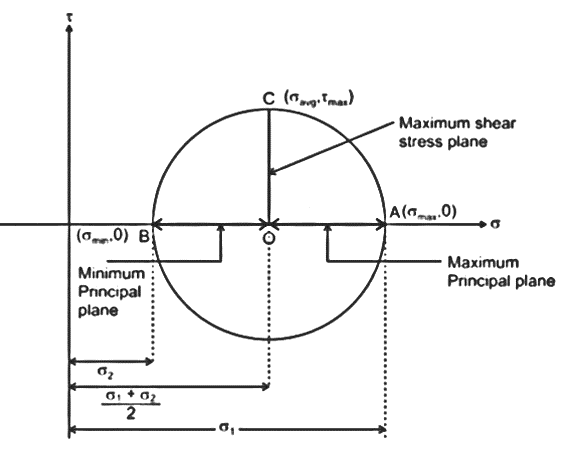 On principal plane shear stress will be zero. |
Comments | Active | |
| 44 | Which of the following factors does NOT affect the buckling load? | Slenderness ratio | Area of cross-section | Modulus of elasticity | Area moment of inertia | b | P=, where, slenderness ratio=l/k, E=modulus of elasticity, I=area moment of inertia \(\frac{Ï€^{2}EI}{L^{2}}\) | Comments | Active | |
| 45 | The process of cooling the refrigerant in vapor compression refrigeration system, known as sub – cooling is done before: | Evaporation | Condensation | Compression | Throttling | d | Subcooling is the process of cooling the liquid refrigerant below the condensing temperature for a given pressure. The difference between the saturation temperature and the temperature of the subcooled liquid at that pressure is called the Degree of subcooling. | Comments | Active | |
| 46 | ________use air refrigeration cycle. | Commercial refrigeration | Cryogenic chambers | Aircraft air-conditioning system | Gas chambers | c | Air refrigeration: Air refrigeration systems belong to the class of gas cycle refrigeration systems, in which a gas is used as the working fluid • The air refrigeration system works on the Joule cycle or reverse Brayton cycle or Bell-Coleman Cycle. |
Comments | Active | |
| 47 | Single – stage piston compressors are used to compress air up to pressure of approximately _______bar. | 50 | 5 | 150 | 100 | b | The pressure range of the Reciprocating Compressor. Number of Stages Maximum discharge Pressure Single-stage Up to 5.6 bar Double Stage 5.6 -35 bar Triple Stage 180 bar |
Comments | Active | |
| 48 | For a given system, if heat is denoted by ‘Q’ and work is denoted by ‘w’, the cyclic integral of (dQ – dw) for a closed system will be: | Positive | Negative | Zero | Unpredictable | c | The first law of thermodynamics states that for a cyclic process, the cyclic integral of heat is equal to the cyclic integral of work. | Comments | Active | |
| 49 | Which of the following is NOT a type of safety valve used for boilers? | Sliding type | Spring type | Lever type | Dead- Weight type | a | Safety valves: The function is to release the excess steam when the pressure of steam inside the boiler exceeds the rated pressure. Types of safety valves: • Deadweight safety valve • Lever safety valve • Spring-loaded safety valve • High steam and low water safety valve. |
Comments | Active | |
| 50 | The approximate percentage of carbon in bituminous coal used as a fuel for boiler is _____. | 40 – 50% | 10 – 20% | 20 – 30% | 65 – 80% | d | Bituminous Coal: This is the most widely used coal and contains 50 to 85 per cent carbon. It is dense, compact, and brittle and is usually black in colour. Good bituminous coal is composed of alternate dull and bright bands. Its calorific value is very high due to the high proportion of carbon and low moisture content. | Comments | Active | |
| 51 | While classifying the boilers into fire-tube and water tube, mark out the odd one out of the options given below. | Lancashire boiler | Locomotive boiler | Cochran boiler | Stirling boiler | d | Stirling boiler is a water tube boiler while Lancashire boiler, Locomotive boiler and Cochran boiler are fire tube boiler. | Comments | Active | |
| 52 | Hardness is induced within the gear teeth to avoid ______. | Abrasion | Pitting | Meshing | Wear | d | Hardness is a commonly used property; it gives a general indication of the strength of the material and of its resistance to scratching and to wear. Hardness is usually defined as resistance to permanent indentation. Hardness, however, is not a fundamental property, because the resistance to indentation depends on the shape of the indenter and on the load applied. | Comments | Active | |
| 53 | ____________process induces compressive residual stresses on a component to nullify the tensile residual stresses with in a steel structure. | Heat treatment | Shot peening | Brazing | Welding | b | Shot peening: It is a cold work process used to finish metal parts to prevent fatigue and stress corrosion failures and prolong product life for the part. • In shot peening, a small spherical shot bombards the surface of the part to be finished. • The shot acts like a peen hammer, dimpling the surface and causing compression stresses under the dimple and nullify the residual stress with in the component. • The surface compression stress strengthens the metal, ensuring that the finished part will resist fatigue failures, corrosion fatigue and cracking, and galling and erosion from cavitation. |
Comments | Active | |
| 54 | ____________involves breaking of fuel into fine particles. | Mixing of fuel and air | Air supply at increased pressure | Fine atomization of fuel | Excess supply of air | c | During the combustion process of fuel when the liquid fuel breaks down into tiny droplets or fine particles then the process is called atomization. Atomization is the process of converting bulk liquid into fine droplets. The basic requirement in the various combustion application such as gas turbines, ramjets, liquid rocket engines, etc. is efficient atomization by the particular atomizer. Coaxial atomization may be generally divided into five unique physical regimes – 1. Turbulent liquid core 2. Primary atomization (liquid/gas interface) 3. Thick spray (turbulent droplet dispersion) 4. Thin spray (turbulent droplet dispersion) 5. Gas flow region (Operational condition) |
Comments | Active | |
| 55 | Flooding of a river is an example of ________flow. | Steady and uniform | Unsteady and non-uniform | Steady and non-uniform | Unsteady and uniform | b | Flooding occurs when there are excessive stream discharge and water spills of the channel onto the adjacent flood plain in all the direction. The flooding of the river is an example of unsteady and non-uniform flow. There are many different types of flow and are classified as below: 1. Steady flow: it is defined as a type of flow in which the fluid characteristics like velocity (V), pressure (P), density (), etc. at a point do not change with time. \(Ï\) Steady flow is mathematically represented as \((\frac{∂V}{∂t})_{x_{0,}y_{0,}z_{0}}=0(\frac{∂P}{∂t})_{x_{0},y_{0},z_{0}}=Ï(\frac{∂Ï}{∂t})_{x_{0},y_{0},z_{0}}=0\) 2. Unsteady flow: is defined as a type of flow in which velocity pressure or density at a point changes with respect to time. 3. Uniform flow: is defined as a type of flow in which velocity at any given time does not change with respect to space (i.e., length of direction of the flow) • Uniform flow: is mathematically represented as = constant = 0 \((\frac{∂V}{∂s})_{t}\) Change of velocity, Length of flow in the direction s \(∂V=\) \(∂s=\) 4. Non uniform flow: is a type of flow in which velocity at any given time changes with respect to space. |
Comments | Active | |
| 56 | The phase where any substance loses the distinction between liquid and vapor is called _____. | Critical point | Ignition point | Dew point | Crystal point | a | The critical point is the temperature and pressure at which the distinction between liquid and gas can no longer be made. | Comments | Active | |
| 57 | For a simply supported beam, the bending moment at the support is _____kNm. | <1 | 1 | >1 | 0 | d | 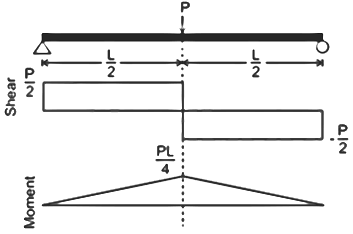 Bending moment will be zero at support and maximum where the shear force is zero. |
Comments | Active | |
| 58 | Specific energy is ________at critical depth for a given discharge in a channel. | Maximum | Zero | Unpredictable | Minimum | d | For a given value of specific energy, the critical depth gives the greatest discharge, or conversely, for a given discharge, the specific energy is a minimum for the critical depth. For rectangular channels, the critical depth, \(d_{c}(m), is given by\) \(d_{c}=(\frac{Q^{2}}{b^{2}g})^{\frac{1}{3}}\) Where \(d_{c}=critical depth (in m), Q=quantity of flow or discharge (in m^{3}/s), B=Width of channel (in m)\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 59 | Refrigerant exits as a high – pressure liquid from the _______in a vapour compression system. | Condenser | Compressor | Throttle valve | Evaporator | a | Condenser: In this device, the heat is rejected at constant pressure. The vapor refrigerant is converted into a liquid refrigerant. The maximum temperature of the cycle is at Condenser. | Comments | Active | |
| 60 | _______boiler has a unique characteristic of NOT having a steam separating drum. | Velox | Benson | LaMont | Loeffler | b | The Benson boiler employs forced circulation and has a unique characteristic of the absence of steam separating the drum. | Comments | Active | |
| 61 | Multi – stage centrifugal pumps are employed to obtain ______. | Pumping of viscous fluids | Higher discharge | Higher head and discharge | Higher head | d |  in a multi stage pump, more than one impeller is used on the same shaft and enclosed in the same casing. It is used to raise a high head or high pressure. | Comments | Active | |
| 62 | For a steam power plant, _________cycle is recommended | Otto | Brayton | Carnot | Rankine | d | The steam power stations run on Rankine cycles using steam as a working fluid. Brayton cycle is used for gas power plant. | Comments | Active | |
| 63 | ______is the presentation of the anti-knock value of diesel fuel. | Octane number | Cetane number | Diesel number | Fuel number | b | Cetane rating, also known as cetane number is a measurement of the quality or performance of diesel fuel. The higher the number, the better the fuel burns within the engine of a vehicle. The cetane number is similar to the Octane Rating in that it is a rating assigned to fuel to rate the quality of its combustion. The main difference between cetane and octane ratings is that the octane rating represents how will a fuel can resist pre – ignition due to compression ensuring the fuel ignites only from a spark from the spark plug. However, the cetane number measures the delay in the ignition time of the fuel. A higher cetane number resulting in quicker ignition of the fuel leads to less non – ignited fuels building up inside the combustion chamber, as well as more compete fuel combustion. Better fuel combustion and quick ignition lead to quicker starting for vehicles, as well as an engine that operates more quietly as only misted fuel is ignited and build – up inside the engine is minimized. Moreover, fuel efficiency improves with more complete combustion and harmful emissions are reduced. |
Comments | Active | |
| 64 | In a Li-Br water absorption cycle ______is used as a refrigerant | Air | Lithium – bromide | Ammonia | Water | d | In a Lithium Bromide (Li-Br) absorption refrigeration system, water acts as the refrigerant. Lithium bromide acts as the absorbent. | Comments | Active | |
| 65 | The vapour compression refrigeration cycle operates on reversed ______cycle. | Joule’s | Rankine | Atkinson | Ericsson | b | Vapour compression refrigerator works on vapour compression refrigeration cycle which is also called the Reverse Rankine cycle. | Comments | Active | |
| 66 | In hydraulic coupling slip is around ____for motors having low to moderate locked rotor torque. | 8 – 10% | 6 – 7% | 2 – 3% | 12 – 15% | c |  slip= \(\frac{ω_{1}-ω_{2}}{ω_{1}}\) Where \(ω_{1}=angular velocity of the driving shaft\) \(ω_{2}= angular velocity of the driven shaft\) The slip is generally very small about 3% at peak load Hydraulic coupling is defined as a device in which a fluid, usually oil, transmits torque from one shaft to another, producing an equal torque in the other shaft. |
Comments | Active | |
| 67 | Inside a boiler surface, scales are formed due to the presence of ____in the boiler feed water. | Insoluble compounds | Dissolved gases | Ca and Mg salts | Oils | c | The presence of calcium and magnesium salts is the main cause of scaling in boilers, along with high concentration of silica to the water alkalinity in the boiler. | Comments | Active | |
| 68 | Liquid enters the centrifugal pump ___. | From the bottom | From the top | Radially | From the centre | d | Â Liquid enters the centrifugal pump from the center.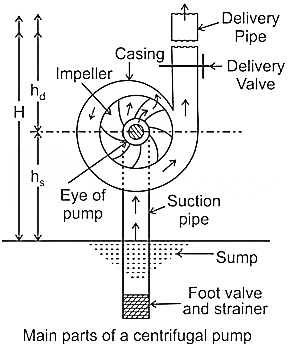 |
Comments | Active | |
| 69 | During the starting of a centrifugal pump, the delivery valve is _____. | Half – open | Fully open | Fully closed | Slightly open | c | The delivery valve connects the pump outlet and the delivery pipe. It remains closed before the pump is switched on. When the pump builds up its pressure, it is opened and can be used to control or vary the discharge. | Comments | Active | |
| 70 | _____occurs when vapour pressure is less than pressure above a liquid surface at a given temperature. | Gauging | Condensation | Freezing | Boiling | d | Boiling: The boiling point is the temperature at which a liquid boils and turns to vapor. In other words, the liquid state turns into a gaseous state. In a more scientific language, it is the temperature at which the pressure exerted by the surroundings upon a liquid is equaled by the pressure exerted by the vapor of the liquid or the vapor pressure drops below the pressure above the liquid surface. • The boiling point of the water at 1 bar pressure is 100°C. • If the pressure is decreased, the boiling point of the substance also decreases. •At high altitudes, water boils at low temperature because atmospheric pressure decreases with increase in altitude. Condensation: Condensation is the process by which water vapor in the air is changed into liquid water. Condensation is crucial to the water cycle because it is responsible for the formation of clouds. Condensation is the opposite of evaporation. Freezing: Freezing is the phase transition process where the liquid turns in to solid when the temperature is lowered below the freezing point temperature. • At normal atmospheric condition freezing point of water is 0 °C. |
Comments | Active | |
| 71 | Which of the following theories is best applied to brittle materials? | Minimum principle strain theory | Maximum principle stress theory | Maximum strain energy theory | Maximum shear stress theory | b | Maximum principal stress theory (Rankine's theory): According to this theory, the permanent set takes place under a state of complex stress, when the value of maximum principal stress is equal to that of yield point stress as found in a simple tensile test. For the design criterion, the maximum principal stress () must not exceed the working stress '' for the material. \(σ_{1}\) \(σ_{y}\) ≤ For no failure \(σ_{1,2} \) \(σ_{y}\) For design \(σ_{1 ,2}≤\frac{σ}{FOS}\) Note: For no shear failure τ ≤ 0.57 \(σ_{y}\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 72 | _________boiler is capable of generating a small quantity of steam per unit time at high pressure. | Lancashire | Locomotive | Scottish marine | Babcock – Wilcox | d | Babcock and Wilcox Boiler: It Is a water tube boiler means water is flowing inside the tubes and hot gases are outside the tubes. It is used when the pressure above 10 bar and capacity in excess of 7000 kg of steam per hour is required. Maximum Working pressure is 40 bar with a steam rate of 40000 kg/hr It consists of a drum connected to series of front end and rear end by short riser tubes to these headers connected a series of incline water tubes of solid drawn mild steel. |
Comments | Active | |
| 73 | An after – cooler provided in reciprocating compressors performs the function of _____ | Reducing temperature of compressed air | Removal of moisture from compressed air | Removal of impurities from compressed air | Reducing the volume of compressed air | a | The after-cooler is a heat exchanger intended to reduce the temperature of the hot air discharged from the compressor to approximately 15°C to 25°C above that of the ambient air. • Two basic types of after-coolers are air-cooled after-cooler and water- cooled after-cooler. • Air-cooled after-cooler uses the ambient air to cool the hot air discharged from the compressor. • In the water-cooled after-cooler, the hot compressed air is passed through the after-cooler tubes and cooling water is passed in the opposite direction through the after-cooler shell. |
Comments | Active | |
| 74 | Intake air filters are provided in compressors primarily to ________from the suction air. | Remove only dirt | Remove dirt and regulate the temperature | Remove dirt and moisture | Remove dirt as well as reduce the pressure | a | Filters remove atmospheric contaminants from the air at the intake to keep your compressed air system clean, and the air output pure. Cleaner machines work more efficiently, keep components from degrading and reduce the frequency of maintenance required. As filters do their jobs, they accrue particulars matter naturally, so they need to be cleaned and replaced regularly depending on the operating environment. It’s critically important to have the right filter for your particular application. Some applications will required specialized oil removing filters and other will require dust and pre – filters. |
Comments | Active | |
| 75 | Identify the position displacement type of flow meter from the following. | Oval gear type | Constant area variable head | Variable area variable head | Constant head variable area | a | Flow meter: A flow meter is simply defined as the device used to measure the speed at which a gas or liquid is moving through a pipe. Head type flowmeters based on differential pressure measurement: In these head type flowmeters, some devices are inserted into a pipe carrying fluid. It obstructs the flow of fluid and creates a pressure difference on either side of the device. The most commonly used devices are as follows: • Orifice plate • Venture plate • Flow nozzle • Doll flow tube • Pilot tube Positive displacement flow meters: These type of flow meters measure the volume filled with fluid, deliver it ahead and fill it again, which calculates the amount of fluid transferred. • It measures the actual flow of any fluid while all other types of flow meters measure some other parameter and convert the values into flowrate. • The output is directly related to the volume passing through the flow meter. • Positive displacement flow meters include cylinder-piston meters, oval-gear meters, mutating disk meters, rotary vane type meters, etc. Variable Area Meters: In variable meters, the area of restriction can be altered to maintain a steady pressure difference. • Common variable area meter is rotameter. • The float will rise to a point in the tube where the drag force (UP) and Buoyant force (UP) is balanced by the weight of the float. • The position of float in the tube is taken as an indication of flow rate. Variable head flow meters: The variable head meter is also called restriction type flow meter. • This results in the change in pressure and this pressure can be measured. • Venturi meter, Orifice Plate, Nozzle, Pitot tube |
Comments | Active | |
| 76 | The value of viscosity of an ideal fluid is ___________. | 0 | 1 | >1 | >2 | a | The relative motion between different layers of liquid or gases is opposed by a force, which is known as the Viscous force and this property is known as Viscosity. • SI unit of Viscosity is Decapoise (Kg/ms) or pascal second. • This is the property of liquids and gases both. • In the case of liquid, it is seen because of the cohesive force between the molecules of the liquid. • In case of a gas, it is seen because of the diffusion of its molecules from one layer to other layers. • The viscosity of gases is very less than that of liquids. • No viscosity is there in solids. • Viscosity of an ideal fluid is always zero. • The viscosity of liquids decreases with the rise in temperature. • The viscosity of gases increases with the rise in temperature. |
Comments | Active | |
| 77 | Thermometer comes into operation at temperature of about _____in automobile water cooling systems. | 80ᵒC | 40ᵒC | 60ᵒC | 20ᵒC | a | In automobile water cooling systems, a thermostat (not thermometer) is a key component that controls the flow of coolant based on engine temperature. The thermostat valve stays closed when the engine is cold to allow it to warm up quickly. It opens at a preset temperature, typically around 80°C to 85°C, allowing coolant to circulate through the radiator to prevent overheating. |
Comments | Active | |
| 78 | For an isolated system, which of the following holds true? | Mass and energy both cross the boundaries | Only mass crosses the boundary | Mass or energy does not cross the boundaries | Only energy crosses the boundary | c | Isolated System Characteristics: No mass transfer across the system boundary No energy transfer (neither heat nor work) The system is completely self-contained. E.g. Imagine a perfect thermos flask that doesn’t allow any heat to enter or escape, and also has no mass exchange. That’s a theoretical isolated system. |
Comments | Active | |
| 79 | Which of the following processes reduces the residual stresses within a steel structure? | Cold forming | Welding | Hot forming | Heat treatment | d | Stress relieving is a heat treatment process where the steel is heated to a sub-critical temperature (typically 550°C to 650°C) and held there for a period, then cooled slowly. This process reduces internal stresses without significantly altering mechanical properties or causing phase transformation. |
Comments | Active | |
| 80 | _______thermodynamic property remains constant in a throttling process. | Entropy | Specific energy | Energy | Enthalpy | d | In a throttling process (also known as isenthalpic expansion), a fluid flows through a restriction (like a valve, porous plug, or capillary tube) and undergoes a sudden drop in pressure without any heat or work interaction. | Comments | Active | |
| 81 | When fluid is flowing through a duct, the local velocity at a point can be measured by a _______. | Pitot – static tube | Flow nozzle | Current meter | Vane anemometer | a | Pitot Tube is a device used for measuring the velocity of flow at any point in a pipe or a channel. • It is based on the principle that if the velocity of flow at a point becomes zero, the pressure there is increased due to the conversion of the kinetic energy into pressure energy. |
Comments | Active | |
| 82 | ____________process is NOT involved in Rankine cycle. | Isentropic expansion | Isentropic compression | Constant volume heat addition | Constant pressure heat addition | c | Process are involved in Rankine cycle: Isentropic compression in a pump. The working fluid is pushed from low to high pressure in this chamber. Heat addition at constant pressure in the boiler. Isentropic expansion in a turbine. Heat rejection under constant pressure in a condenser. |
Comments | Active | |
| 83 | Which of the following metal contains chromium as its major alloying element? | Stainless steel | Carbon steels | Titanium | Copper | a | Steel (Carbon steel) is composed of Iron and carbon, which is the main component of stainless steel. Stainless steel differs from carbon steel by the amount of chromium present, which is added to make it resistant to rust. Stainless steel, also known as inoxidised steel, and a minimum of 10.5% chromium. Stainless steel is notable for its corrosion resistance, and it is widely used for food handling and cutlery among many other applications. NOTE: An alloy is a substance made by melting two or more elements together, at least one of the metal. Name of the alloy Made up of Brass Copper and Zinc Bronze Copper and Tin Stainless steel Iron, chromium, Nickle, Carbon German Silver Copper, Zinc, and Nickle Nickel Steel Iron and Nickel |
Comments | Active | |
| 84 | The refrigerator reaches its higher temperature when the vapourleaves the _______ in a refrigeration system based on vapour compression. | Condenser | Throttle valve | Compressor | Evaporator | c | In a vapour compression refrigeration system refrigerant enters in a liquid state in the evaporator and it absorbs heat then becomes vapour than with the help of compressor and condenser vapour refrigerant comes back to a liquid state. The vapour-compression cycle is a process used to extract heat from a box or a room that underlies most refrigeration and air conditioning techniques. In Compressor, the temperature of the refrigerant increases at constant entropy. It shows work input to the refrigerator. The higher temperature in vapour compression cycle occurs at Compressor discharge. |
Comments | Active | |
| 85 | ________CANNOT be counted as a boiler mounting. | Feed water pump | Stop valve | Fusible plug | Blow-off cock | a | Accessories include the components which are installed to increase the efficiency of the steam power plants and help in the powerful working of the boiler unit. These fitting are called boiler accessories. The accessories are given below. • Air pre-heater • Economizer • Superheater • Injector • Feed water pump |
Comments | Active | |
| 86 | Milk, blood and clay are example of _____fluid | Newtonian | Ideal | Pseudo-plastic | Perfect | c | Pseudoplatsic: Fine particle suspension, gelatine, clay, blood, milk, paper pulp, polymeric solutions such as rubbers, paints. Dilatant fluids: Ultrafine irregular particle suspension, sugar in water, aqueous suspension of rice starch, quicksand, butter printing ink. Ideal plastics or Bingham plastic fluids: Sewage sludge, drilling muds, toothpaste. Thixotropic: Printer's ink, crude oil, lipstick, certain paints and enamels |
Comments | Active | |
| 87 | While running through a bend a bicycle remains stable due to _____. | Curvature action | Centrifugal action | Reaction action | Gyroscopic action | d | Centripetal force is that force that is required to move a body in a circular path with uniform speed. The force acts on the body along the radius and towards the centre. • Centrifugal force is the apparent force that is felt by an object moving in a curved path. This force acts outwardly away from the center of rotation. Turning a Bicycle: A bicycle held straight up will tend to go straight. It is tempting to say that it stabilized by the gyroscopic action of the bicycle wheels, but the gyroscopic action is quite small. • If the rider leans left, a torque will be produced which causes a counterclockwise precession of the bicycle wheel, tending to turn the bicycle to the left. |
Comments | Active | |
| 88 | The anti-knock value of a gasoline engine is defined in terms of a/an ______ | Octane number | Cetane number | Knock number | Crook number | a | gasoline engine is petrol engine. The octane number of ISO – Octane is 100. Octane number is the measure of the resistance of gasoline/petrol against detonation/knocking or pre – ignition of the fuel in the engine. It is measured relative to the mixture of Iso – octane and n – heptane. In this mixture, Iso – octane has an Octane number of 100 and n – heptane has zero octane number. Higher octane fuel has a greater resistance to auto – ignition under higher combustion pressure and heat. |
Comments | Active | |
| 89 | For an orifice meter, an orifice of diameter d is fitted in a pipe of diameter (D) The coefficient of discharge is a friction of ___________. | Grashof number | d/D and Reynolds’ number | d/D and Grashof number | Reynolds number | b | is defined as the ratio of the actual flow and the ideal flow and is always less than one. For the orifice meter, the coefficient of discharge depends on the shape of the nozzle, the ratio of pipe to nozzle diameter and the Reynolds number of the flow. \(C_{d}\) \(C_{d}\) \(C_{d}=\frac{Q_{actual}}{Q_{theoritical}}\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 90 | For an unsteady operation and ___hydraulic transmission through fluid coupling is suitable. | Increasing speed | Low starting torque | Increasing torque | High starting speed | b |  Hydraulic transmission through fluid coupling is suitable for unsteady operation and low starting torque. In hydraulic couplings, input and output torque are equal but the speeds of the output shaft is less than the input shaft | Comments | Active | |
| 91 | Volumetric flow rate of river water is measured directly using ____. | Ultraviolet flow meters | Weirs | Ultrasonic flow meters | Vane meter | b | Weirs: Flow in open channels is called rapidly varied flow (RVF) if the flow depth changes markedly over a relatively short distance in the flow direction. • The flow over a sufficiently high obstruction in an open channel is always critical. Such obstructions placed intentionally in an open channel to measure the flow rate are called weirs. • There are two types of weirs 1. Broad-Crested Weir 2. Sharp-Crested Weirs |
Comments | Active | |
| 92 | ______measures heat loss from a heated wire to measure pressure. | Barometer | Manometer | Pirani gauge | Orifice meter | c | Pirani gauge: It is based on a hot metal wire suspended in a tube that is exposed to gas pressure media. • The Pirani gauge measures the vaccum pressure-dependent thermal conductivity from the heated wire to the surrounding gas. • The heated Pirani sensor filament is typically made of a thin (< 20 µm) Tungsten, Nickel or Platinum wire. • As gas molecules collide with the filament wire, heat is transported from the hot wire. • The heat loss is a function of the gas pressure and at low pressure, the low gas density and the long mean free path between gas molecules provide low thermal conductivity. • At high pressure, the high gas density and the short mean free path between molecules will result in high thermal conductivity. |
Comments | Active | |
| 93 | Stretching tendency of liquid surfaces is known as _________. | Cavitation | Surface tension | Adhesion | Cohesion | b | Surface Tension: It is defined as force per unit length in the plane of the liquid surface at right angles to either side of an imaginary line drawn to the surface. • Mathematically, • Surface Tension = \(\frac{Force}{Length}\) • An unbalanced force is developed at the interface stretched over the entire fluid mass • It is the tendency of the liquid surface to shrink into a minimum surface area. • The SI Unit of surface tension is N m-1 • It allows insects to float and slide on the water's surface, usually denser than water. • The molecules at the surface have an unbalanced force rather than molecules at deeper and the resultant force moves downward this is surface tension. |
Comments | Active | |
| 94 | The range of coefficient of discharge for a Venturimeter is generally ________. | 0.7 – 0.8 | 0.5 – 0.6 | 0.95 – 0.97 | 0.6 – 0.7 | c | The coefficient of discharge is the ratio of actual discharge to theoretical discharge. Coefficient of discharge Venturimeter -0.95 to 0.99 Orifice meter - 0.62 to 0.65 Nozzle meter -0.93 to 0.98 |
Comments | Active | |
| 95 | ____________fluid is incompressible. | Real | Newtonian | Non- Newtonian | Ideal | d | Ideal fluid: A fluid that is incompressible and is having no viscosity is known as an ideal fluid. • Ideal fluid is an imaginary fluid as all the fluids, which exist, have some viscosity. Real fluid: A fluid that possesses viscosity, is known as real fluid. • All the fluid in practice is real fluids. Newtonian fluid: Fluids for which shear stress () is directly proportional to the deformation rate or velocity gradient are Newtonian fluid. \(τ\) Non-Newtonian fluid: Fluids for which shear stress () is not directly proportional to the deformation rate or velocity gradient are non-Newtonian fluid. \(τ\) |
Comments | Active | |
| 96 | A two-stroke cycle engine ______as compared to a four – stroke cycle engine of the same size. | Has greater volumetric efficiency | Produces more power | Has greater thermal efficiency | Has less wear and tear of moving parts | b | Two – stroke engines: In this engine, one power stroke is obtained in each revolution of the crankshaft. Four – stroke engines: In this type of engine, one power stroke is obtained in two revolutions of the crankshaft. Low cost More uniform torque and hence lighter flywheel is needed Because of one power stroke for one revolution, power produced for same size of engine is more. Lightweight and simplicity due to the absence of the valve mechanism. |
Comments | Active | |
| 97 | In ______process, the cross- section of the bar is increased at the cost of reducing its length. | Drawing down | Reaming | Spinning | Upsetting | d | In upsetting, a forging process, the length of the work piece is reduced and the cross-sectional area is increased by compressive force applied along the axis. It is commonly used in processes like bolt head formation, rivet heads, etc. The process is typically carried out using a hammer or a press. |
Comments | Active | |
| 98 | The octane rating is a measure of the ability of the ________ to resist detonation during combustion. | Fuel | Piston | Cylinder | Air mixture | a | Octane Rating: The S.I. engine fuel has been given an anti – knocking rating which is known as Octane Rating. It basically shows the resistance of the fuel to create knocking by auto – ignition. According to standard practice, the antiknock value of an SI engine fuel is determinded by comparing its antiknock property with a mixture of two reference fuels, normal heptane ( and iso – octane. \(C_{7}H_{18})\) \((C_{8}H_{18})\) Iso – octane chemically being a very good antiknock fuel, is arbitrarily assigned a rating of “100 octane number.†\((C_{8}H_{18})\) Normal Heptane has very poor antiknock qualities and is given a rating of “0 octane numberâ€. \((C_{7}H_{16})\) Thus, if the content of Iso – octane is high in the fuel then it will ensure high octane number resulting in better fuel anti – knock quality. Because of the high Octane number, the fuel will not auto – ignite as the possibilities of knocking has been diminished by the fuel quality. |
Comments | Active | |
| 99 | The upward force on a body immersed in water, because of the fluid surrounding it, is known as _____________. | Buoyancy force | Gravitational force | Force of viscosity | Archimedes force | a | Buoyant Force: When a solid body is either wholly or partially immersed in a fluid, the hydrostatic lift due to the net vertical component of the hydrostatic pressure forces experienced by the body is called the buoyant force. • The buoyant force on a submerged or floating body is equal to the weight of the liquid displaced by the body and acts vertically upward through the centroid of a displaced volume known as the center of buoyancy. |
Comments | Active | |
| 100 | In a steam nozzle, heat supplied to steam during the expansion process equals _______. | Zero | Work done | Change in kinetic energy | Heat drop | a | The steam flow through the nozzle may be assumed as adiabatic flow since during the expansion of steam in the nozzle, neither any heat is supplied nor rejected, work however is performed by increasing the kinetic energy of the steam. As the steam passes through the nozzle it loses its pressure as well as the heat. The work done is equal to the adiabatic heat drop which in turn is equal to the Rankine area. | Comments | Active |










